Content for TS 23.527 Word version: 19.0.0
8.4 Restoration procedures for AMF failure
8.4.1 Multicast MBS session (de)activation or update after an AMF failure
8.4.1.1 General
8.4.1.2 N2 MBS session request distribution with list of NG RAN Node IDs provided by MB-SMF to AMF
8.5 Broadcast MBS session restoration Procedure for N3mb path failure
8.4 Restoration procedures for AMF failure |R18| p. 50
8.4.1 Multicast MBS session (de)activation or update after an AMF failure p. 50
8.4.1.1 General p. 50
Different NG-RAN nodes may establish shared delivery for the same MBS session via different AMFs of a same AMF set. During the shared delivery establishment:
- each AMF involved in the establishment of shared delivery stores in its multicast MBS session context the RAN-ID of the NG-RAN nodes that have established shared delivery via this AMF, for subsequent signaling related to the multicast MBS Session (Multicast MBS session activation, deactivation or update); and
- the MB-SMF stores in its multicast MBS session context the NF Instance ID of each AMF involved in the establishment of shared delivery to enable subsequent signalling towards these AMFs.
8.4.1.2 N2 MBS session request distribution with list of NG RAN Node IDs provided by MB-SMF to AMF p. 50
During the shared delivery establishment procedure (see clause 7.2.1.4 of TS 23.247), the MB-SMF stores, for each AMF involved in the establishment of shared delivery, the list of NG-RAN Node IDs having shared delivery established through the AMF.
The MB-SMF may then send any multicast MBS session activation, deactivation and update request towards the NG-RAN nodes that established shared delivery as defined in Figure 8.4.1.2-2.
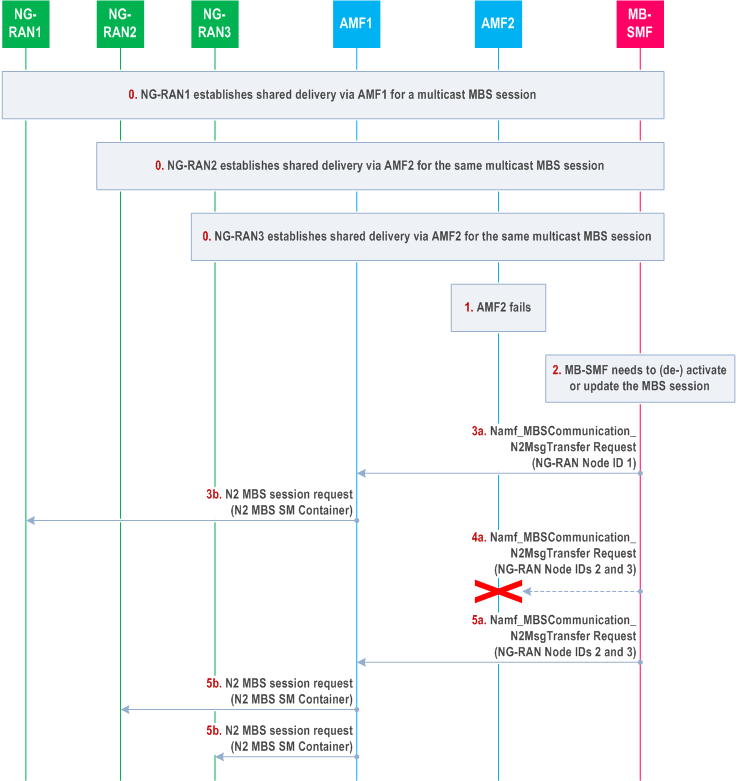
Step 0.
If the MB-SMF is already aware at the start of this procedure that AMF2 has failed, the MB-SMF may already include in step 3 the list of NG RAN Node IDs known by the MB-SMF to have established shared delivery through the failed AMF (AMF2).When using unicast transport over N3mb, the MB-SMF may determine that a NG-RAN node has failed or restarted as specified in clause 8.3.4. In this case, the MB-SMF shall remove this NG RAN node from its MBS session context.
In scenarios where the MB-SMF would request an AMF to distribute an activate, deactivate or update request to a NG RAN node that has no longer shared delivery established (e.g. the NG RAN node has restarted but this has not been detected by the MB-SMF), the NG RAN will return an activation or update failure to the AMF. To enable the MB-SMF to be notified about this failure and to remove the NG RAN node ID from its MBS session context, the MB-SMF shall include a notification URI in every Namf_
NG RAN1 establishes shared delivery for the multicast MBS session via AMF1. NG RAN2 and NG RAN3 do so via AMF2. MB-SMF stores corresponding information in its MBS session context.
Step 1.
AMF2 becomes no longer available/reachable.
Step 2.
The MB-SMF needs to activate, deactivate or update the MBS session.
Step 3.
The MB-SMF sends an Namf_MBSCommunication_N2MessageTransfer Request to every AMF of the same AMF set that was involved in the establishment of shared delivery, as specified in clauses 7.2.5.2, 7.2.5.3 and 7.2.6 of TS 23.247, but with the request further including the list of NG RAN Node IDs known by the MB-SMF to have established shared delivery through the respective AMF. AMF1 distributes the request to the list of NG-RAN nodes received from the MB-SMF, if any, otherwise to the list of the NG-RAN nodes it has stored locally, if any.
Step 4.
If the MB-SMF is not yet aware that AMF2 has failed, it sends an Namf_MBSCommunication N2MessageTransfer Request to AMF2 as described in step 3 and detects that AMF2 is no longer available.
Step 5.
The MB-SMF sends an Namf_MBSCommunication_N2MessageTransfer Request to an alternative AMF (AMF1 in this example) of the same AMF set including the list of NG RAN Node IDs known by the MB-SMF to have established shared delivery through the failed AMF (AMF2). AMF1 distributes the request to the list of NG-RAN nodes received from the MB-SMF.
8.5 Broadcast MBS session restoration Procedure for N3mb path failure |R18| p. 52
The procedure specified in this clause may be supported to restore a Broadcast MBS session affected by an N3mb path failure when unicast transport is used over the N3mb interface.
When the procedure is supported, when the MB-UPF detects and reports an N3mb path failure towards the MB-SMF, the MB-SMF may initiate the Broadcast Session Modification procedure as specified in Figure 8.5-1 towards the NG-RAN affected by the failure.
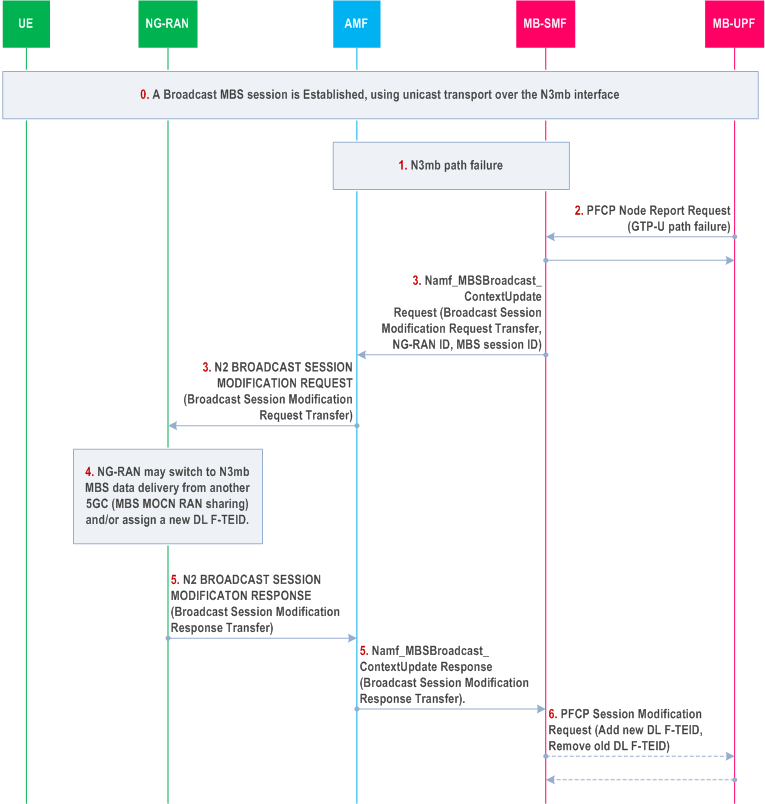
Step 0.
A Broadcast MBS session has been established at the NG-RAN, with N3mb data delivery from the MB-UPF.
Step 1.
A N3mb path failure occurs.
Step 2.
The MB-SMF receives a PFCP Node Report Request message from the MB-UPF reporting the GTP-U path failure and including the IP address of the remote GTP-U peer towards which the user plane path failure has been detected.
Step 3.
The MB-SMF determines the NG-RAN affected by the N3mb path failure based on the IP address of the remote GTP-U peer and sends a Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextUpdate Request including the MBS Session ID, the NG-RAN ID of the NG-RAN affected by the N3mb path failure and a Broadcast Session Modification Request Transfer including an N3mb path failure indication.
Step 4.
Upon receipt of the Broadcast Session Modification Request with the N3mb path failure indication, the NG-RAN may switch to N3mb data delivery from another 5GC as specified in clause 7.3.7 of TS 23.247 if MBS MOCN RAN sharing is supported, and/or it may provide a new DL F-TEID for N3mb data delivery from the MB-UPF.
Step 5.
The NG-RAN returns a Broadcast Session Modification Response to the MB-SMF via the AMF.
Step 6.
If a new DL F-TEID is received from the NG-RAN, the MB-SMF instructs the MB-UPF to start delivering MBS data towards the new DL F-TEID and to stop doing so towards the old DL F-TEID.