Content for TS 23.247 Word version: 19.0.0
1…
4…
4.2…
4.3
5…
6…
6.6…
7…
7.1.1.2
7.1.1.3
7.1.1.4…
7.1.1.6…
7.1.2…
7.2…
7.2.2…
7.2.3…
7.2.4…
7.2.4.3…
7.2.5…
7.2.6…
7.3…
7.3.5…
7.5…
8…
9…
9.2…
9.3…
9.4…
A…
7.2 MBS procedures for multicast Session
7.2.1 MBS join and Session establishment procedure
7.2.1.1 General
7.2.1.2 Establishment of a PDU Session that can be associated with multicast session(s)
7.2.1.3 Multicast session join and session establishment procedure
7.2.1.4 Establishment of shared delivery toward RAN node
...
...
7.2 MBS procedures for multicast Session p. 61
7.2.1 MBS join and Session establishment procedure p. 61
7.2.1.1 General p. 61
MBS Session Join procedure is used by UEs to inform the 5GC of the UE interest in joining a multicast MBS session. The first accepted UE join request will trigger the multicast MBS session establishment towards the NG-RAN and the UE.
7.2.1.2 Establishment of a PDU Session that can be associated with multicast session(s) p. 62
The PDU Session associated with Multicast MBS session(s) (i.e. the associated PDU Session) is established using the procedures as specified in clause 4.3.2.2 of TS 23.502 with the following differences:
- In step 2, the AMF selects an SMF capable of handling Multicast MBS sessions based on DNN and S-NSSAI, locally configured data or a corresponding SMF profile stored in the NRF. For indirect discovery, the AMF requests the SCP to select an SMF capable of handling Multicast MBS sessions.
-
In step 4, if MBS subscription data for the UE (i.e. corresponding SUPI), DNN and S-NSSAI of the HPLMN or subscribed SNPN is not available, the SMF retrieves the MBS subscription data using Nudm_
SDM_ (SUPI, MBS subscription data, selected DNN, S-NSSAI of the HPLMN or subscribed SNPN, Serving PLMN ID (or PLMN ID and NID)) and subscribes to be notified when this subscription data is modified using Nudm_Get SDM_ (SUPI, MBS subscription data, selected DNN, S-NSSAI of the HPLMN or SNPN, Serving PLMN ID (or PLMN ID and NID)). UDM may get this information from UDR by Nudr_Subscribe DM_ (SUPI, MBS data, selected DNN, S-NSSAI of the HPLMN or subscribed SNPN, Serving PLMN ID (or PLMN ID and NID)) and may subscribe to notifications from UDR for the same data by Nudr_Query DM_ . The MBS subscription data can also be retrieved along with the Session Management Subscription data, i.e. with additional input parameter for MBS subscription data in the Nudm_subscribe SDM services.
7.2.1.3 Multicast session join and session establishment procedure p. 62
The following steps are executed before the UE requests to join the MBS session:
- The MBS Session may have been created in the 5GC (see clause 7.1.1 for details).
- The UE registers in the PLMN or SNPN and may have established a PDU session that can be associated with multicast session(s).
- The UE has known at least the MBS Session ID of a multicast group that the UE can join, e.g. via service announcement.
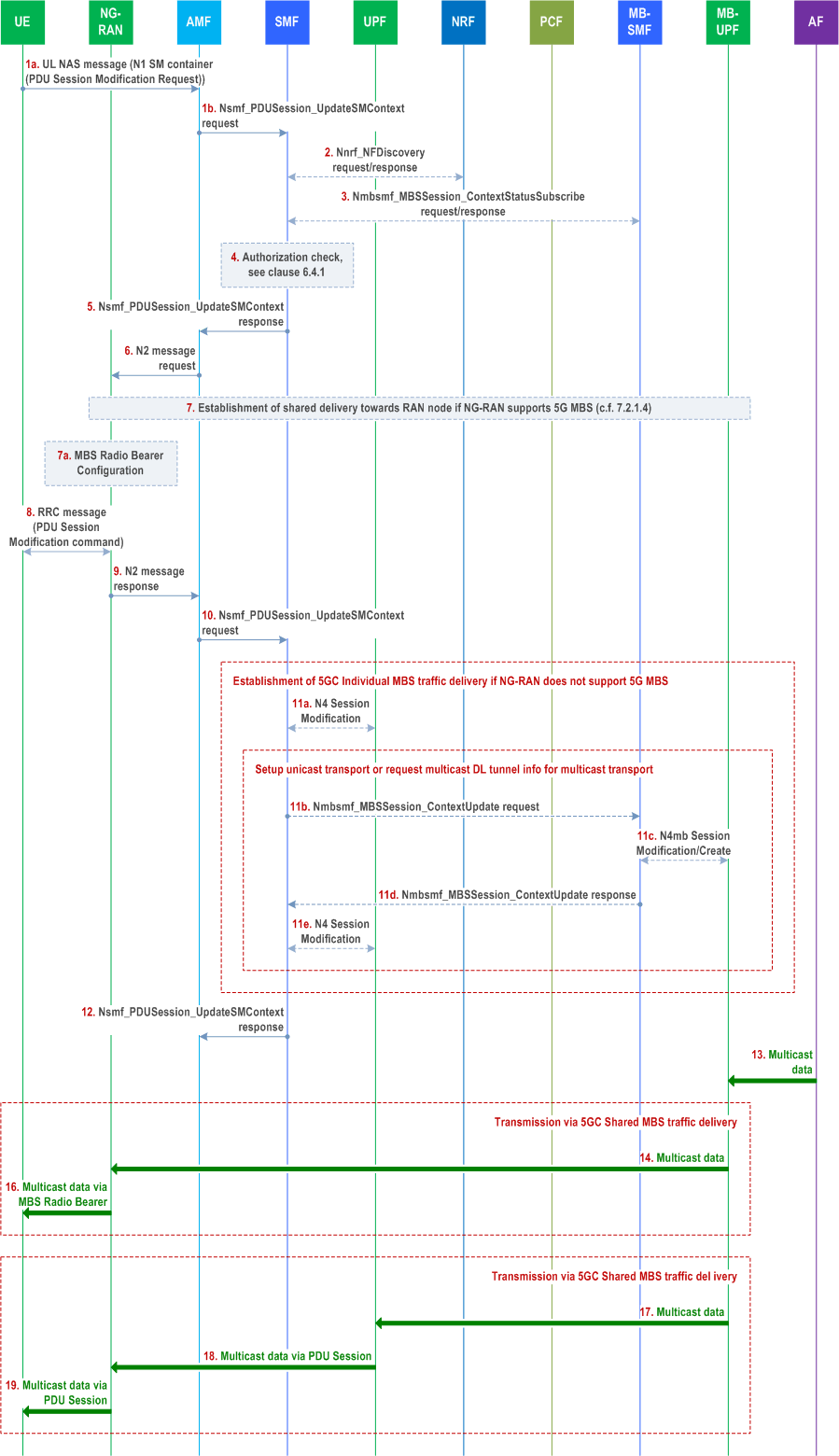
Step 1.
[Conditional] This step is used for 5GC Individual MBS traffic delivery, if the related NG-RAN does not support MBS. If a shared tunnel between the UPF (PSA) and MB-UPF for 5GC Individual MBS traffic delivery has not yet been established by the SMF for the multicast MBS session, steps 11a to 11d are executed. Step 11e is executed irrespective of that.
To join a multicast group:
Step 2.
- if there is an existing PDU session that can be used to send the UE join request for the multicast MBS Session, the UE sends a PDU Session Modification Request over that PDU session (i.e. associated PDU Session) which additionally contains one or several MBS Session ID(s) and join request. The MBS Session ID(s) indicate the multicast MBS session(s) that UE wants to join.
- if the UE has no appropriate PDU session established with the DNN and S-NSSAI for the multicast MBS session, the UE joins the multicast MBS session by sending PDU Session Establishment Request for associated PDU session together with one or several MBS Session ID(s) and join request. In that case, before step 2, the network proceeds with establishment of the associated PDU session executing steps 4 to 10 of PDU Session Establishment procedure as specified in clause 4.3.2.2 of TS 23.502.
[Conditional] Based on the received MBS Session ID and join request, the SMF determines this is MBS Session join request.
If SMF has no information about MBS Session Context for the indicated MBS Session ID(s), SMF discovers and selects an MB-SMF for the MBS Session via the NRF as described in clause 7.1.2. If no MB-SMF is assigned for the MBS Session ID (i.e. the NRF provides empty MB-SMF profile), the SMF may select an MB-SMF and request it to configure the multicast MBS session or the SMF may reject the join request and respond to the UE with an appropriate cause value.
Step 3.
[Conditional] For each MBS session in step 1, if the SMF has not subscribed to the MBS Session Context, it invokes Nmbsmf_MBSSession_ContextStatusSubscribe request (MBS Session ID) towards the MB-SMF to subscribe to events notifications related to the multicast MBS session and to request information about the MBS Session Context. The MB-SMF responds with the information about the indicated multicast MBS session in Nmbsmf_MBSSession_ContextStatusSubscribe response (multicast QoS flow information (e.g. QoS profile(s) for the multicast MBS session), [start time], [session state (Active/Inactive)], [Any UE indication], [multicast DL tunnel info], [multicast session security context]).
If it is the first time for the MB-SMF to receive Nmbsmf_MBSSession_ContextStatusSubscribe request of the indicated MBS Session from any SMF, the MB-SMF learns it is the first UE joining the multicast MBS session. For multicast transport between MB-UPF and content provider, if it is the first UE joining the multicast MBS session, and MB-UPF has not joined the multicast tree in the MBS session creation procedure, described in clause 7.1.1, the MB-SMF requests the MB-UPF to join the multicast tree towards the AF/MBSF, otherwise MB-SMF will not send the request to the MB-UPF.
Step 4.
The SMF determines whether the user is authorized to join the Multicast MBS session taking into account the MBS subscription data received from the UDM and the Any UE indication if received from the MB-SMF. The SMF considers the UE as authorized to the Multicast MBS session if the UE is authorized to use multicast MBS services, and if the MBS Session ID(s) in the PDU Session Modification Request is included in the MBS subscription data or Any UE indication is received. If authorization check fails, the SMF rejects the join request with a cause value. If a UE joins prior to the start time of the multicast MBS session, the SMF may accept the join request and indicate to the UE the start time, or it may reject the join request with an appropriate error cause and optionally a back-off timer. If a UE joins while the multicast MBS session is inactive, the SMF accepts the join request. The MBS subscription data from the UDM may also contain MBS assistance information.
Step 5.
If the join request is accepted, the SMF responds to the AMF through Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext response (N2 SM information (PDU Session ID, MBS Session ID, [updated PDU Session information], [mapping information between unicast QoS flow(s) and multicast QoS flow (s)], [MBS Assistance Information for the MBS session]), N1 SM container (PDU Session Modification Command, [multicast session security context])) to:
Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer service operation towards the AMF, as described in step 11 of clause 4.3.2.2.1 in TS 23.502. The N2 SM information also includes the MBS Session ID and, if 5GC individual MBS traffic delivery fall-back is supported, the mapping information between unicast QoS flow(s) and multicast QoS flow(s).
If the join request is rejected, the SMF responds to the AMF through Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext response (N1 SM container (PDU Session Modification Reject)) and the message will not contain any MBS Session Context or the N2 SM information for the associated PDU session. The PDU Session Modification Reject message is forwarded to the UE via the NG-RAN, and the following steps are skipped.
The SMF may also include the MBS assistance information for the MBS session in N2 SM Information, if the MBS subscription data from the UDM contains the MBS assistance information which includes the ID of the MBS session that the UE requests to join. The MBS assistance information for the MBS session sent to NG-RAN is described in clause 6.17.
Step 6.
- create an MBS Session Context for the indicated MBS session in the RAN, if it does not exist in the RAN already; and
- inform the NG-RAN about the relation between the Multicast MBS Session Context and the UE's PDU Session context by including the MBS Session ID and the mapping between the multicast QoS flow(s) and associated QoS flow(s).
The N2 message, which includes the MBS Session ID(s) the UE has joined and, if applicable, associated QoS Flow, is sent to the NG-RAN.
If the MBS is supported by NG-RAN, 5GC Shared MBS traffic delivery is adopted. If the MBS is not supported by NG-RAN, 5GC Individual MBS traffic delivery is used if the PDU Session's unicast QoS Flow include QoS Flows for the multicast session.
If the NG-RAN supports MBS, the NG-RAN uses the MBS Session ID to determine that the PDU Session identified by the PDU Session ID is associated with the indicated multicast MBS session.
If the NG-RAN supports MBS, the associated unicast QoS flow information, if provided, is not used to allocate the radio resource and CN resource for corresponding QoS flows.
Step 7.
[Conditional] If shared tunnel has not been established for the multicast MBS session towards the NG-RAN node, the procedures in clause 7.2.1.4 for the establishment of shared delivery toward NG-RAN node are executed. This step is executed separately for each multicast MBS session.
Step 7a.
If the MBS Session is active, the NG-RAN configures radio resources for MBS session.
Step 8.
If the MBS Session is active, the NG-RAN node performs AN specific signalling exchange with the UE to configure the UE with radio resources for the multicast MBS session. If the NG-RAN does not support MBS and the MBS Session is active, radio resources are reconfigured for unicast transmission of the MBS data over the associated PDU session. As part of the AN specific signalling exchange, the N1 SM container (PDU Session Modification Command) is provided to the UE.
Step 9.
The NG-RAN node sends the PDU session modification response.
If the MBS is not supported by NG-RAN, the accepted unicast QoS flow is included in the N2 SM information. If the MBS is supported by NG-RAN, the N2 SM information further includes the indication of supporting MBS. If the target NG-RAN node support MBS multicast with reception in RRC_INACTIVE state, it indicates that in the N2 SM information.
Step 10.
The AMF invokes Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext request ([N2 SM information]) to the SMF.
Per the indication of whether the NG-RAN supports MBS, the SMF determines whether 5GC Individual MBS traffic delivery is used for multicast data transmission.
Step 11a.
Steps 14 to 16 are for 5GC Shared MBS traffic delivery:
The SMF contacts the UPF to request the creation of a tunnel and provides the MBS Session ID. The UPF indicates to the SMF whether the tunnel for this multicast MBS session is newly allocated (as there can be multiple SMFs interacting with the same UPF for the same multicast MBS Session).
If the UPF determines to use unicast transport over N19mb, the UPF allocates a DL N19mb Tunnel endpoint for the multicast MBS session if the SMF request is the first one to allocate DL N19mb Tunnel endpoint for the multicast MBS Session in the UPF. The UPF includes the DL Tunnel Info in the response to the SMF. The DL tunnel info includes the downlink tunnel ID and the UPF address.
If the UPF determines to use multicast transport over N19mb, the UPF joins the multicast distribution if the SMF request is the first one for the MBS Session in the UPF. Steps 11b to 11d are skipped.
Step 11b.
If the UPF indicates the DL N19mb Tunnel is newly allocated, the SMF invokes Nmbsmf_MBSSession_ContextUpdate request (MBS Session ID, [DL tunnel info]) towards the MB-SMF for establishing the multicast MBS session transport between MB-UPF and UPF.
Step 11c.
If the DL tunnel info of the UPF is received, the MB-SMF configures the MB-UPF to transmit the multicast MBS session data towards UPF using the possibly received downlink tunnel ID.
Step 11d.
The MB-SMF responds to the SMF through Nmbsmf_MBSSession_ContextUpdate response (MBS Session ID, [multicast DL tunnel info]). If the UPF DL tunnel info for unicast transport is not received by the MB-SMF, multicast transport between MB-UPF and UPF is to be used, and the MB-SMF includes the downlink tunnel information with the low layer transport multicast address for the multicast MBS session.
Step 11e.
The SMF configures the UPF to forward the received multicast MBS session data within the PDU session. (This step may be combined with step 11a).
Step 12.
The SMF responds to the AMF with Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext response message.
Step 13.
The MB-UPF receives multicast PDUs, either directly from the content provider or via the MBSTF that can manipulate the data.
Step 14.
Steps 17 to 19 are for 5GC Individual MBS traffic delivery:
The MB-UPF sends multicast PDUs in the N3mb tunnel associated to the multicast MBS session to the NG-RAN. There is only one tunnel per multicast MBS session per MBS service area and NG-RAN node, i.e. all the UEs which have joined the multicast MBS session via the NG-RAN node share this tunnel for reception of the multicast MBS session data.
Step 15.
Void.
Step 16.
The NG-RAN transmits the multicast MBS session data to the UE(s) via the MBS Radio Bearer using either PTP or PTM transmission.
In this step or at later stage, the NG-RAN may determine to apply delivery enabling reception by UEs in RRC_INACTIVE state for the MBS session, as defined in clause 6.17.
Step 17.
The MB-UPF sends multicast PDUs in the N19mb tunnel associated to the multicast MBS session to the UPF. There is only one tunnel per multicast MBS session and destination UPF, i.e. all associated PDU sessions served by the destination UPF share this tunnel.
Step 18.
The UPF forwards the multicast data towards the NG-RAN via unicast (i.e. in the N3 tunnel of the associated PDU Session).
Step 19.
The NG-RAN forwards the multicast MBS session data to the UE via unicast (i.e. over the radio bearer(s) corresponding to the associated QoS flow(s) of the associated PDU Session).
7.2.1.4 Establishment of shared delivery toward RAN node p. 67
In the following cases, the shared tunnel for shared delivery is established between the NG-RAN and MB-UPF:
- The first UE is included in the context of the MBS session in the NG-RAN.
- Handover to the target NG-RAN when the shared delivery tunnel is not established in the target RAN node for this multicast MBS session.
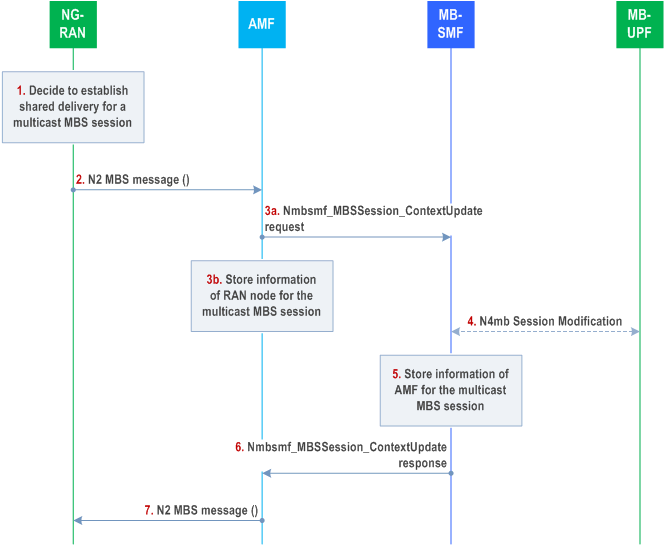
Step 1.
A NG-RAN node decides to establish shared delivery for a multicast MBS session when it serves at least one UE within the multicast MBS session. For location dependent services, the NG-RAN node needs to establish shared delivery for the location dependent contents of a multicast MBS session if it serves at least one UE assigned to an MBS Session ID and Area Session ID.
Step 2.
The NG-RAN sends an N2 MBS Session request message (MBS Session ID, [Area Session ID], N2 SM information ([unicast DL tunnel Info])) towards the AMF.
If the NG-RAN node is configured to use unicast transport for the shared delivery, it allocates a GTP tunnel endpoint and provides the unicast DL tunnel Info in the request, which includes the GTP tunnel endpoint and NG-RAN node address. For location dependent MBS services, the NG-RAN node also provides the Area Session ID.
Step 3.
The AMF selects the MB-SMF serving the multicast MBS session, e.g. using the NRF discovery service or locally stored information. It invokes Nmbsmf_MBSSession_ContextUpdate request (MBS Session ID, [Area Session ID], N2 SM information, NG-RAN Node ID) to the MB-SMF.
The AMF stores the information of the NG-RAN nodes (e.g. NG-RAN Node ID) for the subsequent signaling related to the multicast MBS Session.
Step 4.
[Conditional] If the MB-SMF receives the unicast DL tunnel Info in step 3 in a deployment where NG-RAN nodes share a common user plane entity, the MB-SMF only establishes the shared tunnel towards the DL GTP tunnel endpoint if the shared tunnel has not yet been established (as determined based on the stored DL GTP Tunnel endpoint(s) for the MBS session). The MB-SMF also stores the received DL GTP Tunnel and corresponding NG-RAN Node ID for the MBS session.
To establish the shared tunnel towards the DL GTP tunnel endpoint, the MB-SMF configures the MB-UPF to send multicast data for the multicast MBS session (or location dependent content of the multicast MBS session if an Area Session ID was received) towards that GTP tunnel endpoint via unicast transport.
Step 5.
The MB-SMF stores the information of the AMF (e.g. AMF ID) in the Multicast MBS session context (or location dependent part of the Multicast MBS Session Context if an Area Session ID was received) to enable subsequent signalling towards that AMF.
Step 6.
The MB-SMF sends Nmbsmf_MBSSession_ContextUpdate response (MBS Session ID, [Area Session ID], N2 SM information ([TMGI], multicast QoS flow information, session state (Active/Inactive), [multicast DL tunnel Info], [MBS service areas])) to the AMF. If the MB-SMF did not receive unicast DL tunnel Info in step 3, it provides the multicast DL tunnel info that includes transport multicast address (e.g. a LL SSM) and a GTP tunnel endpoint for multicast transport of the shared delivery.
Step 7.
The AMF sends an N2 MBS Session response message (MBS Session ID, [Area Session ID], N2 SM information) to the NG-RAN node. If the NG-RAN node receives the multicast DL tunnel Info of the shared delivery, it uses the transport multicast address included in the multicast DL tunnel info to join the multicast transport distribution.