Content for TS 23.482 Word version: 19.0.0
5 Application architecture for enabling AI/ML services
5.1 General
5.2 Application enablement architecture
5.2.1 On-Network AIML Enablement (AIMLE) Functional Architecture
5.2.2 Off-Network AIMLE Functional Architecture
5.2.3 Functional Entities Description
5.2.4 Reference Points Description
...
...
5 Application architecture for enabling AI/ML services p. 15
5.1 General p. 15
The functional architecture enhancements for the AIML enablement service are based on the generic functional model specified in clause 6.2 of TS 23.434. The architecture enhancements are organized into functional entities to describe a functional architecture enhancement which addresses the support for AIML enablement aspects for vertical applications.
5.2 Application enablement architecture p. 15
5.2.1 On-Network AIML Enablement (AIMLE) Functional Architecture p. 15
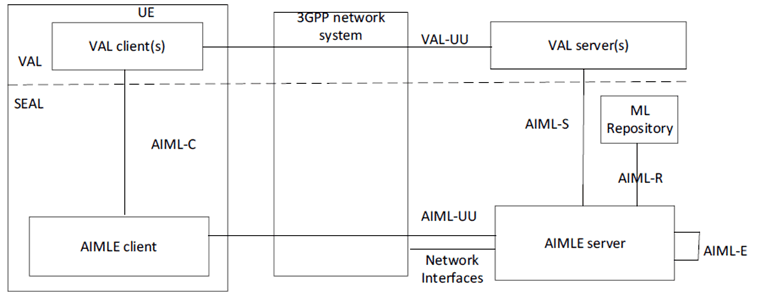
Figure 5.2.1-1 illustrates the on-network functional model of AIMLE. In the vertical application layer, the VAL client communicates with the VAL server over VAL-UU reference point. VAL-UU supports both unicast and multicast delivery modes. The AIMLE functional entities on the UE and the server are grouped into AIMLE client(s) and AIMLE server(s) respectively.
The AIMLE includes of a common set of services for comprehensive enablement of AIML functionality, including federated and distributed learning (e.g., FL client registration management, FL client discovery and selection), and reference points. The AIMLE services are offered to the vertical application layer (VAL).
The AIMLE client communicates with the AIMLE server(s) over the AIML-UU reference points. The AIMLE client provides functionality to the VAL client(s) over AIML-C reference point. The VAL server(s) communicate with the AIMLE server(s) over AIML-S reference points. The AIMLE servers communicate with the underlying 3GPP network systems using the respective 3GPP interfaces specified by the 3GPP network system. AIML-E reference point enables interactions between two AIMLE servers (e.g. central and edge AIMLE servers).
The AIMLE server interacts with the ML repository which serves as repository for ML model and ML participants over AIML-R.
5.2.1.1 Service-based AIMLE architecture representation p. 16
Figure 5.2.1.1-1 exhibits the service-based interfaces for providing and consuming AIMLE services. The AIMLE server could provide service to VAL server and AIMLE client through interface SAiml.
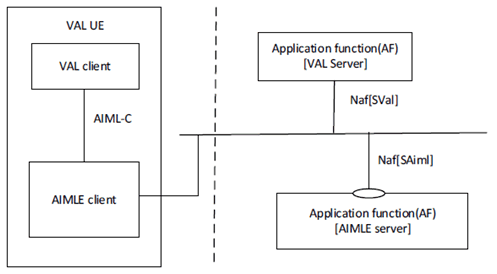
Figure 5.2.1.1-1: Architecture for AIML enablement - Service based representation.
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Figure 5.2.1.1-2 illustrates the service-based representation for utilization of the 5GS network services based on the 5GS SBA specified in TS 23.501.
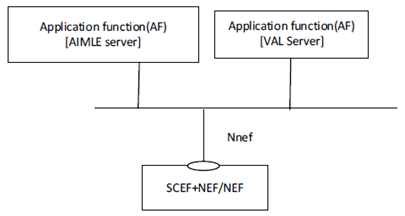
Figure 5.2.1.1-2: Architecture for AIMLE utilizing the 5GS network services based on the 5GS SBA - Service based representation,
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The AIMLE server as well as ADAES is deployed as a SEAL server; hence enhancements to SEAL architecture (as specified in TS 23.434) are needed to incorporate the AIMLE service. Figure 5.2.1.1-3 illustrates the service-based representation including AIMLE server as part of the SEAL framework.
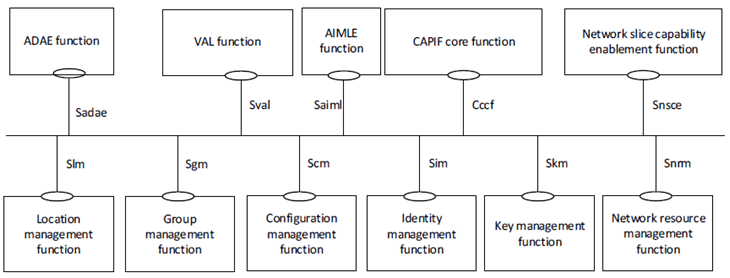
Figure 5.2.1.1-3: SEAL functional model representation using service-based interfaces and including AIMLE function.
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
5.2.2 Off-Network AIMLE Functional Architecture p. 17
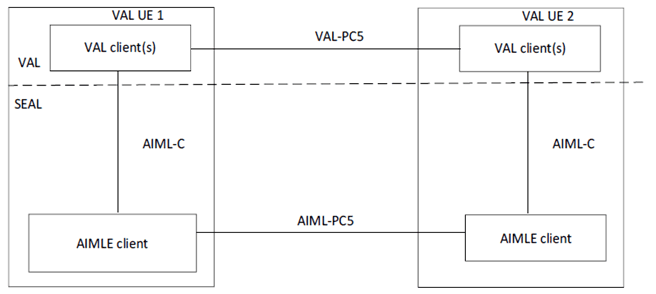
Figure 5.2.2-1 illustrates the off-network (UE-to-UE) functional model of AIML enablement. In the vertical application layer, the VAL client communicates with a further VAL client over VAL-PC5 reference point. VAL-PC5 supports both unicast and multicast delivery modes. The UE1, if connected to the network via Uu reference point, can also act as a UE-to-network relay, to enable UE2 to access the VAL server(s) over the VAL-UU reference point.
The AIMLE client communicates with a further AIMLE client(s) over the AIML-PC5 reference points. The AIMLE client provides functionality to the VAL client(s) over AIML-C reference point. Such communication is performed for supporting local ML operations (training, distribution, inference) in a coordinated manner.
The off network functional architecture is similar to SEAL off-network architecture (as specified in TS 23.434).
5.2.3 Functional Entities Description p. 17
5.2.3.1 General p. 17
Each subclause is a description of a functional entity and does not imply a physical entity.
5.2.3.2 AIMLE client p. 18
The AIMLE client functional entity acts as the application client supporting AIMLE services. It interacts with the AIMLE server.
5.2.3.3 AIMLE server p. 18
The AIMLE server functional entity provides AIMLE services supported within the vertical application layer. It interacts with the AIMLE client, the 3GPP network, other SEAL services, and VAL server.
5.2.3.4 ML repository p. 18
The ML repository is a logical entity that serves both as a registry for ML/FL members and as a repository for application layer ML model related information. It can be accessed by the AIMLE server.
5.2.4 Reference Points Description p. 18
5.2.4.1 General p. 18
The reference points for the functional model related to AIMLE are described in the following subclauses.
5.2.4.2 AIML-UU p. 18
The interactions related to AIML enablement functions between the AIMLE client and AIMLE server are supported by AIML-UU reference point. This reference point utilizes Uu reference point as described in TS 23.401 and TS 23.501.
5.2.4.3 AIML-S p. 18
The interactions related to AIML enablement functions between the VAL server(s) and the AIMLE server are supported by AIML-S reference point.
5.2.4.4 AIML-C p. 18
The interactions related to AIML enablement functions between the VAL client(s) and the AIMLE client within a VAL UE are supported by AIML-C reference point.
5.2.4.5 AIML-R p. 18
The interactions related to AIML enablement functions between the AIMLE server, and the ML repository are supported by AIML-R reference point.
5.2.4.6 AIML-E p. 18
The interactions related to AIML enablement functions between AIMLE servers (e.g., central and edge AIMLE servers).
5.2.4.7 AIML-PC5 p. 18
The interactions related to AIML enablement functions between AIMLE clients in off-network deployments.