Content for TS 23.272 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4…
5…
5.4…
6…
6.3
6.4…
7…
7.3
7.4…
7.5a…
8…
8.2.4a…
8.3…
8.4…
B…
B.2…
B.2.2…
B.2.3a…
B.2.3a.4…
B.2.4…
B.3…
C…
C.8…
6.4 Mobile Originating call in Idle Mode
6.5 Returning back to E-UTRAN
6.6 Mobile Originated or Mobile terminated call rejected by the MME
...
...
6.4 Mobile Originating call in Idle Mode p. 35
Mobile Originating call in Idle Mode procedure is specified by reusing the Mobile Originating Call in Active mode procedures as specified in clause 6.2 and clause 6.3 with Extended Service Request for mobile originating CS fallback to the MME where the messages S1-AP UE Context Modification Request and Response are replaced by S1-AP Initial UE Context Request and Response. The LAI is included in the S1-AP Initial UE Context Request message and sent to the eNodeB. The UE is transited to ECM-CONNECTED mode by following the applicable procedures specified in TS 23.401.
If UE has only LIPA PDN connection and the cell accessed by the UE does not link to the L-GW where the UE had the LIPA PDN Connection, the MME shall reject the Extended Service Request with a reason code which results in the UE selecting GERAN or UTRAN as specified in TS 24.301.
If the UE has only SIPTO at the Local Network PDN connections:
- in a network with collocated L-GW deployment and the (H)eNB accessed by the UE is not collocated with the L-GW providing the SIPTO at the Local Network connectivity; or
- in a network with stand-alone GW deployment and the (H)eNB accessed by the UE is not connected to the Local Network where the stand-alone GW (with S-GW and L-GW collocated) providing the SIPTO at the Local Network connectivity is residing,
- the SIPTO at the Local Network PDN connections fulfil criterion (i) or (ii) above; and
- the cell accessed by the UE does not link to the L-GW where the UE had the LIPA PDN connection,
6.5 Returning back to E-UTRAN p. 36
Once CS service ends in CS domain, existing mechanisms can be used to move the UE to E-UTRAN, no specific CS Fallback mechanisms are needed.
During the release of an RR connection the MSC should indicate to GERAN/UTRAN that the RR connection (for call or CISS or LCS) was established as a result of CS fallback. GERAN and UTRAN may use the indication to determine which of the existing mechanisms should be used to move the UE to E-UTRAN.
When configured to support the return to the last used PLMN after CSFB, after a successful setup of an RR connection or during the release of the UTRAN RR connection, the MSC shall further indicate to GERAN/UTRAN the last used LTE PLMN ID. GERAN and UTRAN shall take the last used LTE PLMN ID into account when selecting the target cell in PS handover to E-UTRAN or when selecting the dedicated target frequency list for idle mode mobility to E-UTRAN in RR Connection Release procedure.
When the UE moves to E-UTRAN, if the EPS service was suspended during the CS service, it is resumed according to the procedure shown in the Figure 6.5-1 below.
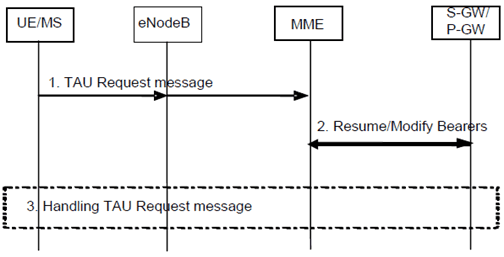
Step 1.
The UE sends a TAU Request message, to the MME.
Step 2.
If the UE context in the MME indicates that UE is in suspended status, the MME informs the S-GW and P-GW(s) to re-activate the EPS bearers for the UE.
If the procedure triggered by the NAS message in step 1 activates Modify Bearer Request message to the S-GW, this message should be used as an implicit resume. The S-GW is aware of the suspend state of the bearers and shall forward the Modify Bearer request to the P-GW. The P-GW and S-GW shall clear the suspend state and confirm with Modify Bearer response to the MME.
Step 3.
The NAS message is processed accordingly.
6.6 Mobile Originated or Mobile terminated call rejected by the MME |R9| p. 37
The MME may reject an Extended Service Request either for mobile originated or mobile terminated CSFB. The following procedure covers this scenario.
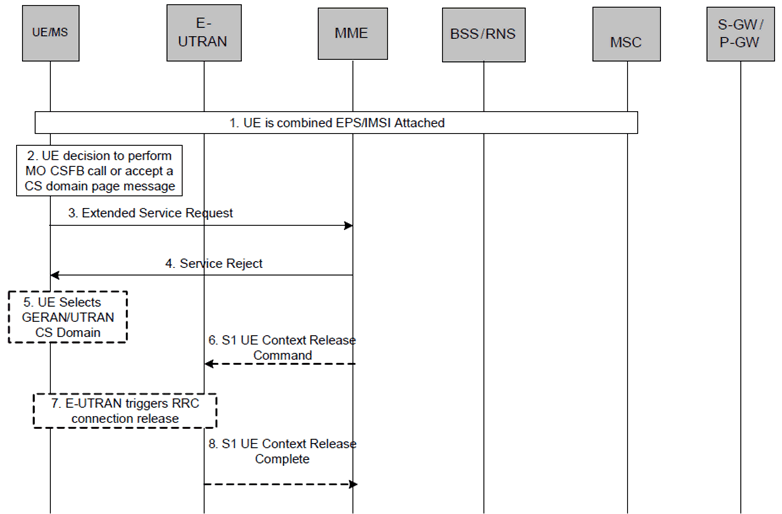
Step 1.
Steps 5 - 8 are executed when Service Reject is sent with a reason code which results in the UE selecting GERAN or UTRAN, as specified in TS 24.301.
UE is combined EPS/IMSI attached.
Step 2.
UE makes a decision to perform a mobile originated CS call or accepts CS paging for the CS Fallback to GERAN/UTRAN.
Step 3.
UE sends an Extended Service Request for mobile originating/mobile terminating CS fallback to the MME.
Step 4.
If the MME decides to reject the Extended Service Request, the MME sends a Service Reject message to the UE.
Step 5.
The UE selects GERAN or UTRAN CS Domain without waiting for RRC Release.
Step 6.
The MME releases S1 by sending the S1 UE Context Release Command (Cause) message to the eNodeB. Cause value indicates that release is triggered due to CS Fallback procedure.
Step 7.
If the RRC connection is not already released, the E-UTRAN sends a RRC Connection Release message to the UE.
Step 8.
The E-UTRAN confirms the S1 Release by returning an S1 UE Context Release Complete message to the MME.