Content for TS 23.207 Word version: 18.0.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions and Abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.2 Abbreviations
4 High Level Requirements for End-to-End IP QoS
4.1 End-to-End QoS Negotiation Requirements
4.2 QoS Policy Requirements
...
...
1 Scope p. 6
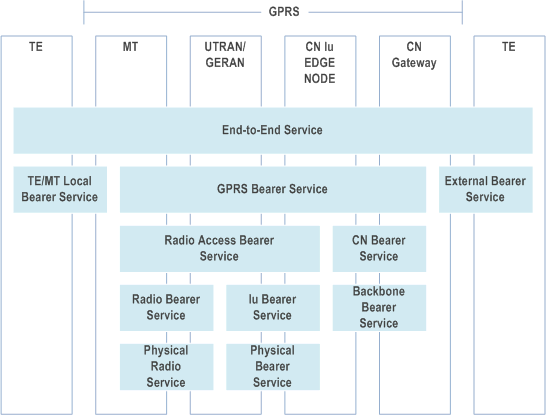
The present document provides the framework for end-to-end Quality of Service involving GPRS and complements TS 23.107 which describes the framework for Quality of Service within UMTS. The end-to-end QoS architecture is provided in Figure 1. The document describes the interaction between the TE/MT Local Bearer Service, the GPRS Bearer Service, and the External Bearer Service, and how these together provide Quality of Service for the End-to-End Service. The document also describes IP level mechanisms necessary in providing end-to-end Quality of Service involving GPRS networks, including possible interaction between the IP level and the GPRS level, as well as the application level and the IP level.
This document covers different architectural aspects of the end-to-end Quality of Service concept and architecture with varying level of detail. In general, other specifications shall be referred to for further details; these other specifications enable the reader to acquire the full understanding of the end-to-end Quality of Service concept and architecture. In particular, the stage 2 specification for the PCC architecture is specified in TS 23.203. The present document does not contain any requirements for the PCC architecture.
In contrast to the TS 23.107, the present document is only applicable to GPRS packet switched access services, and includes aspects of interworking to the IM subsystem as well as PSTN and other networks. The document does not cover the circuit switched access services.
2 References p. 6
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TS 22.228: "Service requirements for the Internet Protocol (IP) multimedia core network subsystem (IMS); Stage 1".
[2]
TS 23.002: "Network Architecture".
[3]
TS 23.107: "QoS Concept and Architecture".
[4]
TS 23.228: "IP Multimedia (IM) Subsystem - stage 2".
[4a] Void.
[4b] Void.
[4c] Void.
[5]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[6]
RFC 2475: "An Architecture for Differentiated Services (DiffServ)".
[7]
RFC 2753: "A Framework for Policy-based Admission Control ".
[8]
RFC 2748: "Common Open Policy Service protocol (COPS)".
[9]
RFC 2205: "Resource ReSerVation Protocol (RSVP)".
[10]
RFC 2209: "Resource ReSerVation Protocol (RSVP) Message Processing Rules".
[11]
RFC 2210: "The use of RSVP with IETF integrated Services".
[12]
RFC 1633: "Integrated Services in the Internet Architecture: an Overview".
[13]
RFC 3261: "SIP: Session Initiation Protocol".
[14]
RFC 2327: "Session Description Protocol".
[15]
RFC 2998: "A Framework For Integrated Services Operation Over DiffServ Networks".
[16]
RFC 2750: "RSVP Extensions for Policy Control".
[17]
RFC 2474: "Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field) in the IPv4 and IPv6 Headers".
[18] Void.
[19]
TS 23.060: "General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Service description; Stage 2".
[20]
TS 23.221: "Architecture requirements".
[21]
TS 23.203: "Policy and Charging Control Architecture".
[22]
TS 29.212: "Policy and Charging Control (PCC); Reference points".
[23]
TS 29.213: "Policy and Charging Control signalling flows and QoS parameter mapping".
[24]
TS 29.214: "Policy and Charging Control over Rx reference point".
[25]
TS 29.208: "End-to-end Quality of Service (QoS) signalling flows".
3 Definitions and Abbreviations p. 8
3.1 Definitions p. 8
RSVP:
Resource ReSerVation Protocol: The RSVP protocol, RFC 2205, is used by a host to request specific qualities of service from the network for particular application data streams or flows. The network responds by explicitly admitting or rejecting RSVP requests.
DiffServ:
DiffServ networks classify packets into one of a small number of aggregated flows or "classes", based on the DiffServ codepoint (DSCP) in the packet's IP header. This is known as behaviour aggregate (BA) classification (RFC 2475). At each DiffServ router, packets are subjected to a "per-hop behaviour" (PHB), which is invoked by the DSCP (RFC 2474).
IntServ:
The integrated services architecture RFC 1633 defined a set of extensions to the traditional best effort model of the Internet with the goal of allowing end-to-end QOS to be provided to applications. One of the key components of the architecture is a set of service definitions; the current set of services consists of the controlled load and guaranteed services. The architecture assumes that some explicit setup mechanism is used to convey information to routers so that they can provide requested services to flows that require them. While RSVP is the most widely known example of such a setup mechanism, the IntServ architecture is designed to accommodate other mechanisms.
Application Function:
The Application Function (AF) is an element offering applications that require the control of IP bearer resources . The AF is capable of communicating with the PCRF to transfer dynamic QoS-related service information. One example of an AF is the P-CSCF of the IM CN subsystem.
AF session:
An AF session is established by an application level signalling protocol offered by the AF that requires a session set-up with explicit session description before the use of the service. One example of an AF session is an IMS session.
AF session signalling:
AF session signalling is used to control the AF session. One example of AF session signalling is SIP/SDP.
Policy control:
The process whereby the Policy and Charging Rules Function (PCRF) indicates to the Policy and Charging Enforcement Function (PCEF) how to control the IP-CAN bearer. Policy control includes QoS control and/or gating control.
3.2 Abbreviations p. 8
For the purpose of the present document, the following abbreviations apply:
AF
Application Function
APN
Access Point Name (*)
DiffServ
Differentiated Services
DSCP
DiffServ Code Point
GERAN
GSM/EDGE Radio Access Network (*)
GGSN
Gateway GPRS Support Node (*)
HTTP
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (*)
IMS
IP Multimedia Subsystem
IntServ
Integrated Services
LAN
Local Area Network
LDP
Label Distribution Protocol
MPLS
Multiprotocol Label Switching Architecture
PCC
Policy and Charging Control
PCEF
Policy and Charging Enforcement Function
PHB
Per Hop Behaviour
PCRF
Policy and Charging Rules Function
RNC
Radio Network Controller (*)
SDP
Session Description Protocol
SIP
Session Initiation Protocol (*)
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (*)
TFT
Traffic Flow Template (*)
*
This abbreviation is covered in TR 21.905, version 4.2.0.
4 High Level Requirements for End-to-End IP QoS p. 9
4.1 End-to-End QoS Negotiation Requirements p. 9
- The UMTS QoS negotiation mechanisms used for providing end-to-end QoS shall be backward compatible with UMTS Release 1999.
- The UMTS QoS negotiation mechanisms used for providing end-to-end QoS shall not make any assumptions about the situation in external networks which are not within the scope of 3GPP specifications.
- The UMTS QoS negotiation mechanisms used for providing end-to-end QoS shall not make any assumptions about application layer signalling protocols.
- No changes to non-UMTS specific QoS negotiation mechanisms.
- The UMTS QoS negotiation mechanisms used for providing end-to-end QoS shall not make any assumptions about applications which may be used on terminal equipment attached to mobile terminals.
- Unnecessary signalling complexity and processing complexity in the network elements as well as the mobile terminal shall be avoided.
- Unnecessary signalling traffic due to end-to-end QoS negotiation shall be avoided.
- Methods for user authentication as well as billing and charging mechanisms related to the end-to-end QoS negotiation shall be kept as simple as possible.
- Minimum changes to network architecture and mechanisms due to introduction of end-to-end QoS negotiation.
- It shall be possible for an application on the external device to request end-to-end QoS.
4.2 QoS Policy Requirements p. 9
- The UMTS policy mechanisms described in TS 23.060 shall be used for control of the UMTS bearers.
- Interaction between UMTS bearer services and IP bearer services shall only occur at the translation function in the UE and GGSN.