Content for TS 23.204 Word version: 19.1.0
B Group chat sessions
B.1 Service-level interworking: IM or CPM user initiates a group chat and sends an Instant Message to a group list including SMS users
B Group chat sessions |R10| p. 55
B.1 Service-level interworking: IM or CPM user initiates a group chat and sends an Instant Message to a group list including SMS users p. 55
The flow in this clause is the same as that described in clause 6.15.1 with the difference that it is required that the IP-SM-GW assign an MSISDN for this group chat session so that it is clear for the SMS user that any message sent to the assigned MSISDN will be delivered to the group chat session participants, not just to the CPM UE that invited the SMS user.
In this flow, the IP-SM-GW is in the PLMN of the CPM UE, but it could also be in the PLMN of the SMS user if that user was also a CPM user and had terminating user preferences to deliver the session invitation via SMS.
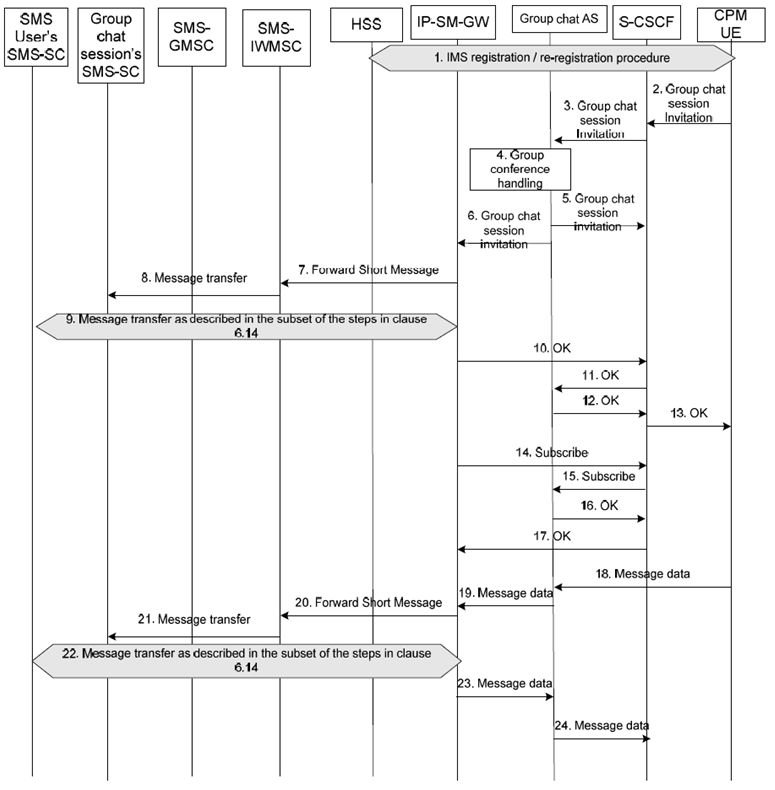
Figure B.1: CPM user initiates a group chat and messages are exchanged within the group chat via service-level interworking
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The UE registers to S-CSCF according the IMS registration procedure.
Step 2.
The UE generates a chat session invitation which includes group information, e.g. Group identifier in the Request-URI and/or recipient list in the body of the chat session invitation. UE submits the Instant Message to the S-CSCF using an appropriate SIP method.
Step 3.
Based on the stored iFC, S-CSCF forwards the session invitation to an AS in charge of handling group chat requests, e.g., the controlling function server defined in OMA-TS-SIMPLE_IM-V1_0 [12] or the controlling function server defined in OMA-TS-CPM_Conv_Fnct-V1_0 [17].
Step 4.
The group chat AS replicates a session invitation per recipient according to the group information it obtains acting as a B2BUA. See details in OMA-TS-SIMPLE_IM-V1_0 [12] or in OMA-TS-CPM_Conv_Fnct-V1_0 [17].
Step 5.
The group chat AS sends the generated multiple session invitations to the S-CSCF.
Step 6.
The group chat AS forwards one of the chat session invitations to the IP-SM-GW according to normal routing procedures (e.g., via S-CSCF).
Step 7.
The IP-SM-GW translates the chat session invitation request to a Short Message (SMS- SUBMIT) and forwards it towards the group chat SMS-SC (SC Address) via the SMS-IWMSC (as described in TS 23.040). The IP-SM-GW assigns an MSISDN representing the group chat session to ensure that the reply to this SMS is sent back to this particular IP-SM-GW. Any SMS sent from the SMS user to this MSISDN will be interworked into the group chat session with which this MSISDN is correlated. The text in the Short Message is defined by the operator and conveys information to the SMS user that he is invited to send and receive messages in the context of a group chat session, and includes instructions on how to accept, reject and end the session. The identity of the original sender (CPM user or group) is included as part of the operator provided invitation text.
Step 8.
The SMS-IWMSC forwards the Short Messages (SMS- SUBMIT) to the group chat SMS-SC and the SMS is delivered to the SMS user using standard SMS procedures (see TS 23.040).
Step 9.
A Short Message is received from the SMS user via the SMS-GMSC by the IP-SM-GW, in accordance to steps 2 to 4 and steps 10 to 13 from clause 6.14, indicating the response to the group chat session invitation. The message is targeted to the MSISDN representing the group chat session which was assigned in step 7.
Step 10.
If the answer is positive or if operator policy is to accept the session invitation on behalf of the SMS user, the IP-SM-GW acknowledges the session invitation. Otherwise the IP-SM-GW will consider the session rejected and send back an appropriate response.
Step 11.
The session invitation acknowledgement is forwarded by S-CSCF to the group chat AS.
Step 12-13.
The group chat AS responds back to the group chat session initiator once the first user joins the group chat session.
Step 14-17.
The IP-SM-GW subscribes to the participant information changes.
Step 18.
The CPM UE (or any group chat session participant) sends a message containing data to the group chat AS.
Step 19.
For the group chat session participant who is an SMS user, the message is routed towards the IP-SM-GW.
Step 20.
The IP-SM-GW identifies that a session exists between the SMS user and group chat AS and transforms the received message into a Short Message and sends a Short Message (SMS- SUBMIT) carrying the SC Address, then forwards it towards the group chat SMS-SC (SC Address) via the SMS-IWMSC (as described in TS 23.040). The IP-SM-GW inserts the address representing the group chat session as the sender of the message to ensure that the reply to this SMS is sent back to this particular IP-SM-GW.
Step 21.
The SMS-IWMSC forwards the Short Message (SMS- SUBMIT) to the group chat SMS-SC and the SMS is delivered to the SMS user using standard SMS procedures (see TS 23.040).
Step 22.
A Short Message is received from the SMS user via the SMS-GMSC by the IP-SM-GW, in accordance to steps 2 to 13 from clause 6.14. The message is targeted to the MSISDN representing the group chat session which was assigned in step 7.
Step 23.
The IP-SM-GW identifies that a session exists between the SMS user and the group chat AS and transforms the received message into message data and sends it within the session towards the group chat AS.
Step 24.
The group chat AS forwards the message to all group chat participants.