Content for TS 23.204 Word version: 19.1.0
6.12 Delivery report for an Instant Message delivered as encapsulated Short Message
6.13 Service-level interworking: IM or CPM capable UE sends an Instant Message to an SMS user with Interworking in the terminating side
6.14 Service-level interworking: IM or CPM user receives Short Message from an SMS user
...
...
6.12 Delivery report for an Instant Message delivered as encapsulated Short Message |R8| p. 38
This procedure follows the procedure described in clause 6.11, when the original Instant Message included a delivery notification request.
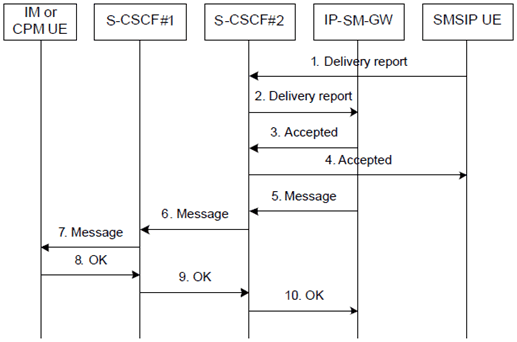
Figure 6.12: Delivery report after a successful Instant Message to encapsulated Short Message procedure
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1-2.
The SMSIP UE has received the Short Message as described in clause 6.11 and sends a Delivery report (SMS-DELIVER-REPORT) to the IP-SM-GW via the S-CSCF.
Step 3-4.
The IP-SM-GW acknowledges, at the SIP level, the Delivery report to the SMSIP UE via the S-CSCF.
Step 5-7.
The IP-SM-GW sends a Delivery Notification to the IM UE or CPM UE.
Step 8-10.
The IM UE or CPM UE acknowledges the reception of the Delivery Notification.
6.13 Service-level interworking: IM or CPM capable UE sends an Instant Message to an SMS user with Interworking in the terminating side |R8| p. 39
This procedure describes the delivery of an Instant Message to a registered or an un-registered IMS subscriber. For the unregistered case, the S-CSCF forwards the Instant Message to the IP-SM-GW based on the unregistered iFC of the subscriber.
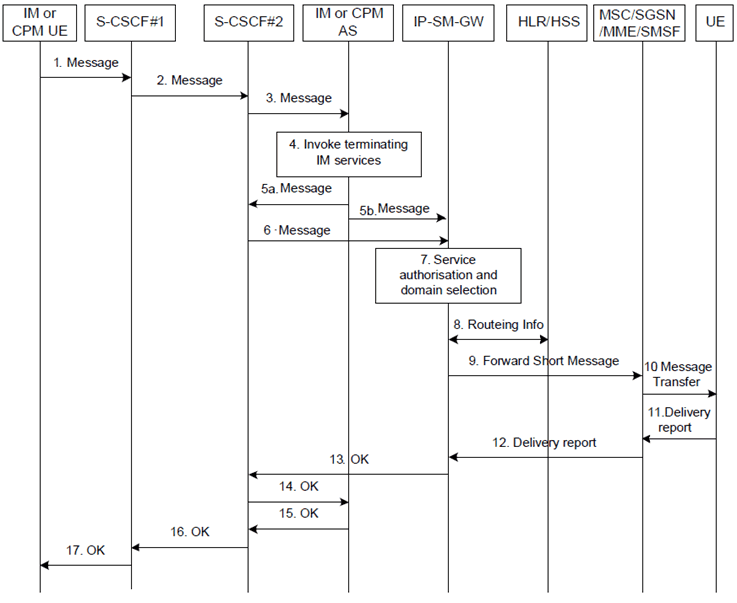
Figure 6.13: Successful IM terminating to SMS procedure with Interworking in the Terminating Side
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
UE submits an Instant Message, destined to another IM user or CPM user in another IMS domain, using an appropriate SIP method. The UE may request to hide its Public User Identity from the recipient within the Instant Message, as described in OMA-TS-SIMPLE_IM-V1_0 [12] and in OMA-TS-CPM_Conv_Fnct-V1_0 [17]. If the P-CSCF (not shown in the figure) has received an indication from the S-CSCF that MPS for Messaging is enabled for the originating UE in the HSS (see TS 23.228), the P-CSCF sets the Resource-Priority information on the Instant Message to a value appropriate for MPS, sets the transport priority of the outgoing Instant Message to a value appropriate for MPS and handles the Instant Message with priority.
Step 2.
The S-CSCF resolves the destination domain and routes the message towards the S-CSCF in the terminating network ("Terminating S-CSCF").
Step 3.
The terminating S-CSCF forwards the Instant Message to the IM AS ("Terminating IM AS") or to the CPM AS ("Terminating CPM AS") based on stored iFC.
Step 4.
The terminating IM AS or CPM AS invokes terminating IM or CPM services as applicable for the destination IM or CPM user.
Step 5a.
The IM AS or CPM AS can forward the Instant Message back to the terminating S-CSCF, e.g. the terminating IM user is offline or the CPM user has no terminating interworking user preferences.
Step 5b.
In the case of the CPM AS, if terminating interworking user preferences are set, the Instant Message is routed directly to the IP-SM-GW in which case the procedure continues with step 7.
Step 6.
The terminating S-CSCF forwards the Instant Message to the IP-SM-GW, e.g. based on stored iFC.
Step 7.
If the user is authorized, the IP-SM-GW performs service-level interworking by converting the Instant Message to Short Message. The IP-SM-GW shall obtain the routeing information for the UE from the HLR/HSS and deliver the message to the UE. If the sender of the Instant Message requests to hide its Public User Identity from the recipient and operator policy allows for this, the IP-SM-GW shall anonymise the identity of the user to the recipient. Otherwise, if operator policy prohibits this, the IP-SM-GW shall return an appropriate error to the user.
Step 8.
The IP-SM-GW obtains the routeing information for the destination UE from the HLR/HSS. The HLR/HSS also returns the indication whether MPS for Messaging is enabled for the UE in the HSS (see TS 23.228) and if the MPS for Messaging is enabled for the UE, the HLR/HSS sets the transport priority of the message to a value appropriate for MPS and handles the message with priority.
Step 9.
The IP-SM-GW sends the Forward Short Message message to the target MSC/SGSN/MME/SMSF. If the Resource-Priority information on the Instant Message is a value appropriate for MPS, the IP-SM-GW sets the transport priority of the outgoing Short Message to a value appropriate for MPS and handles the Short Message with priority.
Step 10.
The MSC/SGSN/MME/SMSF sends the Short Message to the UE.
Step 11.
The UE acknowledges the receipt of the Short Message.
Step 12.
The MSC/SGSN/MME/SMSF sends a Delivery report (SMS-DELIVER-REPORT) to the IP-SM-GW.
Step 13.
The IP-SM-GW sends OK response to the terminating S-CSCF.
Step 14.
The S-CSCF forwards the OK to the terminating IM AS or CPM AS.
Step 15.
The terminating IM AS or CPM AS forwards the OK response back to the terminating S-CSCF.
Step 16.
The terminating S-CSCF forwards the OK back towards the originating S-CSCF.
Step 17.
The originating S-CSCF forwards the OK to the originating UE.
6.14 Service-level interworking: IM or CPM user receives Short Message from an SMS user |R8| p. 40
An IMS registered user with SIMPLE IM or CPM service receives a Short Message formatted via service-level interworking to an Instant Message.
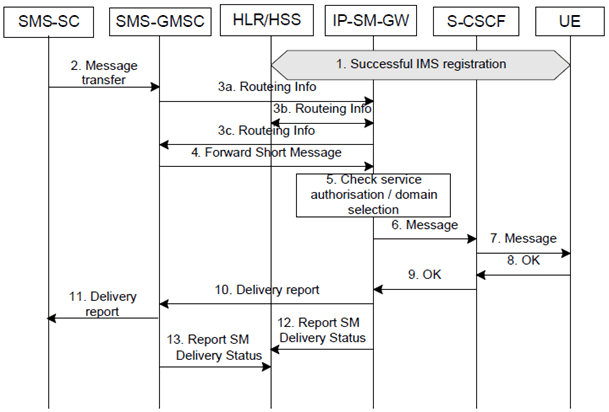
Figure 6.14: Successful IM termination after service-level interworking
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The UE registers to the S-CSCF according to the IMS registration procedure.
Step 2.
The SMS-SC forwards a Short Message to the SMS-GMSC.
Step 3a.
The SMS-GMSC interrogates the HLR/HSS to retrieve routeing information. Based on the pre-configured IP-SM-GW address for the user, the HLR/HSS forwards the request to the corresponding IP-SM-GW. The SMS GMSC also interrogates the HLR/HSS to check whether MPS for Messaging is enabled for the UE (see TS 23.228). If the MPS for Messaging is set (enabled) for the UE (see TS 23.228), the HLR/HSS sets the transport priority of the message to a value appropriate for MPS and handles the message with priority.
Step 3b.
The HLR/HSS returns the IMSI and the address(es) of the current MSC, SGSN, MME and/or SMSF to the IP-SM-GW for delivery of the SM in CS/PS domain. The HLR/HSS also returns the indication whether MPS for Messaging is set (enabled) for the UE (see TS 23.228), sets the transport priority of the message to a value appropriate for MPS and handles the message with priority.
Step 3c.
The IP-SM-GW creates an MT Correlation ID as per TS 23.040, which associates the Routing Info retrieval with the subsequent Forward Short Message messages(s), and stores this along with the IMSI of the receiving subscriber. The IP-SM-GW returns to the SMS-GMSC the address of itself, along with the MT Correlation ID in the IMSI field, as routeing information. The IP SM GW returns the indication whether MPS for Messaging is set (enabled) for the UE in the HLR/HSS (see TS 23.228). If MPS for Messaging is enabled for the UE, the IP-SM-GW sets the transport priority of the message to a value appropriate for MPS and handles the message with priority.
Step 4.
The SMS-GMSC delivers the Short Message to the IP-SM-GW in the same manner that it delivers the Short Message to an MSC, SGSN, MME or SMSF, including the MT Correlation ID received from the IP-SM-GW, in place of the IMSI. If MPS for Messaging is enabled for the UE in the HLR/HSS (see TS 23.228), the SMS-GMSC sets the transport priority of the message to a value appropriate for MPS and handles the Short Message with priority.
Step 5.
The IP-SM-GW checks whether the recipient is authorized for the interworking service.
Step 6.
If the user is authorized for service-level interworking, the IP-SM-GW converts the Short Message to an Instant Message. It sends the Instant Message using the appropriate SIP method towards the S-CSCF. If the MPS for Messaging indication for the UE is activated, the IP-SM-GW applies an MPS appropriate Resource-Priority information to the SIP message, sets the transport priority of the message to a value appropriate for MPS and handles the message with priority.
Step 7.
The S-CSCF forwards the Instant Message to the UE.
The mechanism defined in clause 5.3.4.3 of TS 23.401 and clause 4.2.3.3 of TS 23.502 ensures that if the UE needs to be paged, the MME/AMF pages the UE with priority.
Step 8.
The UE acknowledges the SIP request to the S-CSCF.
Step 9.
The S-CSCF forwards the acknowledgement of the SIP request to the IP-SM-GW.
Step 10.
The IP-SM-GW acknowledges the Forward Short Message to the SMS-GMSC.
Step 11.
The SMS-GMSC sends a Delivery report (SMS-DELIVER-REPORT) to the SMS-SC.
Step 12.
The IP-SM-GW may send a Report SM Delivery Status to the HLR/HSS.
Step 13.
The SMS-GMSC may send a Report SM Delivery Status to the HSS. The HSS shall ignore the information provided in this report.