Content for TS 23.003 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
2…
2.8…
3…
4…
5…
6…
7…
8…
9…
10…
11
12…
13…
14…
15…
16…
17…
18…
19…
19.4…
19.5…
20…
21…
22…
23…
24…
25…
26…
27…
28…
28.3.2.2…
28.3.2.2.6…
28.3.2.3…
28.4…
28.7…
28.8…
29…
A…
B…
C…
D
E…
10 Identification of the Cordless Telephony System entities
10.1 General description of CTS-MS and CTS-FP Identities
10.2 CTS Mobile Subscriber Identities
10.3 Fixed Part Beacon Identity
10.4 International Fixed Part Equipment Identity
10.5 International Fixed Part Subscription Identity
...
...
10 Identification of the Cordless Telephony System entities p. 47
10.1 General description of CTS-MS and CTS-FP Identities p. 47
Every CTS-FP broadcasts a local identity - the Fixed Part Beacon Identity (FPBI) - which contains an Access Rights Identity. Every CTS-MS has both an Access Rights Key and a CTS Mobile Subscriber Identity (CTSMSI). These operate as a pair. A CTS-MS is allowed to access any CTS-FP which broadcasts an FPBI which can be identified by any of the CTS-MS Access Rights Keys of that CTS-MS. The CTS-MS Access Rights Key contains the FPBI and the FPBI Length Indicator (FLI) indicating the relevant part of the FPBI used to control access.
10.2 CTS Mobile Subscriber Identities p. 47
10.2.1 General p. 47
Each CTS-MS has one or more temporary identities which are used for paging and to request access. The structure and allocation principles of the CTS Mobile Subscriber Identities (CTSMSI) are defined below.
10.2.2 Composition of the CTSMSI p. 47
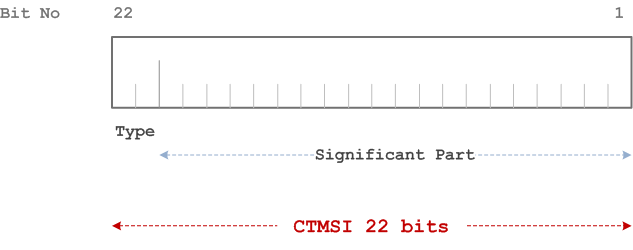
The CTSMSI is composed of the following elements:
- CTSMSI Type. Its length is 2 bits;
- Significant Part. Its length is 20 bits.
00
Default Individual CTSMSI;
01
Reserved;
10
Assigned Individual CTSMSI;
11
Assigned Connectionless Group CTSMSI.
10.2.3 Allocation principles p. 47
The default Individual CTSMSI contains the least significant portion of the IMSI. This is the default CTS-MS identity.
Assigned CTSMSIs are allocated by the CTS-FP during enrolment, registration and other access procedures. Significant Part of the assigned CTSMSI shall be allocated in the range 00001-FFFFE. CTS-FP shall not allocate Significant Part equal to 00000 or to FFFFF and shall not allocate Assigned CTSMSI using Reserved Type value. Such assignments shall be ignored by the CTS-MS.
Assigned CTSMSIs are allocated in ciphered mode.
The value FFFFF from the set of Assigned Connectionless Group CTSMSI shall be considered in all CTS-MS as the value of the Connectionless Broadcast Identifier.
10.2.4 CTSMSI hexadecimal representation p. 48
The 22 bits of CTSMSI are padded with 2 leading zeroes to give a 6 digit hexadecimal value.
EXAMPLE:
binary CTSMSI value: 11 1001 0010 0000 1011 1100
hexadecimal CTSMSI value: 39 20 BC.
10.3 Fixed Part Beacon Identity p. 48
10.3.1 General p. 48
Each CTS-FP has one Fixed Part Beacon Identity known by the enrolled CTS-MSs. The FPBI is periodically broadcast on the BCH logical channel so that the CTS-MSs are able to recognise the identity of the CTS-FP. The FPBI contains an Access Rights Identity.
Enrolled CTS-MSs shall store the FPBI to which their assigned CTSMSIs are related.
Below the structure and allocation principles of the Fixed Part Beacon Identity (FPBI) are defined.
10.3.2 Composition of the FPBI p. 48
10.3.2.1 FPBI general structure p. 48
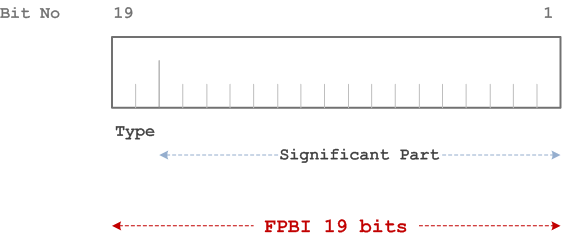
The FPBI is composed of the following elements:
- FPBI Type. Its length is 2 bits;
- FPBI Significant Part. Its length is 17 bits.
00
All other values are reserved and CTS-MSs shall treat these values as FPBI class A.
FPBI class A: residential and single-cell systems;
01
FPBI class B: multi-cell PABXs.
10.3.2.2 FPBI class A p. 49
This class is intended to be used for small residential and private (PBX) single cell CTS-FP.
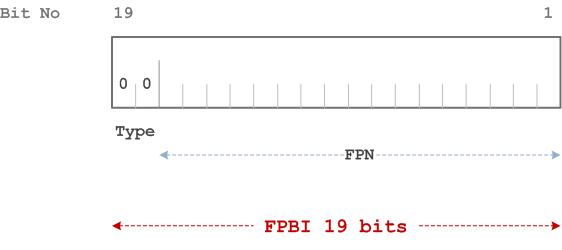
The FPBI class A is composed of the following elements:
- FPBI Class A Type. Its length is 2 bits and its value is 00;
- Fixed Part Number (FPN). Its length is 17 bits. The FPN contains the least significant bits of the Serial Number part of the IFPEI.
10.3.2.3 FPBI class B p. 49
This class is reserved for more complex private installation such as multi-cell PABXs.
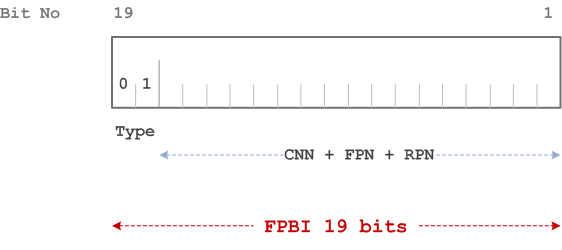
The FPBI class B is composed of the following elements:
- FPBI Class B Type. Its length is 2 bits and its value is 01;
- CTS Network Number (CNN). Its length is defined by the manufacturer or the system installer;
- Fixed Part Number (FPN). Its length is defined by the manufacturer or the system installer;
- Radio Part Number (RPN) assigned by the CTS manufacturer or system installer. Its length is defined by the manufacturer or the system installer.
10.3.3 Allocation principles p. 49
The FPBI shall be allocated during the CTS-FP initialisation procedure. Any change to the value of the FPBI of a given CTS-FP shall be considered as a CTS-FP re-initialisation; i.e. each enrolled CTS-MS needs to be enrolled again.
FPBI are not required to be unique (i.e. several CTS-FP can have the same FPBI in different areas). Care should be taken to limit CTS-MS registration attempts to a fixed part with the same FPBI as another fixed part.
10.4 International Fixed Part Equipment Identity p. 50
10.4.1 General p. 50
The structure and allocation principles of the International Fixed Part Equipment Identity (IFPEI) are defined below.
10.4.2 Composition of the IFPEI p. 50

The IFPEI is composed of the following elements (each element shall consist of decimal digits only):
- Type Approval Code (TAC). Its length is 6 decimal digits;
- Final Assembly Code (FAC). Its length is 2 decimal digits;
- Serial NumbeR (SNR). Its length is 6 decimal digits;
- Software Version Number (SVN) identifies the software version number of the fixed part equipment. Its length is 2 digits.
10.4.3 Allocation and assignment principles p. 50
The Type Approval Code (TAC) is issued by a global administrator.
The place of final assembly (FAC) is encoded by the manufacturer.
Manufacturers shall allocate unique serial numbers (SNR) in a sequential order.
The Software Version Number (SVN) is allocated by the manufacturer after authorisation by the type approval authority. SVN value 99 is reserved for future use.
10.5 International Fixed Part Subscription Identity p. 50
10.5.1 General p. 50
The structure and allocation principles of the International Fixed Part Subscription Identity (IFPSI) are defined below.
10.5.2 Composition of the IFPSI p. 51
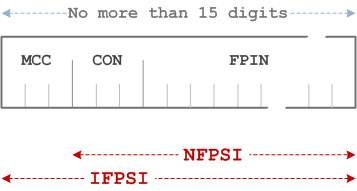
The IFPSI is composed of the following elements (each element shall consist of decimal digits only):
- Mobile Country Code (MCC) consisting of three digits. The MCC identifies the country of the CTS-FP subscriber (e.g. 208 for France);
- CTS Operator Number (CON). Its length is three digits;
- Fixed Part Identification Number (FPIN) identifying the CTS-FP subscriber.
10.5.3 Allocation and assignment principles p. 51
IFPSI shall consist of decimal characters (0 to 9) only.
The allocation of Mobile Country Codes (MCCs) is administered by the ITU.
The allocation of CTS Operator Number (CON) and the structure of National Fixed Part Subscriber Identity (NFPSI) may be responsibility of each national numbering plan administrator.
CTS Operators shall allocate unique Fixed Part Identification Numbers.