Content for TS 38.114 Word version: 18.2.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.2 Symbols
3.3 Abbreviations
...
...
1 Scope p. 8
The present document covers the assessment of NR repeater, network-controlled repeater and ancillary equipment in respect of Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC). For network-controlled repeater (NCR), requirements for NCR-Fwd and NCR-MT apply.
The present document specifies the applicable requirements, procedures, test conditions, performance assessment and performance criteria for NR repeater, NCR and associated ancillary equipment in the following categories:
- NR repeater equipped with antenna connectors which are possible to be terminated during EMC testing, meeting the repeater type 1-C RF requirements of TS 38.106, with conformance demonstrated by compliance to TS 38.115-1.
- NR repeater not equipped with antenna connectors, i.e. with antenna elements radiating during the EMC testing, meeting the repeater type 2-O RF requirements of TS 38.106, with conformance demonstrated by compliance to TS 38.115-2.
- NCR equipped with antenna connectors or TAB connectors which are possible to terminated during EMC testing, meeting the NCR-Fwd/MT type 1-C and type 1-H RF requirements of TS 38.106, with conformance demonstrated by compliance to TS 38.115-1.
- NCR not equipped with antenna connectors, i.e. with antenna elements radiating during the EMC testing, meeting the NCR-Fwd/MT type 2-O RF requirements of TS 38.106, with conformance demonstrated by compliance to TS 38.115-2.
2 References p. 8
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications"
[2]
TS 38.106: "NR Repeater Radio Transmission and Reception"
[3]
TS 38.115-1: "NR; Repeater conformance testing - Part 1: Conducted conformance testing"
[4]
TS 38.115-2: "NR; Repeater conformance testing - Part 1: Radiated conformance testing"
[5]
CISPR 32: "Electromagnetic compatibility of multimedia equipment - Emission requirements".
[6]
IEC 61000-6-1: "Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-1: Generic standards - Immunity for residential, commercial and light-industrial environments".
[7]
IEC 61000-6-3: "Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-3: Generic standards - Emission standard for equipment in residential environments".
[8]
IEC 61000-3-2: "Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-2: Limits - Limits for harmonic current emissions (equipment input current ≤ 16 A per phase)".
[9]
IEC 61000-3-3: "Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-3: Limits - Limitation of voltage changes, voltage fluctuations and flicker in low-voltage supply systems, for equipment with rated current ≤ 16 A per phase and not subject to conditional connection".
[10]
IEC 61000-3-11: "Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-11: Limits - Limitation of voltage changes, voltage fluctuations and flicker in low-voltage supply systems - Equipment with rated current ≤ 75 A and subject to conditional connections".
[11]
IEC 61000-3-12: "Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-12: Limits - Limits for harmonic currents produced by equipment connected to public low-voltage system with input current >16 A and ≤ 75 A per phase".
[12]
IEC 61000-4-2: "Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 4-2: Testing and measurement techniques - Electrostatic discharge immunity test".
[13]
IEC 61000-4-3:2006+AMD1:2007+AMD2:2010 CSV: "Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 4-3: Testing and measurement techniques - Radiated, radio-frequency, electromagnetic field immunity test".
[14]
IEC 61000-4-4: "Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 4-4: Testing and measurement techniques - Electrical fast transient/burst immunity test".
[15]
IEC 61000-4-5: "Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 4-5: Testing and measurement techniques - Surge immunity test".
[16]
IEC 61000-4-6: "Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 4-6: Testing and measurement techniques - Immunity to conducted disturbances, induced by radio frequency fields".
[17]
IEC 61000-4-11: "Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 4-11: Testing and measurement techniques - Voltage dips, short interruptions and voltage variations immunity tests".
[18]
IEC 61000-4-21: "Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 4-21: Testing and measurement techniques - Reverberation chamber test methods".
[19]
ITU-R SM.329: "Unwanted emissions in the spurious domain".
[20]
IEC 60050-161: "International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 161: Electromagnetic compatibility".
[21]
ETSI EN 301 489-1: "Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) standard for radio equipment and services - Part 1: Common technical requirements - Harmonised Standard for Electromagnetic Compatibility".
[22]
ETSI EN 301 489-50: "Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 50: Specific conditions for cellular communication base station (BS), repeater and ancillary equipment; Harmonised standard covering the essential requirements of article 3.1(b) of the Directive 2014/53/EU".
[23]
TS 38.101-4: "NR; User Equipment (UE) radio transmission and reception; Part 4: Performance requirements".
[24]
IEC 61000-6-8: "Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-8: Generic standards - Emission standard for professional equipment in commercial and light-industrial locations".
[25]
CISPR 16-1-4: "Specification for radio disturbance and immunity measuring apparatus and methods - Part 1-4: Radio disturbance and immunity measuring apparatus - Antennas and test sites for radiated disturbance measurements".
[26]
ITU-R SM.1539-1: "Variation of the boundary between the out-of-band and spurious domains required for the application of Recommendations ITU-R SM.1541 and ITU-R SM.329 ".
[27]
CISPR 16-4-2: "Specification for radio disturbance and immunity measuring apparatus and methods - Part 4-2: Uncertainties, statistics and limit modelling - Measurement instrumentation uncertainty".
[28]
ETSI TR 100 028-1:"Electromagnetic Compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); Uncertainties in the Measurement of Mobile Radio Equipment Characteristics; Part 1".
[29]
TR 38.867: "Study on NR network-controlled repeaters".
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations p. 10
3.1 Definitions p. 10
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
ancillary equipment:
electrical or electronic equipment, that is intended to be used with a receiver or transmitter
antenna port:
for EMC purposes, port for connection of an antenna used for intentional transmission and/or reception of radiated RF energy, equivalent to an RF antenna connector.
channel bandwidth:
the RF bandwidth supporting a single NR RF carrier with the transmission bandwidth configured in the uplink or downlink of a cell. The channel bandwidth is measured in MHz and is used as a reference for transmitter and receiver RF requirements.
continuous phenomena:
electromagnetic disturbance, the effects of which on a particular device or equipment cannot be resolved into a succession of distinct effects (IEC 60050-161 [20]).
exclusion band:
frequency range(s) not subject to test or assessment.
multi-band repeater:
Repeater Type 1-C whose antenna connector is associated with a transmitter and/or receiver that is characterized by the ability to process two or more passband(s) in common active RF components simultaneously, where at least one passband is configured at a different operating band than the other passband(s) and where this different operating band is not a sub-band or superseding-band of another supported operating band
NCR-MT:
the NCR-MT is defined as a function entity to communicate with a gNB via a Control link (C-link) to enable exchange of control information (e.g. side control information at least for the control of NCR-Fwd). The C-link is based on NR Uu interface.
NCR-Fwd:
the NCR-Fwd is defined as a function entity to perform the amplify-and-forwarding of UL/DL RF signal between gNB and UE via backhaul link and access link. The behavior of the NCR-Fwd will be controlled according to the received side control information from gNB.
NCR type 1-C:
network-controlled repeater including both NCR-MT and NCR-Fwd operating at FR1 with requirements set consisting only of conducted requirements defined at individual antenna connectors.
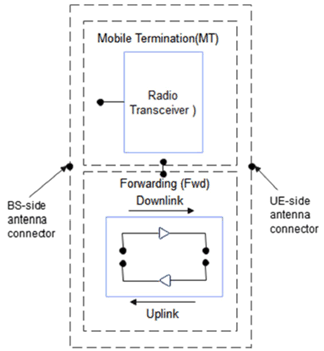
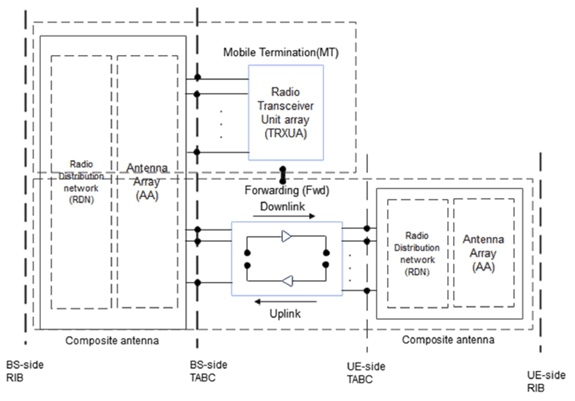
NCR type 1-H:
network-controlled repeater including both NCR-MT and NCR-Fwd operating at FR1 with a requirement set consisting of conducted requirements defined at individual TAB connectors and OTA requirements defined at RIB.
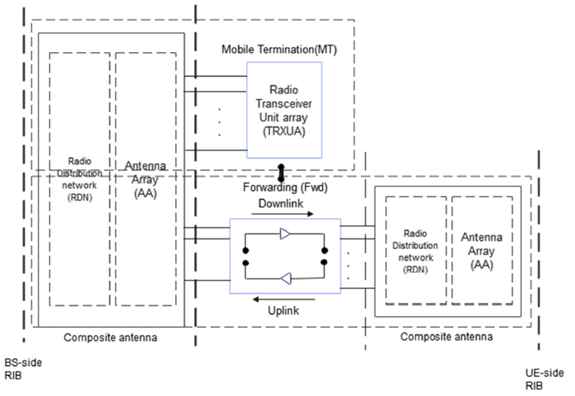
NCR type 2-O:
network-controlled repeater including both NCR-MT and NCR-Fwd operating at FR2 with a requirement set consisting only of OTA requirements defined at the RIB.
operating band:
frequency range in which NR operates (paired or unpaired), that is defined with a specific set of technical requirements.
passband edge:
Frequency at the edge of the passband.
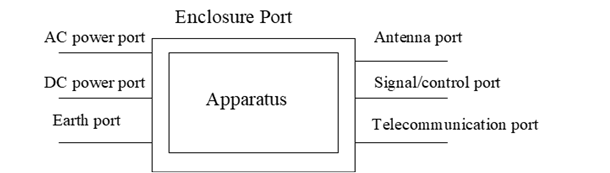
port:
A particular interface, of the specified equipment (apparatus), with the electromagnetic environment. For example, any connection point on an equipment intended for connection of cables to or from that equipment is considered as a port (see Figure 3.1-1).
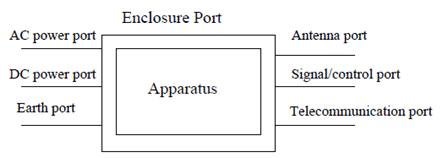
repeater type 1-C:
Repeater operating at FR1 with a requirement set consisting only of conducted requirements defined at individual antenna connectors.
repeater type 2-O:
Repeater operating at FR2 with a requirement set consisting only of OTA requirements defined at the RIB.
radiated interface boundary:
operating band specific radiated requirements reference where the radiated requirements apply.
signal/control port:
port intended for the interconnection of components of an EUT, or between an EUT and associated equipment and used in accordance with relevant functional specifications (for example for the maximum length of cable connected to it).
single-band connector:
Repeater type 1-C antenna connector supporting operation either in a single operating band only, or in multiple operating bands but does not meet the conditions for a multi-band connector
spatial exclusion zone:
range of angles where no tests of radiated immunity are made for repeater type 2-O (i.e. half sphere around the EUT's radiating direction).
telecommunication port:
ports which are intended to be connected to telecommunication networks (e.g. public switched telecommunication networks, integrated services digital networks), local area networks (e.g. Ethernet, Token Ring) and similar networks.
transient phenomena:
pertaining to or designating a phenomena or a quantity which varies between two consecutive steady states during a time interval short compared with the time-scale of interest (IEC 60050-161 [20]).
3.2 Symbols p. 14
For the purposes of the present document, the following symbols apply:
BWChannel
Channel bandwidth
Prated,p,AC
Rated passband output power per antenna connector
Prated,p,TRP
Rated passband TRP output power declared per RIB
Pmax,p,AC
Maximum passband output power measured per antenna connector
Pmax,p,TRP
Maximum passband TRP output power measured per RIB
3.3 Abbreviations p. 14
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
AC
Alternating Current
AMN
Artificial Mains Network
CDN
Coupling/Decoupling Network
C-link
Control link
DC
Direct Current
EMC
Electromagnetic Compatibility
EUT
Equipment Under Test
FR
Frequency Range
NCR
Network-controlled repeater
NCR-MT
NCR-Mobile termination
NCR-Fwd
NCR-Forwarding
NR
New Radio
RF
Radio Frequency
rms
root mean square