TS 37.470
W1 Interface
General Aspects and Principles
V18.0.0 (PDF)
2024/03 16 p.
V17.0.0
2022/03 16 p.
V16.2.0
2020/06 16 p.
- Rapporteur:
- Dr. Cao, Gen
China Unicom
Content for TS 37.470 Word version: 18.0.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions of terms, symbols and abbreviations
4 General aspects
5 Functions of the W1 interface
5.1 General
5.2 W1-C functions
5.3 W1-U functions
6 Procedures of the W1 interface
6.1 Control plane procedures
6.2 User plane procedures
7 W1 interface protocol structure
8 Other W1 interface specifications
$ Change history
1 Scope p. 6
The present document is an introduction to the 3GPP TS 37.4xx series of technical specifications that define the W1 interface. The W1 interface provides means for interconnecting an ng-eNB-CU and an ng-eNB-DU of an ng-eNB within an NG-RAN.
2 References p. 6
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 38.425: "NR user plane protocol".
[3]
TS 38.300: "NR; Overall description; Stage-2"
[4]
TS 37.471: "E-UTRAN and NG-RAN; W1 interface: layer 1".
[5]
TS 37.472: "E-UTRAN and NG-RAN; W1 signalling transport".
[6]
TS 37.473: "E-UTRAN and NG-RAN; W1 application protocol (W1AP)".
3 Definitions of terms, symbols and abbreviations p. 6
3.1 Terms p. 6
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
W1:
interface between an ng-eNB-CU and an ng- eNB-DU, providing an interconnection point between the ng-eNB-CU and the ng-eNB-DU.
W1-C:
Reference point for the control plane protocol between ng-eNB-CU and ng-eNB-DU.
ng-eNB-CU:
a logical node hosting RRC, SDAP and PDCP protocols of the ng-eNB that controls the operation of one or more ng-eNB-DUs. The ng-eNB-CU terminates the W1 interface connected with the ng-eNB-DU.
ng-eNB-DU:
a logical node hosting RLC, MAC and PHY layers of the ng-eNB, and its operation is partly controlled by ng-eNB-CU. One ng-eNB-DU supports one or multiple cells. One cell is supported by only one ng-eNB-DU. The ng-eNB-DU terminates the W1 interface connected with the ng-eNB-CU.
ng-eNB:
as defined in TS 38.300.
3.2 Symbols p. 6
Void.
3.3 Abbreviations p. 7
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
DRB
Data Radio Bearers
W1-U
W1 User plane interface
W1-C
W1 Control plane interface
W1AP
W1 Application Protocol
GTP-U
GPRS Tunnelling Protocol
IP
Internet Protocol
NR-MIB
NR-Master Information Block
O&M
Operation and Maintenance
PA
Paging Area
PF
Paging Frame
PO
Paging Occasion
QoS
Quality of Service
RRC
Radio Resource Control
SCTP
Stream Control Transmission Protocol
SRB
Signalling Radio Bearers
SIB1
System Information Block 1
TNL
Transport Network Layer
4 General aspects p. 7
4.0 General p. 7
This clause captures the W1 interface principles and characteristics.
4.1 W1 interface general principles p. 7
The general principles for the specification of the W1 interface are as follows:
- An ng-eNB may consist of an ng-eNB-CU and ng-eNB-DUs. An ng-eNB-CU and an ng-eNB-DU is connected via W1 logical interface.
- One ng-eNB-CU controls one or more ng-eNB-DUs.
- One ng-eNB-DU supports one or multiple cells. One cell is supported by only one ng-eNB-DU.
- ng-eNB-DU ID is used to identify ng-eNB-DU only over W1AP procedures, ng-eNB-DU ID is not connected to cell identifier.
- The ng-eNB-CU terminates W1 interface connected with the ng-eNB-DU.
- The ng-eNB-DU terminates W1 interface connected with the ng-eNB-CU.
- The W1 interface shall separate Radio Network Layer and Transport Network Layer.
- The W1 interface shall enable exchange of UE associated information and non-UE associated information.
- The W1 interface is open;
- From a logical standpoint, the W1 is a point-to-point interface between an ng-eNB-CU and an ng-eNB-DU.
- The W1 interface supports control plane and user plane separation;
- The W1 interface enables exchange of UE associated information and non-UE associated information;
- The standard should not prevent to separated CP and UP.
4.2 W1 interface specification objectives p. 8
The W1 interface specifications facilitate the following:
- inter-connection of an ng-eNB-CU and an ng-eNB-DU supplied by different manufacturers.
4.3 W1 interface capabilities p. 8
The W1 interface supports:
- procedures to establish, maintain and release radio bearers for the NG-RAN part of PDU sessions and for E-UTRAN Radio Access Bearers;
- the separation of each UE on the protocol level for user specific signalling management;
- the transfer of RRC signalling messages between the UE and the ng-eNB-CU.
4.4 W1 interface characteristics p. 8
5 Functions of the W1 interface p. 8
5.1 General p. 8
The following clauses describe the functions supported over W1-C and W1-U.
5.2 W1-C functions p. 8
5.2.1 Interface management function p. 8
The W1 setup function allows to exchange application level data needed for the ng-eNB-DU and ng-eNB-CU to interoperate correctly on the W1 interface. The W1 setup is initiated by the ng-eNB-DU.
The ng-eNB-CU Configuration Update and ng-eNB-DU Configuration Update functions allow to update application level configuration data needed between ng-eNB-CU and ng-eNB-DU to interoperate correctly over the W1 interface, and may activate or deactivate cells.
For NG-RAN, the W1 setup and ng-eNB-DU Configuration Update functions allow to inform the S-NSSAI(s) supported by the ng-eNB-DU.
The error indication function is used by the ng-eNB-DU or ng-eNB-CU to indicate to the ng-eNB-CU or ng-eNB-DU that an error has occurred.
The reset function is used to initialize the peer entity after node setup and after a failure event occurred. This procedure can be used by both the ng-eNB-DU and the ng-eNB-CU.
The W1 resource coordination function is used to transfer information about frequency resource sharing between ng-eNB-CU and ng-eNB-DU.
The ng-eNB-DU status indication function allows the ng-eNB-DU to indicate overload status to ng-eNB-CU.
5.2.2 System Information management function p. 9
Scheduling of system broadcast information is carried out in the ng-eNB-DU. The ng-eNB-DU is responsible for transmitting the system information according to the scheduling parameters available.
The ng-eNB-DU is responsible for the encoding of ng-eNB-MIB. In case broadcast of SIB1 and other SI messages is needed, the ng-eNB-DU is responsible for assembling SIB1, SIB2, SIB3, SIB8 and SIB16 and the ng-eNB-CU is responsible for assembling other SIBs.
5.2.3 Paging function p. 9
The ng-eNB-DU is responsible for transmitting the paging information.
The ng-eNB-CU provides paging information to enable the ng-eNB-DU to calculate the exact PO and PF. The ng-eNB-CU determines the PA. The ng-eNB-DU consolidates all the paging records for a particular PO, PF and PA, and encodes the final RRC message and broadcasts the paging message on the respective PO, PF in the PA.
5.2.4 UE context management function p. 9
The W1 UE context management function supports the establishment and modification of the necessary overall UE context.
The establishment of the W1 UE context is initiated by the ng-eNB-CU and accepted or rejected by the ng-eNB-DU based on admission control criteria (e.g., resource not available).
The modification of the W1 UE context can be initiated by either ng-eNB-CU or ng-eNB-DU. The receiving node can accept or reject the modification. The W1 UE context management function also supports the release of the context previously established in the ng-eNB-DU. The release of the context is triggered by the ng-eNB-CU either directly or following a request received from the ng-eNB-DU. The ng-eNB-CU requests the ng-eNB-DU to remove the UE Context when the UE enters RRC_IDLE or RRC_INACTIVE.
This function can be also used to manage DRBs and SRBs, i.e., establishing, modifying and releasing DRB and SRB resources. The establishment and modification of DRB resources are triggered by the ng-eNB-CU and accepted/rejected by the ng-eNB-DU based on resource reservation information and QoS information to be provided to the ng-eNB-DU. For each DRB to be setup or modified, the S-NSSAI may be provided by ng-eNB-CU to the ng-eNB-DU in the UE Context Setup procedure and the UE Context Modification procedure.
For NG-RAN, the mapping between QoS flows and radio bearers is performed by ng-eNB-CU and the granularity of bearer related management over W1 is radio bearer level, and the ng-eNB-CU decides an aggregated DRB QoS profile for each radio bearer based on received QoS flow profile, and provides both aggregated DRB QoS profile and QoS flow profile to the ng-eNB-DU, and the ng-eNB-DU either accepts the request or rejects it with appropriate cause value.
With this function, ng-eNB-DU could also notify ng-eNB-CU whether the QoS for already established DRBs is not fulfilled any longer or it is fulfilled again.
The UE Inactivity Notification function is initiated by the ng-eNB-DU to indicate the UE activity event.
The Notify function is to enable the ng-eNB-DU to inform the ng-eNB-CU that the QoS of an already established GBR DRB cannot by fulfilled any longer or that it can be fulfilled again.
With this function, the ng-eNB-CU indicates the UL UE AMBR limit to the ng-eNB-DU, and the ng-eNB-DU enforces the indicated limit.
With this function, the ng-eNB-CU indicates the UL UE AMBR limit to the ng-eNB-DU, and the ng-eNB-DU enforces the indicated limit.
With this function, ng-eNB-CU requests the ng-eNB-DU to setup or change of the SpCell for the UE, and the ng-eNB-DU either accepts or rejects the request with appropriate cause value.
With this function, the ng-eNB-CU requests the setup of the SCell(s) at the ng-eNB-DU side, and the ng-eNB-DU accepts all, some or none of the SCell(s) and replies to the ng-eNB-CU. The ng-eNB-CU requests the removal of the SCell(s) for the UE.
With this function, the ng-eNB-DU indicates that a bearer, or a UE is inactive or active. The ng-eNB-CU consolidates all the serving ng-eNB-DUs for the UE and takes further action.
5.2.5 RRC message transfer function p. 10
This function allows to transfer RRC messages between ng-eNB-CU and ng-eNB-DU. RRC messages are transferred over W1-C. The ng-eNB-CU is responsible for the encoding of the dedicated RRC message with assistance information provided by ng-eNB-DU. This function also allows ng-eNB-DU to report to ng-eNB-CU if the downlink RRC message has been successfully delivered to UE or not.
5.2.6 Warning messages information transfer function p. 10
This function allows to cooperate with the warning message transmission procedures over NG interface. The ng-eNB-CU is responsible for encoding the warning related SI message and sending it together with other warning related information for the ng-eNB-DU to broadcast over the radio interface.
5.3 W1-U functions p. 10
5.3.1 Transfer of user data p. 10
This function allows to transfer of user data between ng-eNB-CU and ng-eNB-DU.
5.3.2 Flow control function p. 10
This function allows to control the downlink user data flow to the ng-eNB-DU. The detailed protocol is specified in TS 38.425
6 Procedures of the W1 interface p. 10
6.1 Control plane procedures p. 10
6.1.1 Interface Management procedures p. 10
The W1 Interface management procedures are listed below:
- Reset procedure
- Error Indication procedure
- W1 Setup procedure
- ng-eNB-DU Configuration Update procedure
- ng-eNB-CU Configuration Update procedure
- ng-eNB-DU Resource Coordination procedure
- ng-eNB-DU Status Indication procedure
6.1.2 Context Management procedures p. 10
The W1 Context management procedures are listed below:
- UE Context Setup procedure
- UE context Release Request (ng-eNB-DU initiated) procedure
- UE context Release (ng-eNB-CU initiated) procedure
- UE Context Modification (ng-eNB-CU initiated) procedure
- UE Context Modification Required (ng-eNB-DU initiated) procedure
- UE Inactivity Notification procedure
- Notify procedure
6.1.3 RRC Message Transfer procedures p. 11
The W1 RRC message transfer procedures are listed below:
- Initial UL RRC Message Transfer procedure
- UL RRC Message Transfer procedure
- DL RRC Message Transfer procedure
- RRC Delivery Report procedure
6.1.3A Void
6.1.4 Warning Message Transmission procedures p. 11
The W1 Warning message transmission procedures are listed below:
- Write-Replace Warning procedure
- PWS Cancel procedure
- PWS Restart Indication procedure
- PWS Failure Indication procedure
6.1.5 Paging procedures p. 11
The W1 Paging procedures are listed below:
- Paging
6.2 User plane procedures p. 11
7 W1 interface protocol structure p. 12
7.1 W1 Control Plane Protocol (W1-C) p. 12
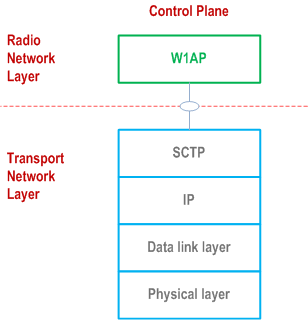
Figure 7.1-1 shows the protocol structure for W1-C. The TNL is based on IP transport, comprising the SCTP on top of IP. The application layer signalling protocol is referred to as W1AP (W1 Application Protocol).
7.2 W1 User Plane Protocol (W1-U) p. 12
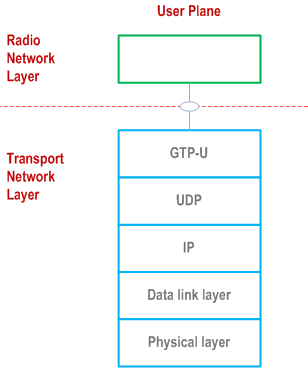
Figure 7.2-1 shows the protocol structure for W1-U. The TNL is based on IP transport, comprising the UDP and GTP-U on top of IP.
8 Other W1 interface specifications p. 12
8.0 General p. 12
This clause contains the description of the other related 3GPP specifications.
8.1 E-UTRAN and NG-RAN; W1 interface: layer 1 (3GPP TS 37.471) p. 13
3GPP TS 37.471 specifies the physical layer technologies that may be used to support the W1 interface.
8.2 E-UTRAN and NG-RAN; W1 signalling transport (3GPP TS 37.472) p. 13
3GPP TS 37.472 specifies the signalling bearers for the W1AP for the W1-C interface.
8.3 E-UTRAN and NG-RAN; W1 application protocol (W1AP) (3GPP TS 37.473) p. 13
3GPP TS 37.473 specifies the F1AP protocol for radio network control plane signalling over the W1 interface.
8.4 NG-RAN; NR user plane protocol (3GPP TS 38.425) p. 13
3GPP TS 38.425 specifies the user plane protocol being used over the W1-U interface.