Content for TS 29.536 Word version: 18.6.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions, abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.2 Abbreviations
4 Overview
4.1 General
4.1A NSAC Architecture Options
4.2 NSAC support in roaming
4.3 Interaction between NSACFs
...
...
1 Scope p. 9
The present document specifies the stage 3 protocol and data model for the Nnsacf Service Based Interface. It provides stage 3 protocol definitions and message flows, and specifies the API for each service offered by the NSACF.
The 5G System stage 2 architecture and procedures are specified in TS 23.501 and TS 23.502.
The Technical Realization of the Service Based Architecture and the Principles and Guidelines for Services Definition are specified in TS 29.500 and TS 29.501.
2 References p. 9
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 23.501: "System Architecture for the 5G System; Stage 2".
[3]
TS 23.502: "Procedures for the 5G System; Stage 2".
[4]
TS 29.500: "5G System; Technical Realization of Service Based Architecture; Stage 3".
[5]
TS 29.501: "5G System; Principles and Guidelines for Services Definition; Stage 3".
[6]
OpenAPI: "OpenAPI Specification Version 3.0.0", https://spec.openapis.org/oas/v3.0.0 .
[7]
TR 21.900: "Technical Specification Group working methods".
[8]
TS 33.501: "Security architecture and procedures for 5G system".
[9]
RFC 6749: "The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework".
[10]
TS 29.510: "5G System; Network Function Repository Services; Stage 3".
[11]
RFC 9113: "HTTP/2".
[12]
RFC 8259: "The JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) Data Interchange Format".
[13]
RFC 9457: "Problem Details for HTTP APIs".
[14]
RFC 6902: "JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) Patch".
[15]
TS 29.518: "5G System; Access and Mobility Management Service; Stage 3".
[16]
TS 29.571: "5G System; Common Data Types for Service Based Interfaces Stage 3".
[17]
TS 29.510: "5G System; Network Function Repository Services; Stage 3".
[18]
TS 23.288: "Architecture enhancements for 5G System (5GS) to support network data analytics services".
3 Definitions, abbreviations p. 10
3.1 Definitions p. 10
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
3.2 Abbreviations p. 10
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
AF
Application Function
5GC
5G Core Network
AMF
Access Management Function
DCCF
Data Collection Coordination Function
EAC
Early Admission Control
MCX
Mission Critical Service
MPS
Multimedia Priority Service
NEF
Network Exposure Function
NID
Network identifier
NSAC
Network Slice Admission Control
NSACF
Network Slice Admission Control Function
NSCE
Network Slice Capability Enablement
NWDAF
Network Data Analytics Function
SMF
Session Management Function
SNPN
Standalone Non-Public Network
4 Overview p. 10
4.1 General p. 10
Within the 5GC of a PLMN or a SNPN, the NSACF offers services to the AMF, SMF (or combined SMF+PGW-C), NWDAF, NEF, DCCF, NSCE and NSACF via the Nnsacf service based interface (see TS 23.501 and TS 23.502).
Figure 4-1 provides the reference model (in service based interface representation and in reference point representation), with focus on the NSACF and the scope of the present specification.
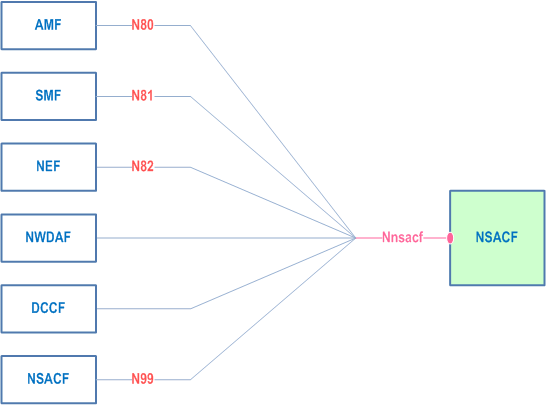
The functionalities supported by the NSACF are listed in clause 6.2.28 of TS 23.501.
The services and service operations provided by the Nnsacf interface are listed in clause 5.2.21 of TS 23.502.
When the UE connects to EPS and EPS counting is required, it is the combined SMF+PGW-C invokes NSACF services to perform network slice admission control, during PDN connection establishment procedure and PDN connection release procedure, as specified in clause 5.15.11.5 of TS 23.501.
4.1A NSAC Architecture Options |R18| p. 11
If the network is configured with a single NSAC service area, there is a single NSACF deployed to handle the admissions for an S-NSSAI.
If the network is configured with multiple NSAC service areas, one of the three NSAC architecture options, i.e. non-hierarchical NSAC architecture, centralized NSAC architecture and hierarchical NSAC architecture (as specified in clause 5.15.11.0 of TS 23.501), may be selected to handle the admissions for an S-NSSAI based on operator's policy.
In different NSAC architectures, there are different roles of NSACFs as:
- independent NSACFs are deployed in each NSAC service area in non-hierarchical NSAC architecture;
- a single centralized NSACF is deployed in the whole network in centralized NSAC architecture; and
- a primary NSACF and several distributed NSACFs are deployed in hierarchical NSAC architecture.
4.2 NSAC support in roaming p. 12
In the roaming scenario, depending on operator's policy and roaming agreement, a specific NSAC admission mode (i.e. VPLMN NSAC admission, VPLMN with HPLMN assistance admission or HPLMN NSAC admission) is determined for the NSAC procedure for roaming UEs (see clause 5.15.11.3 of TS 23.501).
For roaming UEs with LBO PDU session:
- if VPLMN NSAC admission (with or without HPLMN assistance) is determined, the vNSACF offers service to the NF in the VPLMN (e.g. AMF and SMF in VPLMN);
- if HPLMN NSAC admission is determined, the hNSACF offers service to the NF in the VPLMN (e.g. AMF and SMF in VPLMN). The AMF and SMF in VPLMN interact with hNSACF to perform NSAC procedure.
- the hNSACF offers service to the SMF in the HPLMN;
- if HPLMN NSAC admission is determined, the hNSACF offers service to the AMF in the VPLMN. Otherwise, the vNSACF offers services to the AMF in the VPLMN.
4.3 Interaction between NSACFs |R18| p. 12
NSACF interactions may exist in the following cases:
- for roaming case, if VPLMN with HPLMN assistance NSAC admission mode is determined, the NSACF in VPLMN may interact with the NSACF in HPLMN to fetch the quota for number of UEs or number of PDU sessions, and the NSACF in HPLMN may interact with the NSACF in VPLMN to provide the updated number of UEs or number of PDU sessions;
- for roaming case, if VPLMN NSAC admission mode is determined, the NSACF in VPLMN may interact with the NSACF in HPLMN to fetch the maximum number of registered UEs to be enforced and the maximum number of LBO PDU sessions to be enforced;
- in hierarchical NSAC architecture, a distributed NSACF may interact with the primary NSACF to fetch the quota for number of UEs or number of PDU sessions, and the primary NSACF may interact with the distributed NSACF to provide the updated number of UEs or number of PDU sessions, as specified in clause 5.15.11 of TS 23.501.