Content for TS 29.510 Word version: 18.7.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions and abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.2 Abbreviations
4 Overview
...
...
1 Scope p. 12
The present document specifies the stage 3 protocol and data model for the Nnrf Service Based Interface. It provides stage 3 protocol definitions and message flows, and specifies the API for each service offered by the NRF.
The 5G System stage 2 architecture and procedures are specified in TS 23.501 and TS 23.502.
The Technical Realization of the Service Based Architecture and the Principles and Guidelines for Services Definition are specified in TS 29.500 and TS 29.501.
2 References p. 12
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 23.501: "System Architecture for the 5G System; Stage 2".
[3]
TS 23.502: "Procedures for the 5G System; Stage 2".
[4]
TS 29.500: "5G System; Technical Realization of Service Based Architecture; Stage 3".
[5]
TS 29.501: "5G System; Principles and Guidelines for Services Definition; Stage 3".
[6]
TS 29.518: "5G System; Access and Mobility Management Services; Stage 3".
[7]
TS 29.571: "5G System; Common Data Types for Service Based Interfaces; Stage 3".
[8]
ECMA-262: "ECMAScript® Language Specification", https://www.ecma-international.org/ecma-262/5.1/ .
[9]
RFC 9113: "HTTP/2".
[10]
OpenAPI Initiative, "OpenAPI Specification Version 3.0.0", https://spec.openapis.org/oas/v3.0.0 .
[11]
RFC 9457: "Problem Details for HTTP APIs".
[12]
TS 23.003: "Numbering, Addressing and Identification".
[13]
RFC 6902: "JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) Patch".
[14]
RFC 6901: "JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) Pointer".
[15]
TS 33.501: "Security architecture and procedures for 5G system".
[16]
RFC 6749: "The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework".
[17]
RFC 3986: "Uniform Resource Identifier (URI): Generic Syntax".
[18]
RFC 4122: "A Universally Unique IDentifier (UUID) URN Namespace".
[19] Void.
[20]
RFC 9111: "HTTP Caching".
[21]
TS 29.244: "Interface between the Control Plane and the User Plane Nodes; Stage 3".
[22]
RFC 8259: "The JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) Data Interchange Format".
[23]
RFC 2782: "A DNS RR for specifying the location of services (DNS SRV)".
[24]
RFC 7515: "JSON Web Signature (JWS)".
[25]
RFC 7519: "JSON Web Token (JWT)".
[26]
W3C HTML 4.01 Specification: https://www.w3.org/TR/2018/SPSD-html401-20180327/ .
[27]
TS 23.527: "5G System; Restoration Procedures; Stage 2".
[28]
TS 29.513: "5G System; Policy and Charging Control signalling flows and QoS parameter mapping; Stage 3".
[29]
TS 38.413: "NG-RAN; NG Application Protocol (NGAP)".
[30]
RFC 1952: "GZIP file format specification version 4.3".
[31]
TR 21.900: "Technical Specification Group working methods".
[32]
TS 29.520: "5G System; Network Data Analytics Services; Stage 3".
[33]
TS 29.572: "5G System; Location Management Services; Stage 3".
[34]
TS 23.288: "Architecture enhancements for 5G System (5GS) to support network data analytics services".
[35]
TS 29.517: "Application Function Event Exposure Service".
[36]
TS 29.503: "Unified Data Management Services".
[37]
TS 29.336: "Home Subscriber Server (HSS) diameter interfaces for interworking with packet data networks and applications".
[38]
IANA: "SMI Network Management Private Enterprise Codes", http://www.iana.org/assignments/enterprise-numbers .
[39]
Semantic Versioning Specification: https://semver.org .
[40]
RFC 9110: "HTTP Semantics".
[41] Void.
[42]
TS 29.531: "5G System; Network Slice Selection Services; Stage 3".
[43]
TS 23.247: "Architectural enhancements for 5G multicast-broadcast services".
[44]
ITU-T Recommendation E.164: "The international public telecommunication numbering plan".
[45]
TS 23.380: "IMS Restoration Procedures".
[46]
TS 32.255: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; 5G data connectivity domain charging; Stage 2".
[47]
TS 29.514: "5G System; Policy Authorization Service; Stage 3".
[48]
TS 23.540: "5G System; Technical realization of Service Based Short Message Service; Stage 2".
[49]
TS 29.564: "5G System; User Plane Function Services; Stage 3".
[50]
TS 33.310: "Network Domain Security (NDS); Authentication Framework (AF)".
[51]
TS 29.536: "5G System; Network Slice Admission Control Services; Stage 3".
[52]
RFC 7858: "Specification for DNS over Transport Layer Security (TLS)".
[53]
RFC 8310: "Usage Profiles for DNS over TLS and DNS over DTLS".
[54]
RFC 8094: "DNS over Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS)".
3 Definitions and abbreviations p. 14
3.1 Definitions p. 14
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
Canary Release:
When an NF Instance is software upgraded, a canary release allows to have features incrementally tested by a small set of users, which can be targeted by geographic locations or user attributes (e.g., SUPI, PEI, …). If a feature's performance is not satisfactory, then it can be rolled back without any adverse effects on the rest of the system.
3.2 Abbreviations p. 14
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
5GC
5G Core Network
CEF
Charging Enablement Function
CH
Credentials Holder
CHF
Charging Function
DCS
Default Credentials Server
DCSF
Data Channel Signaling Function
IPUPS
Inter-PLMN User Plane Security
MBS
Multicast/Broadcast Service
MB-SMF
Multicast/Broadcast Session Management Function
NF
Network Function
NRF
NF Repository Function
NWDAF
Network Data Analytics Function
PFD
Packet Flow Description
PRU
Positioning Reference Unit
SNPN
Stand-alone Non-Public Network
SSM
Source Specific IP Multicast (address)
TNGF
Trusted Non-3GPP Gateway Function
TSCTSF
Time Sensitive Communication and Time Synchronization Function
TWIF
Trusted WLAN Interworking Function
W-AGF
Wireline Access Gateway Function
4 Overview p. 15
The Network Function (NF) Repository Function (NRF) is the network entity in the 5G Core Network (5GC) supporting the following functionality:
- Maintains the NF profile of available NF instances and their supported services;
- Maintains the SCP profile of available SCP instances;
- Maintains the SEPP profile of available SEPP instances;
- Allows other NF or SCP instances to subscribe to, and get notified about, the registration in NRF of new NF instances of a given type or of SEPP instances. It also allows SCP instances to subscribe to, and get notified about, the registration in NRF of new SCP instances;
- Supports service discovery function. It receives NF Discovery Requests from NF or SCP instances, and provides the information of the available NF instances fulfilling certain criteria (e.g., supporting a given service);
- Support SCP discovery function. It receives NF Discovery Requests for SCP profiles from other SCP instances, and provides the information of the available SCP instances fulfilling certain criteria (e.g., serving a given NF set);
- Support SEPP discovery function. It receives NF Discovery Requests for SEPP profiles from other NF or SCP instances, and provides the information of the available SEPP instances fulfilling certain criteria (e.g. supporting connectivity with a remote PLMN).
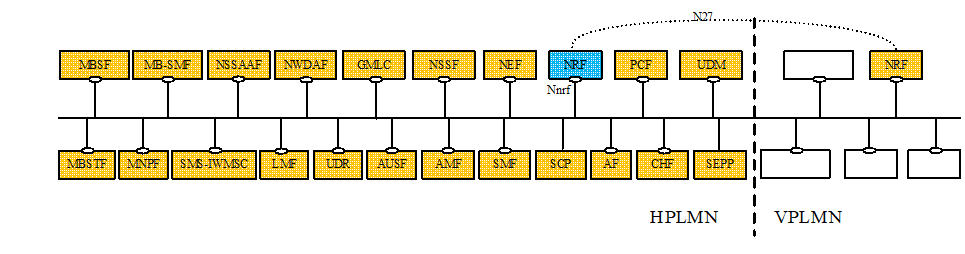
Figure 4-1 illustrates PLMN level scenarios, but this architecture is also applicable to the SNPN scenarios, as explained below.
For the sake of clarity, the NRF is never depicted in reference point representation figures, given that the NRF interacts with every other NF in the 5GC. As an exception, in the roaming case, the reference point between the vNRF and the hNRF is named as N27. The reference point name of N27 is used only for representation purposes, but its functionality is included in the services offered by the Nnrf Service-Based Interface.
In the case of SNPN, the NRF provides services e.g. in the following scenarios:
- For a SNPN for which roaming is not supported (see clause 5.30.2.0 of TS 23.501);
- For the case of UE access to SNPN using credentials from Credentials Holder (see clause 5.30.2.9 of TS 23.501);
- For the case of Onboarding of UEs for SNPNs (see clause 5.30.2.10 of TS 23.501).