Content for TS 29.364 Word version: 18.1.0
0 Introduction
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.2 Abbreviations
4 General
5 Architecture
...
...
0 Introduction p. 7
Application Servers can store their service data on the HSS through the Sh interface as transparent data, meaning that the HSS may not be aware of the structure and the semantics of this data, only the Application Server has this knowledge. Standardizing the data formats would facilitate interoperation among Application Servers supplied by the same, or different, vendors. These Application Server vendors may be primary and secondary suppliers of the same service provider within a service provider's IMS network. This is especially true for the Multimedia Telephony supplementary services that can achieve a wide deployment and are here addressed by this specification.
IMS CAMEL subscription data may be transferred to the IM-SSF AS using Sh interface.
1 Scope p. 7
This specification standardizes
- the structure and the coding of the service data that are transported over the Sh interface between an Application Server supporting Multimedia Telephony supplementary services as defined in 3GPPP TS 22.173 and the HSS. Two optional formats are specified. One is based on a binary coding of the service data and supports the subset of MMTEL services corresponding to PSTN/ISDN and CS supplementary services. The other uses an XML format and supports the full set of MMTEL Services.
- the structure and the coding of a set of generic IMS user group data over the Sh interface.
- the structure and the coding of the service data (ODB Information for IMS Oriented Services) that are transported over the Sh interface between an Application Server supporting services that are subject to IMS-ODB as defined in TS 22.041 and the HSS.
- the structure and the coding of the IMS CAMEL subscription data transported using Sh interface.
2 References p. 8
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TS 22.173: "IP Multimedia Core Network Subsystem (IMS) Multimedia Telephony Service and supplementary services; Stage 1".
[2]
TS 24.604: "Communication Diversion (CDIV); Protocol specification using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification ".
[3]
TS 24.605: "Conference (CONF) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification".
[4]
TS 24.606: "Message Waiting Indication (MWI) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification".
[5]
TS 24.607: "Originating Identification Presentation (OIP) and Originating Identification Restriction (OIR) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification".
[6]
TS 24.608: "Terminating Identification Presentation (TIP) and Terminating Identification Restriction (TIR) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification".
[7]
TS 24.610: "Communication HOLD (HOLD) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification".
[8]
TS 24.611: "Anonymous Communication Rejection (ACR) and Communication Barring (CB) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification".
[9]
TS 24.615: "Communication Waiting (CW) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification".
[10]
TS 24.616: "Malicious Communication Identification (MCID) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification".
[11]
TS 24.629: "Explicit Communication Transfer (ECT) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification".
[12]
TS 24.642: "Completion of Communications to Busy Subscriber (CCBS), Completion of Communications by No Reply (CCNR) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification".
[13]
TS 24.647: "Advice Of Charge (AOC) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification".
[14]
TS 24.654: "Closed User Group (CUG) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification".
[15]
TS 24.239: "Flexible Alerting (FA) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification".
[16]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[17]
TS 29.328: "IP Multimedia (IM) Subsystem Sh interface; Signalling flows and message contents".
[18]
TS 24.238: " Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) based user configuration; Stage 3".
[19]
RFC 2045: "Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension (MIME) Part One: Format of Internet Message Bodies".
[20]
TS 22.182: "Customized Alerting Tones (CAT) Requirements; Stage 1".
[21]
TS 24.182: " IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Customized Alerting Tones (CAT); Protocol specification".
[22]
TS 32.280: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Advice of Charge (AoC) service".
[23]
ISO 4217: "Codes for the representation of currencies and funds ".
[24]
TS 23.003: "Numbering, addressing and identification".
[25]
TS 22.041: "Operator Determined Barring (ODB)".
[26]
TS 23.278: "Customised Applications for Mobile network Enhanced Logic (CAMEL); IP Multimedia System (IMS) interworking; Stage 2".
[27]
TS 29.002: "Mobile Application Part (MAP) specification".
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations p. 9
3.1 Definitions p. 9
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 apply.
3.2 Abbreviations p. 9
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
3PTY
Three-Party Communication
ACR
Anonymous Communication Rejection
AOC-C
Advice Of Charge - Charging
AOC-D
Advice Of Charge - During the communication
AOC-E
Advice Of Charge - at the End of the communication
AOC-I
Advice Of Charge - for Information
AOC-S
Advice Of Charge - at communication Set-up time
AS
Application Server
CAT
Customized Alerting Tones
CB
Communication session Barring
CCBS
Completion of Communication sessions to Busy Subscriber
CCNR
Completion of Communication sessions on No Reply
CD
Communication Deflection
CDIV
Communication DIVersion
CFB
Communication Forwarding Busy
CFNL
Communication Forwarding on Not Logged-in
CFNR
Communication Forwarding No Reply
CFNRc
Communication Forwarding on Subscriber Not Reachable
CFU
Communication Forwarding Unconditional
CONF
CONFerence
CUG
Closed User Group
CW
Communication Waiting
ECT
Explicit Communication Transfer
FA
Flexible Alerting
GRUU
Globally Routable User agent URI
HOLD
Communication HOLD
ICB
Incoming Communications Barring
MCID
Malicious Communication IDentification
MMTEL
MultiMedia Telephony
MWI
Message Waiting Indication
OCB
Outgoing Communications Barring
OIP
Originating Identification Presentation
OIR
Originating Identification Restriction
TIP
Terminating Identification Presentation
TIR
Terminating Identification Restriction
4 General p. 10
MMTEL/IMS CAMEL Services are supported by Application Servers that may store the Service Data attached to each user in the HSS via the Sh Interface. This data is referred to as transparent data and is understood syntactically but not semantically by the HSS.
Different ASs providing MMTEL/IMS CAMEL services for a given user may be required. Therefore several ASs should access, utilise and update the Service Data for the user stored in the HSS. The ASs should interoperate and share the Service Data attached to this user.
To aid the interoperability between ASs, this specification defines:
- the structure and the coding of the Service Data transferred over the Sh interface between the HSS and the ASs for MMTEL/IMS CAMEL services,
- the use of the Sh procedures to ensure the sharing and synchronization of these Service Data between ASs,
- additional transfer mechanism such as base64 encoding.
- A XML format supporting the Service Data for the complete MMTEL Services.
- A binary format supporting the Service Data for the subset of MMTEL Services corresponding to the PSTN/ISDN and CS supplementary services.
5 Architecture p. 10
Figure 5-1 presents the functional architecture for AS interoperability.
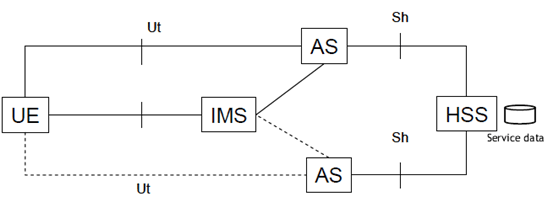
The MMTEL communications of a given user equipment are routed to an AS according to the content of the filter criteria.
If AS interoperability is supported, the Service Data attached to a user shall be stored in the HSS and the AS shall access and update, when required, the Service Data via the Sh interface.
The user may configure some of its Service Data via the Ut interface, via SIP based user configuration as described in TS 24.238, or via other means.
Some Service Data is configured by the service provider e.g. from its OSS, either directly into the HSS or via an AS that will store these Service Data in the HSS.
The AS associated to a given user for MMTEL services may vary over time.
The same format of the Service Data stored in the HSS shall be supported for interoperability between ASs utilising the Service Data.