Content for TS 29.334 Word version: 18.1.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.2 Symbols
3.3 Abbreviations
4 Applicability
...
...
1 Scope p. 7
The present document describes the protocol to be used on the IMS Application Level Gateway (ALG) - IMS Access Gateway (IMS-AGW) interface. The basis for this protocol is the H.248 protocol as specified in ITU-T. The IMS architecture is described in TS 23.228. The underlying reference model and stage 2 information is described in Annex G of TS 23.228 and in TS 23.334.
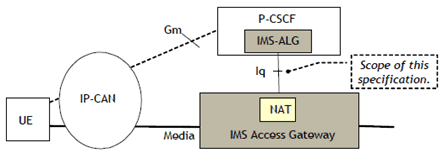
This specification describes the application of H.248 on the Iq interface (see Figure 1). Required extensions use the H.248 standard extension mechanism. In addition certain aspects of the base protocol H.248 are not needed for this interface and thus excluded by this profile.
The reference model for the IMS-ALG and the IMS-AGW supporting the ATCF/ATGW function is shown in Figure 1a below.
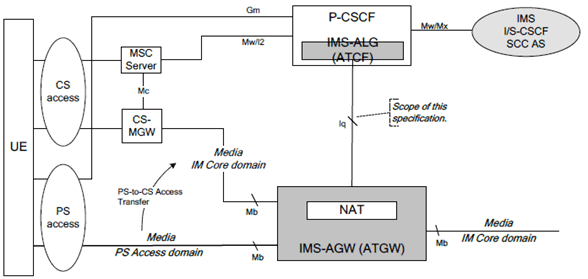
Figure 1a: Reference model for IMS-ALG/IMS-AGW with ATCF/ATGW function
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
See clause 5.2 of TS 23.237 for a comprehensive description of the reference model.
The reference model for the P-CSCF enhanced for WebRTC (eP-CSCF) and the IMS-AGW enhanced for WebRTC (eIMS-AGW) to support WebRTC client access to IMS is shown in Figure 1b as below, see TS 23.228 Annex U for a comprehensive description of the reference model.
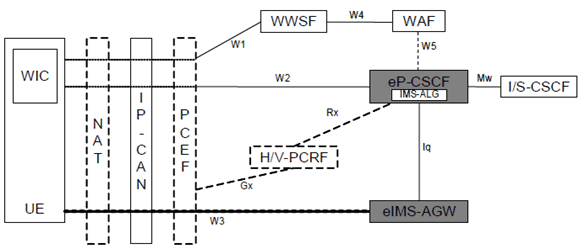
Figure 1b: Reference Architecture for eP-CSCF/eIMS-AGW supporting WebRTC access to IMS
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
2 References p. 8
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 23.228: "IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Stage 2".
[3]
ETSI TS 183 018 V3.5.1 (2009-07): "Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); Resource and Admission Control: H.248 Profile Version 3 for controlling Border Gateway Functions (BGF) in the Resource and Admission Control Subsystem (RACS); Protocol specification".
[4]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.37 (06/2008): "Gateway control protocol: IP NAPT traversal package".
[5]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.57 (10/2014): "Gateway control protocol: RTP Control Protocol Package".
[6]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.43 (06/2008): "Gateway control protocol: Gate Management and Gate Control packages".
[7]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.53 (03/2009): "Gateway control protocol: Traffic management packages".
[8]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.41 Amendment 1 (06/2008): "Gateway control protocol: IP domain connection package: IP Realm Availability Package".
[9]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.36 (09/2005): "Gateway control protocol: Hanging Termination Detection package".
[10]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.1 (05/2002): "Gateway Control Protocol: Version 2" including the Corrigendum1 for Version 2 (03/04).
[11]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.14 (03/2009): "Gateway control protocol: Inactivity timer package".
[12]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.52 (06/2008): "Gateway control protocol: QoS support packages".
[13]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.11 (11/2002): "Gateway control protocol: Media gateway overload control package".
Inclusive Corrigendum 1 (06/2008) to H.248.11 " Gateway control protocol: Media gateway overload control package: Clarifying MG-overload event relationship to ADD commands".
[14]
Inclusive Corrigendum 1 (06/2008) to H.248.11 " Gateway control protocol: Media gateway overload control package: Clarifying MG-overload event relationship to ADD commands".
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.10 (07/2001): "Media gateway resource congestion handling package".
[15]
RFC 5234 (2008): "Augmented BNF for Syntax Specifications: ABNF".
[16]
RFC 4960 (2007): "Stream control transmission protocol".
[17]
RFC 4566 (2006): "SDP: Session Description Protocol".
[18]
RFC 4975 (2007): "The Message Session Relay Protocol (MSRP)".
[19]
RFC 3551 (2003): "RTP Profile for Audio and Video Conferences with Minimal Control".
[20]
RFC 4145 (2005): "TCP-Based Media Transport in the Session Description Protocol (SDP)".
[21]
RFC 3605 (2003): "Real Time Control Protocol (RTCP) attribute in Session Description Protocol (SDP)".
[22]
ITU-T Recommendation X.690 (11/2008): "ASN.1 encoding rules: Specification of Basic Encoding Rules (BER), Canonical Encoding Rules (CER) and Distinguished Encoding Rules (DER)".
[23]
TS 23.334: "IMS Application Level Gateway (IMS-ALG) - IMS Access Gateway (IMS-AGW) interface: Procedures Descriptions".
[24]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.40 (01/2007): "Gateway control protocol: Application Data Inactivity Detection package".
[25]
RFC 4585 (2006): "Extended RTP Profile for Real-time Transport Control Protocol (RTCP) - Based Feedback (RTP/AVPF)".
[26]
TS 26.114: "IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Multimedia telephony; Media handling and interaction".
[27]
TS 33.210: "Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects;3G Security; Network Domain Security; IP Network Layer Security".
[28]
RFC 3556 (2003): "Session Description Protocol (SDP) Bandwidth Modifiers for RTP Control Protocol (RTCP) Bandwidth".
[29]
RFC 4568 (2006): "Session Description Protocol (SDP) Security Descriptions for Media Streams".
[30]
RFC 3711 (2004): "The Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP)".
[31]
RFC 5124 (2008): "Extended Secure RTP Profile for Real-time Transport Control Protocol (RTCP)-Based Feedback (RTP/SAVPF)".
[32]
RFC 2216 (1997): "Network Element Service Specification Template".
[33]
Supplement 7 to ITU-T H-series Recommendations H.Sup7 (05/2008): "Gateway control protocol: Establishment procedures for the H.248 MGC-MG control association".
[34]
TS 33.328: "IMS Media Plane Security".
[35] Void
[36] Void
[37] Void
[38]
TS 23.237: "IP Multimedia subsystem (IMS) Service Continuity; Stage 2".
[39]
TS 22.153: "Multimedia Priority Service".
[40]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.82 (03/2013): "Gateway control protocol: Explicit Congestion Notification Support".
[41]
RFC 5285 (2008): "A General Mechanism for RTP Header Extensions".
[42]
RFC 6236: "Negotiation of Generic Image Attributes in the Session Description Protocol (SDP)".
[43]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.50 (07/2016): "Gateway control protocol: NAT traversal toolkit packages".
[44] Void.
[45]
TS 24.229: "IP Multimedia Call Control Protocol based on SIP and SDP".
[46]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.84 (07/2012): "Gateway control protocol: NAT traversal for peer-to-peer services".
[47]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.89 (10/2014): "Gateway control protocol: TCP support packages".
[48]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.90 (10/2014): "Gateway control protocol: ITU-T H.248 packages for control of transport security using transport layer security (TLS)".
[49]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.92 (10/2014): "Gateway control protocol: Stream endpoint interlinkage package".
[50]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.93 (10/2014): "Gateway control protocol: ITU-T H.248 support for control of transport security using the datagram transport layer security (DTLS) protocol".
[51]
RFC 793: "Transmission Control Protocol - DARPA Internet Program - Protocol Specification".
[52]
RFC 4582: "The Binary Floor Control Protocol (BFCP)".
[53] Void
[54] Void
[55]
RFC 8122: "Connection-Oriented Media Transport over the Transport Layer Security (TLS) Protocol in the Session Description Protocol (SDP)".
[56]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.78 (11/2015): "Gateway control protocol: Bearer-level message backhauling and application level gateway".
[57]
RFC 6714: "Connection Establishment for Media Anchoring (CEMA) for the Message Session Relay Protocol (MSRP)".
[58]
RFC 7675: "Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN) Usage for Consent Freshness".
[59]
RFC 5761: "Multiplexing RTP Data and Control Packets on a Single Port".
[60]
RFC 5763: "Framework for Establishing a Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP) Security Context Using Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS)".
[61]
RFC 5764: "Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) Extension to Establish Keys for the Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP)".
[62]
RFC 4573: "MIME Type Registration for RTP Payload Format for H.224".
[63]
ITU-T Recommendation H.224 (01/2005): "A real time control protocol for simplex applications using the H.221 LSD/HSD/MLP channels".
[64]
ITU-T Recommendation H.281 (11/1994): "A far end camera control protocol for videoconferences using H.224".
[65]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.96 (11/2015): "Gateway control protocol: H.248 support for control of SCTP bearer connections".
[66]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.97 (11/2015): "Gateway control protocol: H.248 support for control of SCTP bearer connections".
[67]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.94 (11/2015): "Gateway control protocol: Web-based real-time communication services - H.248 protocol support and profile guidelines".
[68]
RFC 8841: "Session Description Protocol (SDP) Offer/Answer Procedures for Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) over Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) Transport".
[69]
RFC 8864: "Negotiation Data Channels Using the Session Description Protocol (SDP)".
[70]
RFC 8873: "Message Session Relay Protocol (MSRP)".
[71]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.88 (01/2014): "Gateway control protocol: RTP topology dependent RTCP handling by ITU-T H.248 media gateways with IP terminations".
[72]
RFC 5939: "Session Description Protocol (SDP) Capability Negotiation".
[73]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.80 (01/2014): "Gateway control protocol: Usage of the revised SDP offer/answer model with ITU-T H.248".
[74]
RFC 8858: "Indicating Exclusive Support of RTP and RTP Control Protocol (RTCP) Multiplexing Using the Session Description Protocol (SDP)".
[75]
ITU-T Recommendation T.140 (02/98): "Text conversation presentation protocol".
[76]
RFC 4103: "RTP Payload for Text Conversation".
[77]
RFC 8865: "T.140 Real-Time Text Conversation over WebRTC Data Channels".
[78]
RFC 5104: "Codec Control Messages in the RTP Audio-Visual Profile with Feedback (AVPF)".
[79]
RFC 7728: "RTP Stream Pause and Resume".
[80]
RFC 8445: "Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE): A Protocol for Network Address Translator (NAT) Traversal".
[81]
RFC 8839: "Session Description Protocol (SDP) Offer/Answer Procedures for Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE)".
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations p. 12
3.1 Definitions p. 12
For the purposes of the present document, the following terms and definitions apply.
Address:
term used for "network address" (IP address)
End-to-access edge security:
media protection extending between an IMS UE and the first IMS core network node in the media path without being terminated by any intermediary node.
Port:
term used for "transport port" (L4 port).
Transcoding:
transcoding in general is the translation from one type of encoded media format to another different media format, e.g. G.711 A-law to μ-law or vice versa, G.729 to AMR with 4.75 rate.
Transparent Forwarding:
media gateway packet forwarding behaviour with the characteristic of Lx-PDU integrity. This is a unidirectional characteristic of an Lx-PDU flow.
Transport Address:
term used for the combination of a Network Address and a Transport Port.
For the purposes of the present document, the following terms and definitions as defined in TS 23.334 apply:
ICE lite
Full ICE
3.2 Symbols p. 13
For the purposes of the present document, the following symbols apply:
Iq
Interface between the IMS Application Level Gateway (ALG) (IMS-ALG) and the IMS Access Gateway (IMS-AGW)
3.3 Abbreviations p. 13
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations defined in TR 21.905 apply, with the following additions. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
ABNF
Augmented Backus-Naur Form
ATCF
Access Transfer Control Function
ATGW
Access Transfer Gateway
B-ALG
Bearer Level Application-Level Gateway
BFCP
Binary Floor Control Protocol
CCM
Codec Control Messages
CVO
Coordination of Video Orientation
DBI
Delay Budget Information
DSCP
Differentiated Service Code Point
e2ae
End-to-Access-Edge (security model)
ECN
Explicit Congestion Notification
eIMS-AGW
IMS Access Gateway enhanced for WebRTC
eP-CSCF
P-CSCF enhanced for WebRTC
EVS
Enhanced Voice Services
FECC
Far End Camera Control
FIR
Full Intra Request
GTT
Global Text Telephony
ICE
Interactive Connectivity Establishment
IMS-AGW
IMS Access Gateway
IMS-ALG
IMS Application Level Gateway
IP
Internet Protocol
IVAS
Immersive Voice and Audio Services
LD
Local Descriptor (H.248 protocol element)
MG
Media Gateway
MGC
Media Gateway Controller
MPS
Multimedia Priority Service
MSRP
Message Session Relay Protocol
MTSI
Multimedia Telephony Service for IMS
NA
Not Applicable
NAPT
Network Address and Port Translation
NAPT-PT
NAPT and Protocol Translation
NAT
Network Address Translation
RD
Remote Descriptor (H.248 protocol element)
ROI
Region of Interest
RTCP
RTP Control Protocol
SCTP
Stream Control Transport Protocol
SDP
Session Description Protocol
SDPCapNeg
SDP Capability Negotiation
SRVCC
Single Radio Voice Call Continuity
STUN
Session Traversal Utilities for NAT
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol
TLS
Transport Layer Security (protocol)
TMMBN
Temporary Maximum Media Stream Bit Rate Notification
TMMBR
Temporary Maximum Media Stream Bit Rate Request
ToS
Type-of-Service
TISPAN
Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking
WebRTC
Web Real Time Communication
WIC
WebRTC IMS Client
WWSF
WebRTC Web Server Function
4 Applicability p. 14
The support of the Iq interface capability set shall be identified by the H.248 Iq profile and support of this profile shall be indicated in H.248 ServiceChange procedure (during the (re-)registration phase(s)).