Content for TR 28.865 Word version: 18.1.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions of terms, symbols and abbreviations
3.1 Terms
3.2 Symbols
3.3 Abbreviations
4 Overview and Concepts
4.1 Overview
4.2 Concepts
...
...
1 Scope p. 6
The present document studies potential key issues and solutions for provisioning and assurance of deterministic communication services, e.g. management of related network functions, potential new service requirements and new performance measurements, etc. The present document provides conclusions and recommendations on the normative work.
2 References p. 6
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 22.261: "Service requirements for the 5G system".
[3]
TS 22.104: "Physical control applications in vertical domains".
[4]
TS 23.501: "System architecture for the 5G System (5GS)".
[5]
TS 28.541: "5G Network Resource Model (NRM); Stage 2 and stage 3".
[6]
NG.116: "Generic Network Slice Template"; v7.0; 17 June 2022.
[7]
TS 28.552: "Management and orchestration; 5G performance measurements".
[8]
TS 28.554: "Management and orchestration; 5G end to end Key Performance Indicators (KPI)".
[9]
TR 28.832: "Study on management aspects of Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communications (URLLC) "
[10]
TS 38.323: "NR; Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP) specification "
[11]
TS 38.331: "NR; Radio Resource Control (RRC); Protocol specification "
[12]
TS 37.340: "NR; Multi-connectivity; Overall description; Stage-2 "
[13]
TS 38.321: "NR; Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol specification"
[14]
TS 38.331: "NR; Radio Resource Control (RRC); Protocol specification "
[15]
TS 38.423: "NG-RAN; Xn Application Protocol (XnAP) "
[16]
TS 37.355: "LTE Positioning Protocol (LPP) "
[17]
TR 28.833: "Study on management aspects of 5GLAN "
[18]
TR 28.907: "Study on enhancement of management of non-public networks "
[19]
TS 28.833: "Management and orchestration; Management of Non-Public Networks (NPN); Stage 1 and stage 2 "
[20]
TR 28.903: "Study on alignment with ETSI MEC for edge computing management"
[21]
TS 28.538: "Management and orchestration; Edge Computing Management"
[22]
TS 23.502: "Procedures for the 5G System (5GS)"
[23]
TS 23.273: "5G System (5GS) Location Services (LCS); Stage 2"
[24]
TS 28.530: "Management and orchestration; Concepts, use cases and requirements"
[25]
TS 28.532: "Management and orchestration; Generic management services"
[26]
TS 28.535: "Management and orchestration; Management services for communication service assurance; Requirements"
[27]
TS 28.536: "Management and orchestration; Management services for communication service assurance; Stage 2 and stage 3"
[28]
TS 23.288: "Architecture enhancements for 5G System (5GS) to support network data analytics services"
3 Definitions of terms, symbols and abbreviations p. 7
3.1 Terms p. 7
For the purposes of the present document, the terms given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
None.
3.2 Symbols p. 7
None.
3.3 Abbreviations p. 7
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
DCSA
Deterministic Communication Service Assurance
PLC
Programmable Logic Controller
TSC
Time Sensitive Communication
4 Overview and Concepts p. 7
4.1 Overview p. 7
5G network should satisfy diversified SLA requirements to support different vertical applications. Service requirements are more stringent for deterministic communication services as described in TS 22.261 and TS 22.104, e.g. video monitoring for production environment in a factory, remote control etc. The latency/transmission time of a data package is bounded by a given threshold. There are two typical traffic classes or communication patterns for deterministic communication service: deterministic periodic communication and deterministic aperiodic communication. In clause 5 of TS 22.104, performance requirements for some deterministic communication services are provided. In TS 23.501, QoS characteristics are defined for some deterministic communication services, e.g. some 5QIs for delay critical GBR services. Communication service availability and reliability are more important for these services types. Service experience degradation or violation of the latency requirements such as unstable jitter or unexpected packet loss may result in service interruption or severe consequences. Stable and deterministic communication service experience should be assured.
There are some features in the 5G network to support deterministic communication services, e.g. URLLC related network functions for radio interface and 5GC network, 5GS Integration with TSN and Industrial IoT, high accuracy positioning etc. How to support deterministic communication services from management aspects are investigated in this present document, e.g. provisioning of the related network functions, solutions for the assurance of deterministic communication services such as video monitoring and PLC control, etc.
4.2 Concepts p. 8
4.2.1 Management framework of deterministic communication service assurance p. 7
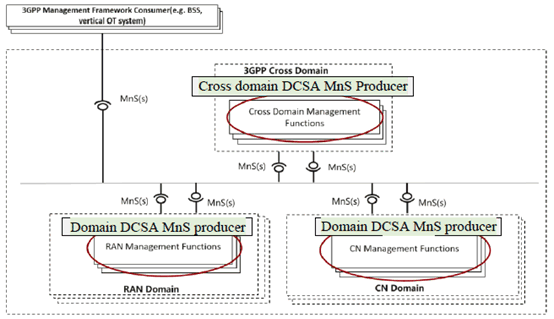
It is assumed that a dedicated management service is used to manage the deterministic communication service assurance. It may also coordinate with other related management services to provide service assurance for deterministic communications when it is needed. Based on the Service based management architecture, Deterministic Communication Service Assurance (DCSA) MnS producer could reside on 3GPP cross domain, RAN domain or CN domain as shown in the following Figure. DCSA MnS producer in 3GPP cross domain coordinates with DCSA MnS producers in RAN domain and CN domain.
To investigate how to support deterministic communication service assurance from management aspects, the management framework of DCSA MnS producer is studied. The following Figure shows the functional framework of DCSA MnS producer, including processes of data collection, service requirement modeling, network preparation, service and network analysis, optimization and verification. The main functionalities of each process is described as follows:
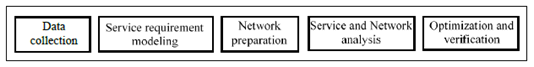
Data collection: Collects network performance and alarm data, signaling-plane and user-plane measurement information and abnormal events, and collects service experience related network performance information. The collected data is used for as input for other processes.
Service requirement modeling: The three-layer model of service experience, service quality, network performance is used for service requirement modeling. The service experience and service quality targets are analysed to derive the network capability requirements.
Network preparation: Based on deterministic communication service requirements, the DCSA MnS producer prepares network capabilities to ensure the SLA, and provides the corresponding network deployment solution, e.g. deployment of network slice, RAN functions and CN functions related to URLLC, Industrial IoT, TSN integration with 5GS to support deterministic communication service.
Service and network analysis: The DCSA MnS producer evaluates and identifies service and network issues through monitoring and analysis, demarcates and analyses the issues, and provides analysis recommendation for further optimization if needed.
Optimization and verification: The optimization is targeted to improve the service and network performance. For example, the optimization may include latency related optimization for a network slice instance. The optimization solution is applied and verification conclusion is conducted. If the optimization result deviates from the SLA target, the optimization solution is adjusted accordingly and the iterative optimization process is performed.