Content for TS 27.060 Word version: 18.0.0
0 Introduction
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions abbreviations and symbols
4 Access reference configuration
5 Functions to support data services
...
...
0 Introduction p. 5
The present document defines the requirements for TE-MT interworking over the R-reference point for the Packet Domain, within the 3GPP systems. It is up to the manufacturer how to implement the various functions but the present document and existing TS 27.001, TS 27.002, and TS 27.003 shall be followed where applicable.
It is the intention that the present document shall remain as the specification to develop a MS for support of Packet Switched services and its text includes references to 3GPP standards.
1 Scope p. 6
The (A/Gb and Iu mode) PLMN supports a wide range of voice and non-voice services in the same network. In order to enable non voice traffic in the PLMN there is a need to connect various kinds of terminal equipments to the Mobile Station (MS). The present document defines the requirements for TE-MT interworking over the R-reference point for the Packet Domain , including the protocols and signalling needed to support Packet Switched services, as defined in TS 22.060 and TS 23.060.
The present document is valid for PLMN in A/Gb mode as well as for PLMN in Iu mode. If text applies only for one of these systems it is explicitly mentioned by using the terms "A/Gb mode" and "Iu mode". Please note, that the A interface does not play any role in the scope of this document although the term "A/Gb mode" is used.
2 References p. 6
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies.
[1] Void.
[2] Void.
[3]
TS 22.060: "General Packet Radio Service (GPRS); Service Description Stage 1".
[4] Void.
[5] Void.
[6] Void.
[7] Void.
[8] Void.
[9]
TS 23.060: "General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Service Description Stage 2".
[10] Void.
[11] Void.
[12]
TS 24.008: "Mobile radio interface layer 3 specification; Core Network protocols; Stage 3".
[13] Void.
[14] Void.
[15] Void.
[16]
TS 27.007: "AT command set for 3GPP User Equipment (UE)".
[17]
TS 29.061: "Packet Domain; Interworking between the Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) supporting Packet Based Services and Packet Data Networks (PDN)".
[18]
ITU-T Recommendation E.164 (02/05): "Numbering plan for the ISDN era".
[19]
ITU-T Recommendation V.42 bis (01/90): "Data communication over the telephone network - Data compression procedures for data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE) using error correction procedures".
[20] Void.
[21] Void.
[22] Void.
[23] Void.
[24] Void.
[25] Void.
[26]
RFC 768 (1980): "User Datagram Protocol" (STD 6).
[27]
RFC 791 (1981): "Internet Protocol" (STD 5).
[28]
RFC 792 (1981): "Internet Control Message Protocol" (STD 5).
[29]
RFC 793 (1981): "Transmission Control Protocol" (STD 7).
[30]
ITU-T Recommendation V.250 (ex V.25ter) (05/99): "Serial asynchronous automatic dialling and control".
[31]
ITU-T Recommendation V.24 (10/96): "List of definitions for interchange circuits between data terminal equipment (DTE) and data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE)".
[32]
ITU-T Recommendation V.28 (03/93): "Electrical Characteristics for unbalanced double-current interchange circuits".
[33]
ITU-T Recommendation V.80 (08/96): "In-band DCE control and synchronous data modes for asynchronous DTE".
[34]
RFC 1661 (1994): "The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)" (STD 51).
[35]
RFC 1662 (1994): "PPP in HDLC-like framing" (STD 51).
[36]
RFC 1700 (1994): "Assigned Numbers" (STD 2).
[37]
RFC 1570 (1994): "PPP LCP Extensions".
[38]
RFC 1989 (1996): "PPP Link Quality Monitoring".
[39]
RFC 1332 (1992): "The PPP Internet Protocol Control Protocol (IPCP)".
[40]
RFC 1877 (1995): "PPP IPCP Extensions for Name Server Addresses ".
[41]
RFC 2153 (1997): "PPP Vendor Extensions".
[42]
RFC 1334 (1992): "PPP Authentication Protocols".
[43]
RFC 1994 (1996): "PPP Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol".
[44]
RFC 2686 (1999): "The Multi-Class Extension to Multi-Link PPP".
[45]
RFC 1990 (1996): "The PPP Multilink Protocol (MP)".
[46]
RFC 2472 (1998): "IP Version 6 over PPP".
[47]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[48]
TS 23.221: "Architectural requirements".
[49]
RFC 2373 (1998): "IP version 6 Addressing Architecture".
[50]
TS 24.228: "Signalling flows for the IP multimedia call control based on SIP and SDP; Stage 3"
[51]
TS 24.229: " IP Multimedia Call Control Protocol based on SIP and SDP; Stage 3".
[52]
TS 29.207: "Policy control over Go interface".
[53]
TS 29.208: "End-to-end QoS signalling flows".
[54]
RFC 3261 (March 2002): "SIP: Session Initiation Protocol".
[55]
RFC 3315 (2003): "Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6)" R. Droms, J. Bound, B. Volz, T. Lemon, C. Perkins, M. Carney.
[56]
RFC 1034 (1987): "Domain Names - Concepts and Facilities" (STD 13).
[57]
RFC 1035 (1987): "Domain Names - Implementation and Specification" (STD 13).
[58]
RFC 1886 (1995): "DNS Extensions to support IP version 6".
3 Definitions abbreviations and symbols p. 8
3.1 Definitions p. 8
For the purposes of the present document, the following terms and definitions given in TS 22.060 and TS 23.060 and the following apply:
2G- / 3G-:
prefixes 2G and 3G refers to functionality that supports only A/Gb mode or Iu mode, respectively, e.g., 2G SGSN refers only to the A/Gb mode functionality of an SGSN. When the prefix is omitted, reference is made independently from the A/Gb mode or Iu mode functionality.
A/Gb mode:
indicates that the text applies only to a system or sub-system which operate in A/Gb mode of operation, i.e. with a functional division that is in accordance with the use of an A or a Gb interface between the radio access network and the core network
Iu mode:
indicates that the text applies only to a system or a sub-system which operates in Iu mode of operation, i.e. with a functional division that is in accordance with the use of an Iu-CS or Iu-PS interface between the radio access network and the core network
3.2 Abbreviations p. 8
For the purposes of the present document, the following abbreviations apply:
APN
Access Point Name
DHCPv6
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Ipv6
DNS
Domain Name System
GGSN
Gateway GPRS Support Node
GPRS
General Packet Radio Service
GSN
GPRS Support Node
GTP-U
GPRS Tunnelling Protocol for user plane
HDLC
High Level Data Link Control
ICMP
Internet Control Message Protocol
IETF
Internet Engineering Task Force
IMS
IP Multimedia Core Network Subsystem
IP
Internet Protocol
IPv4
Internet Protocol version 4
IPv6
Internet Protocol version 6
IPV6CP
IPv6 Control Protocol
LA
Location Area
LCP
Link Control Protocol
LLC
Logical Link Control
MAC
Medium Access Control
MCML
Multi-Class Multi-Link PPP
ME
Mobile Equipment
MP
Multilink PPP
MS
Mobile Station
MT
Mobile Termination
NCP
Network Control Protocol
PCF
Policy Control Function
P-CSCF
Proxy Call Session Control Function
PDCP
Packet Data Convergence Protocol
PDN
Packet Data Network
PDP
Packet Data Protocol , e.g., IP or PPP
PDU
Protocol Data Unit
PPP
Point-to-Point Protocol
PS
Packet Switched
PTM
Point To Multipoint
PTP
Point To Point
PVC
Permanent Virtual Circuit
QoS
Quality of Service
RA
Routing Area
SDP
Session Description Protocol
SGSN
Serving GPRS Support Node
SIP
Session Initiation Protocol
SNDCP
SubNetwork Dependent Convergence Protocol
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol
TE
Terminal Equipment
TFT
Traffic Flow Template
UDP
User Datagram Protocol
3.3 Symbols p. 9
For the purposes of the present document, the following symbols apply:
Gb
Interface between a SGSN and a BSC.
Gi
Reference point between the Packet Domain and an external packet data network.
Gn
Interface between two GSNs within the same PLMN.
Gp
Interface between two GSNs in different PLMNs. The Gp interface allows support of Packet Domain network services across areas served by the co-operating PLMNs.
Gs
Interface between an SGSN and MSC.
Iu
Interface between the RNS and the core network. It is also considered as a reference point.
R
The reference point between a non-ISDN compatible TE and MT. Typically this reference point supports a standard serial interface.
Um
The interface between the MS and the fixed network part in A/Gb mode. The Um interface is the in A/Gb mode network interface for providing packet data services over the radio to the MS. The MT part of the MS is used to access the GSM services through this interface.
Uu
Interface between the mobile station (MS) and the fixed network part in Iu mode. The Uu interface is the Iu mode network interface for providing packet data services over the radio to the MS. The MT part of the MS is used to access the UMTS services through this interface.
4 Access reference configuration p. 9
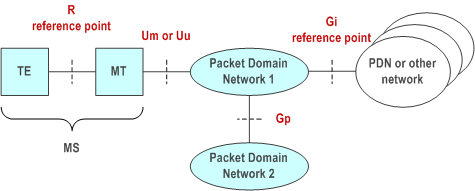
Figure 1 shows the relationship between the MS, its terminal equipment and the PLMN in the overall Packet Domain environment.
5 Functions to support data services p. 10
The main functions of the MT to support data services are:
- physical connection at the reference point R;
- flow control between TE and MT;
- mapping of user signalling to/from the Packet Domain bearer;
- mapping of packets belonging to different flows to appropriate PDP contexts;
- support of data integrity between the terminal equipment and the Packet Domain bearer;
- functions to support packet based data.