Content for TR 23.958 Word version: 18.2.0
5 Alignment of EDGEAPP with ETSI MEC
5.1 General
5.2 Relationship between EDGEAPP and ETSI MEC architectures
5.3 EDGE-3 and Mp1 reference points
5.3.1 EASProfile and AppInfo
5.4 EDGE-9 and Mp3 reference points
5.5 CAPIF and MEC service API management
5.6 Support for Federation
5.6.1 EDGEAPP
5.6.2 ETSI MEC
...
...
5 Alignment of EDGEAPP with ETSI MEC p. 10
5.1 General p. 10
An early effort on alignment between 3GPP EDGEAPP and ETSI MEC was initiated during Rel-17, and a summary is available in a white paper published by ETSI - "Harmonizing standards for edge computing - A synergized architecture leveraging ETSI ISG MEC and 3GPP specifications" [16].
Clause 5.2 provides the relationship between EDGEAPP and ETSI MEC architectures. Clause 5.3 provides the mapping of EAS Profile and AppInfo to allow application registration across the platforms. Clause 5.4 provides description for EDGE-9 and Mp3 reference points. Clause 5.5 provides the description for CAPIF and MEC service API management.
5.2 Relationship between EDGEAPP and ETSI MEC architectures p. 10
Figure 5.2-1 provides the relationship of ETSI ISG MEC architecture with EDGEAPP architecture.
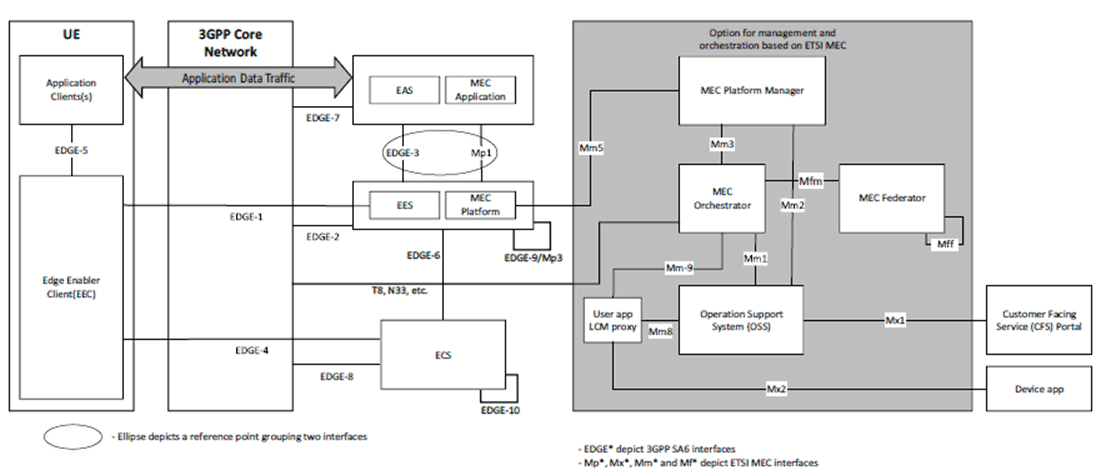
Figure 5.2-1: Relationship between EDGEAPP and ETSI MEC architectures
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Details about MEC entities (MEC Platform, MEC Application, MEC Platform Manager, MEC Orchestrator, MEC Federator, OSS and CFS) can be found in ETSI GS MEC 003 [4].
In ETSI MEC, MEC Applications and MEC Platform can expose services which can include network services, subject to their availability at the core or access network level.
Both EAS and MEC application are application servers and can provide similar application specific functionalities. EAS utilizes the services of EES as specified in TS 23.558 whereas MEC application utilizes the services provided by MEC platform as specified in ETSI GS MEC 003 [4]. The EAS and MEC application can be aligned in an implementation.
Both EES and MEC platform provide application support capabilities towards the application servers. The EES and MEC platform and their interfaces can be aligned in an implementation.
The orchestration and management aspects of architecture for enabling edge applications are specified in TS 28.538.
5.3 EDGE-3 and Mp1 reference points p. 11
5.3.1 EASProfile and AppInfo p. 11
Both EDGEAPP and ETSI MEC supports registration of EAS and MEC application instance with EES and MEC platform respectively. In order to support MEC application instance registration on EES, it is required that registration request includes at least the mandatory IEs that are required for EAS registration, i.e. EAS ID and EAS endpoint. On the other hand, according to ETSI GS MEC 011 [5] the application registration request must include appName.
AppInfo is the data type describing the information exchanged by a MEC application instance at registration to a MEC platform. It is defined in clause 7.1.2.6 of ETSI GS MEC 011 [5] and includes appName as a mandatory IE and endpoint as an optional IE. However, endpoint is mandatory when the AppInfo IE isInsByMec is FALSE and, as stated above, would have to be provided for MEC application instance registration to an EES. The isInsByMec IE of the AppInfo, with type Boolean, indicates whether the application instance is instantiated by a MEC management system. The IE appName can be considered equivalent to EAS ID. Furthermore endpoint can be directly mapped to EAS endpoint and that mapping is explicitly stated in note 2 of Table 7.1.2.6-1 of ETSI GS MEC 011 [5].
Table 5.3.1-1 provides a mapping of MEC attributes to those in the EAS Profile for MEC application registration with EES.
| Information element | Status/ Cardinality | Description | Mapped with |
|---|---|---|---|
| EASID | M | The identifier of the EAS | AppInfo >appName |
| EAS Endpoint | M | Endpoint information (e.g. URI, FQDN, IP address) used to communicate with the EAS. This information maybe discovered by EEC and exposed to ACs so that ACs can establish contact with the EAS. | AppInfo >endpoint |
| ACID(s) | O | Identifies the AC(s) that can be served by the EAS | Not available in case of MEC application registration |
| EAS Provider Identifier | O | The identifier of the ASP that provides the EAS. | AppInfo >appProvider |
| EAS Type | O | The category or type of EAS (e.g. V2X) | AppInfo >appCategory |
| EAS description | O | Human-readable description of the EAS | AppD >appDescriptor |
| EAS Schedule | O | The availability schedule of the EAS (e.g. time windows) | Not available in case of MEC application registration |
| EAS Geographical Service Area | O | The geographical service area that the EAS serves. ACs in UEs that are located outside that area shall not be served. | Not available in case of MEC application registration |
| EAS Topological Service Area | O | The EAS serves UEs that are connected to the Core Network from one of the cells included in this service area. ACs in UEs that are located outside this area shall not be served. See possible formats in Table 8.2.7-1. | Not available in case of MEC application registration |
| EAS Service KPIs | O | Service characteristics provided by EAS, detailed in Table 8.2.5-1 | Not available in case of MEC application registration |
| EAS service permission level | O | Level of service permissions e.g. trial, gold-class supported by the EAS | Not available in case of MEC application registration |
| EAS Feature(s) | O | Service features e.g. single vs. multi-player gaming service supported by the EAS | Not available in case of MEC application registration |
| EAS Service continuity support | O | Indicates if the EAS supports service continuity or not. This IE also indicates which ACR scenarios are supported by the EAS. | Not available in case of MEC application registration |
| General context holding time duration | O | The time duration that the EAS holds the context before the AC connects to the EAS in case of ACR for service continuity planning. It is an indication of the time the EAS holds the application context for a UE to move to its service area after receiving an ACR notification from the EES following an ACR request from the EEC. | Not available in case of MEC application registration |
| List of EAS DNAI(s) | O | DNAI(s) associated with the EAS. This IE is used as Potential Locations of Applications in clause 5.6.7 of TS 23.501. It is a subset of the DNAI(s) associated with the EDN where the EAS resides. | Not available in case of MEC application registration |
| List of N6 Traffic Routing requirements | O | The N6 traffic routing information and/or routing profile ID corresponding to each EAS DNAI. | Not available in case of MEC application registration |
| EAS Availability Reporting Period | O | The availability reporting period (i.e. heartbeat period) that indicates to the EES how often it needs to check the EAS's availability after a successful registration. | Not available in case of MEC application registration |
| EAS Status | O | The status of the EAS (e.g. enabled, disabled, etc.) | Not available in case of MEC application registration |
5.4 EDGE-9 and Mp3 reference points p. 12
EDGE-9 reference point in EDGEAPP architecture is used to provide target EAS discovery to support ACR in case of mobility of user from one EES to another EES. On the other hand, Mp3 reference point between MEC platforms is used for control communication between MEC platforms [4] with a separate application mobility service [7] being provided in support of mobility of users between MEC hosts within a MEC system. Currently, ETSI MEC has not specified APIs over Mp3.
5.5 CAPIF and MEC service API management p. 13
CAPIF is the Common API Framework for northbound APIs specified in TS 23.222. The Edge Enabler Layer supports CAPIF for northbound API exposure of edge service APIs as specified in TS 23.558. The MEC platform supports CAPIF in the form of MEC service management API as specified in ETSI GS MEC 011 [5]. The CAPIF APIs are similar to the MEC service management APIs and the mapping is described in ETSI GS MEC 011 [5].
5.6 Support for Federation p. 13
5.6.1 EDGEAPP p. 13
EDGE-9 and EDGE-10 reference points are used to support federation functionalities as per clause 8.17 and clause 8.18 of TS 23.558. EDGE-9 reference point in EDGEAPP architecture is used to discover EAS from the EES of the partner ECSP for edge node sharing. EDGE-10 reference point in EDGEAPP architecture is used for ECS registration, ECS discovery via ECS-ER and Service provisioning information retrieval from ECS-ER in order to provide support for roaming, federation and edge node sharing. EDN information is exchanged between ECSs/ECS-ERs using EDGE-10 reference point.
Further, application life cycle management for federation is specified in TS 28.538. Once application server is instantiated, it registers with EES, which in turn registers with ECS. The EDN information contains EDN connection information, list of EES along with EASIDs, provider's ID, endpoint information and other required details.
5.6.2 ETSI MEC p. 13
The MEC federator (MEF) as described in clause 7.1.9 of ETSI GS MEC 003 [4] enables a MEC federation between MEC systems. Mff reference point is defined between MEFs within the MEC federation for sharing information, such as MEC system information that includes MEC system ID, MEC system name, MEC system provider and MEF endpoint information. The federation enablement service is summarised in clause 5.2.1 of ETSI GS MEC 040 [6] and enables the shared usage of MEC services and applications across different systems.