Content for TS 23.503 Word version: 19.2.0
0…
4…
5…
6…
6.1.2…
6.1.2.4…
6.1.3…
6.1.3.6…
6.1.3.18…
6.1.3.21…
6.1.4…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.3…
6.4…
6.6…
A…
C
D…
D PCC usage for sponsored data connectivity
D.1 General
D.2 Reporting for sponsored data connectivity
$ Change history
D PCC usage for sponsored data connectivity |R16| p. 179
D.1 General p. 179
With sponsored data connectivity, the Sponsor has a business relationship with the operator and the Sponsor reimburses the operator for the user's data connectivity in order to allow the user access to an associated Application Service Provider's (ASP) services. Alternatively, the user pays for the connectivity with a transaction which is separate from the subscriber's charging. It is assumed the user already has a subscription with the operator.
A possible deployment configuration for sponsored data connectivity in the non-roaming case is illustrated in Figure D.1-1.
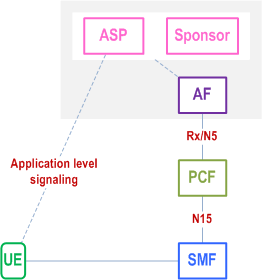
The relationship between the AF and Sponsor and between the Sponsor and ASP is out of scope of this specification. A single AF can serve multiple ASPs and multiple sponsors.
The sponsor may choose to supply the PCF (via the AF) with the usage thresholds that it expects the SMF to enforce. Alternatively, the Sponsor can allow the ASP to enforce such control over the sponsored data connectivity.
The information required for the detection of sponsored HTTP traffic (i.e. server host name) can be verified with the corresponding server IP address/prefix of the IP packets by the SMF. The SMF uses implementation specific logic to perform this verification.
D.2 Reporting for sponsored data connectivity p. 180
There are two deployment scenarios for usage reporting for sponsored data connectivity. The Sponsor Identifier and Application Service Provider Identifier are provided for sponsored services to the PCF from the AF over the Rx/N5 interface.
In the first scenario the PCF assigns a service specific Charging Key for a sponsored IP flow. The Charging key is used by the SMF to generate separate accounting records for offline charging and and/or usage data records for online charging for the sponsored flows. Correlation of accounting records and usage data records from multiple users per sponsor and/or application service provider is then performed using the charging key.
In a second scenario the Sponsor Identifier and Application Service Provider Identity is included in PCC rules from the PCF to the SMF as defined in clause 6.3.1. For this scenario the same Charging Key may be used both for IP flows that are sponsored and for flows that are not sponsored. Accounting records generated by the SMF for offline charging include the Sponsor Identity and the Application Service Provider Identity. Correlation of accounting records from multiple users per sponsor and/or application service provider can then be based on Sponsor Identity and Application Service Provider Identity instead of the Charging Key. Usage reporting for online charging including Sponsor Identity and Application Service Provider Identity has not been specified in this release of the specification. PCC rules that include a Sponsor Identity and an Application Service Provider Identity should include a Charging Method that indicates offline charging.