Content for TS 23.380 Word version: 18.1.0
5.6 P-CSCF restoration for WLAN
5.6.1 Introduction
5.6.2 Basic mechanism for the HSS-based solution
5.6.3 Basic mechanism for the PCRF-based solution
5.6.4 Optional extension for the HSS and PCRF-based solutions for the TWAN access
5.6.5 Optional extension for the HSS and PCRF-based solutions for the untrusted WLAN access
5.6.6 Supported features and capabilities
5.7 Interaction between P-CSCF restoration and NBIFOM
...
...
5.6 P-CSCF restoration for WLAN |R13| p. 34
5.6.1 Introduction p. 34
The clause 5.6 describes solutions to support P-CSCF restoration for UEs with an IMS PDN connection supported over a WLAN access.
The clauses 5.6.2 and 5.6.3 describe the basic mechanism for the HSS-based solution and for the PCRF-based solution. The basic mechanism relies on the release of the IMS PDN connection followed by its re-establishment to trigger a new IMS registration by the UE.
The clauses 5.6.4 and 5.6.5 describe extensions for trusted WLAN and for untrusted WLAN accesses to avoid the release of the IMS PDN connection and to trigger a new IMS registration by the UE over the existing IMS PDN connection. The extensions between the UE and the PGW are common for the HSS-based and for the PCRF-based solutions and rely on the same UE behavior.
5.6.2 Basic mechanism for the HSS-based solution p. 34
5.6.2.1 Overview and principles p. 34
The HSS-based P-CSCF restoration mechanism for WLAN extends the HSS-based P-CSCF restoration mechanism (specified for 3GPP accesses in clause 5.4) to trusted and untrusted WLAN accesses and is based on the same principles to disconnect the UE, which then re-establishes the connection via an available P-CSCF.
If the UE is registered to the EPC via a WLAN access and has an IMS APN subscription permitting non-3GPP accesses, the HSS forwards a P-CSCF restoration indication to the 3GPP AAA Server which transfers it to the PGW. Then the PGW initiates the release of the IMS PDN connection towards the UE via the WLAN access.
Following the release of the IMS PDN connection, the UE re-establishes a new IMS PDN connection and performs a new P-CSCF discovery (according to the existing procedures), and then registers again to IMS.
5.6.2.2 Description p. 34
The call flow for the HSS-based P-CSCF restoration mechanism for WLAN is described in Figure 5.6.2.2-1. The functional entities involved by this call flow shall execute the following procedure if they all support the HSS-based P-CSCF restoration for WLAN.
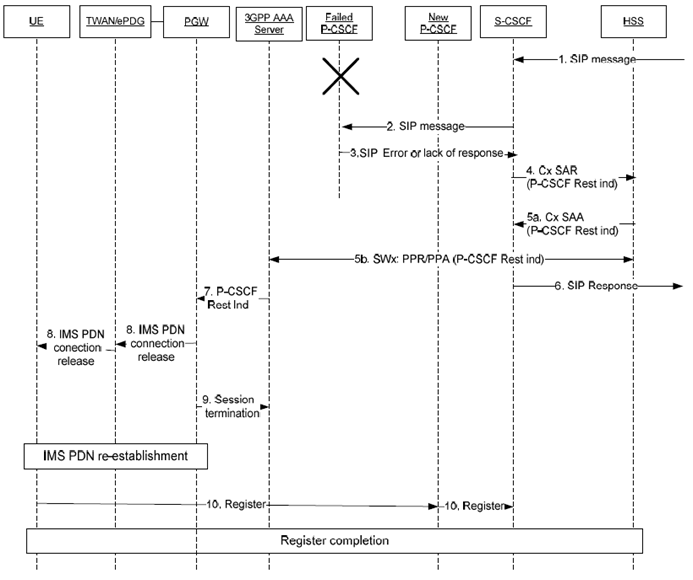
For a WLAN access, the basic mechanism to request the UE to do a new IMS registration is to release the IMS PDN connection over the interface (S2a or S2b) through which the UE is connected. The solution avoids disconnecting other PDN connections than the IMS PDN one.
Steps 1 to 4 are common with the steps 1 to 4 of clause 5.4.2.1.
Step 5.
After having checked that the 3GPP AAA Server supports the HSS-based P-CSCF restoration for WLAN, the HSS, if the user has a non-3GPP access subscription with an IMS APN configuration and if the user has a non-3GPP access registration in the HSS for the WLAN access, shall forward a P-CSCF restoration indication to the 3GPP AAA Server over SWx by using a PPR command, perform either the IMS unregistration or deregistration requested by the S-CSCF and send a successful response to the S-CSCF via a Cx SAA command. The S-CSCF shall set respectively this Public User Identity as unregistered or this UE as not registered.
If the user has also an IMS APN configuration subscription for a 3GPP access and is registered to a 3GPP access, the procedure described in clause 5.4.2.1 from step 5 onwards shall apply in addition.
Otherwise, if the P-CSCF restoration is not triggered over WLAN or 3GPP access, the HSS shall provide an error response in Cx SAA to the S-CSCF.
Step 6.
Step 6 is common with step 6 described in clause 5.4.2.1 for 3GPP accesses.
Step 7.
If the 3GPP AAA Server has the information that an IMS PDN connection is established via a WLAN access for the user, the 3GPP AAA Server, after having checked that the PGW supports the HSS-based P-CSCF restoration for WLAN, shall send a P-CSCF restoration indication to the PGW over S6b in a Re-authorization Request (RAR) command, via a 3GPP AAA Proxy over SWd if a VPLMN is involved.
Step 8.
The PGW shall proceed with the release of the IMS PDN connection as follows:
Step 9.
-
For a TWAN access, the PGW shall initiate over the S2a interface a Delete Bearer Request procedure (GTP) or a Proxy Mobile IPv6 LMA Initiated PDN Connection Deletion procedure (PMIP) to the TWAN which then shall initiate:
- a WLCP PDN Disconnection procedure towards the UE for a UE in multi connection mode as described in TS 24.244;
- a TWAN specific resource release procedure, in single connection mode or transparent single connection mode;
- For an untrusted WLAN access, the PGW shall initiate over the S2b interface a Delete Bearer Request procedure (GTP) or a Proxy Mobile IPv6 LMA Initiated PDN Connection Deletion procedure (PMIP) to the ePDG which then initiates the release of the associated IKEv2 tunnel.
The PGW shall indicate the termination of the associated session to the 3GPP AAA Server by sending a Session Termination Request (STR).
Step 10.
As a result of the release of the IMS PDN connection, the UE shall re-establish the IMS PDN connection, and also perform a new P-CSCF discovery (as the IMS PDN connection was lost). After discovering a new P-CSCF, the UE shall perform a new initial IMS registration towards IMS.
5.6.3 Basic mechanism for the PCRF-based solution p. 36
The basic mechanism for the PCRF-based P-CSCF restoration for WLAN is part of the PCRF-based solution described in clause 5.5.
5.6.4 Optional extension for the HSS and PCRF-based solutions for the TWAN access p. 36
5.6.4.1 Overview and principles p. 36
The basic mechanism for P-CSCF restoration over WLAN is optionally extended for the TWAN access to avoid the need to deactivate and reactivate the IMS PDN connection. This P-CSCF restoration extension applies to the HSS-based and the PCRF-based solutions.
Upon receipt of a P-CSCF restoration indication from the 3GPP AAA Server, the PGW may invoke this P-CSCF restoration extension procedure if
- the UE is accessing the EPC via a TWAN in the multi-connection mode;
- the UE indicated support of this extension for the TWAN access (as further described in clause 5.6.4.3); and
- if the TWAN indicated support of the WLCP PDN connection modification procedure.
5.6.4.2 Description p. 37
The call flow for the P-CSCF restoration extension for the TWAN access is described in Figure 5.6.4.2-1. The functional entities involved by this call flow shall execute the following procedure if they all support the P-CSCF restoration extension for the TWAN access.
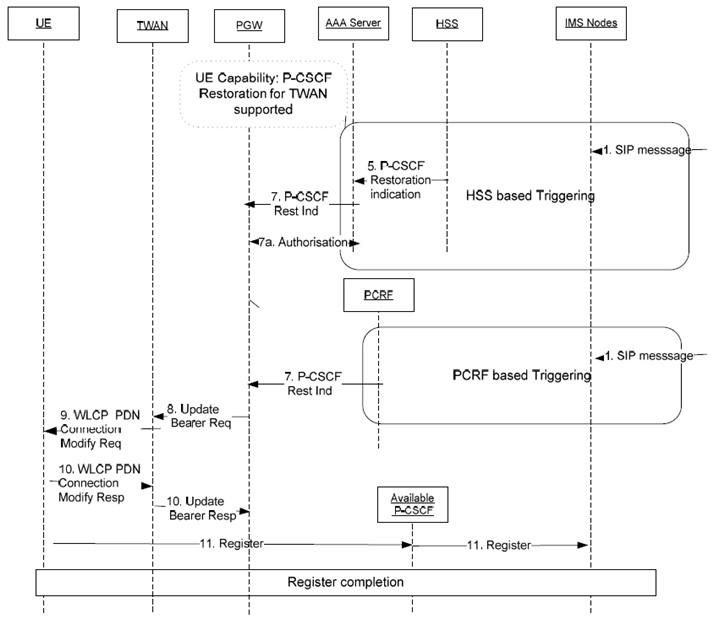
Figure 5.6.4.2-1: P-CSCF restoration extension for the TWAN access - GTP-based S2a
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
For the HSS-based solution, steps from 1 to 7 are the same as those explained in clause 5.6.2.2 for the P-CSCF restoration basic mechanism for WLAN. In step 7, the 3GPP AAA Server, when receiving a P-CSCF restoration indication from the HSS, transfers this indication to the PGW in a Re-authorization Request (RAR) command, This generates an authorisation procedure (step 7a) as according to TS 29.273.
For the PCRF-based solution, steps from 1 to 7 are the same as those explained in clause 5.3.2 for the P-CSCF restoration basic mechanism. In step 7, the PCRF transfers the P-CSCF restoration indication to the PGW.
Hereafter steps 8 to 11 are common to the HSS-based solution and to the PCRF-based solutions:
Step 8.
The same call flow applies to PMIP-based S2a, whereby, in step 8, the PGW shall initiate an LMA Initiated Update Notification procedure to provide the TWAN with the available P-CSCF addresses.
If the PGW has previously received the indication that the UE supports the P-CSCF restoration extension for the TWAN access and that the TWAN supports the WLCP PDN connection modification procedure, and if the UE is accessing the TWAN in multi-connection mode, the PGW shall send an Update Bearer Request to the TWAN including the PCO information element set with a list of available P-CSCF addresses,
Step 9.
The TWAN shall initiate a WLCP PDN connection modification request procedure towards the UE as described in TS 24.244 to transparently forward the PCO information element received from the PGW.
Step 10.
The UE shall send a response to the TWAN which then shall send an Update Bearer Response to the PGW.
Step 11.
As per the P-CSCF restoration procedures described in TS 24.229, the UE shall select one P-CSCF from the received list and proceed with an IMS registration.
5.6.4.3 Indication of UE support of the P-CSCF restoration extension for the TWAN access p. 38
If the UE supports the P-CSCF restoration extension for the TWAN access, it shall send an indication of this capability to the PGW via the PCO information element at the establishment (or handover) of the IMS PDN connection over the WLAN access.
5.6.5 Optional extension for the HSS and PCRF-based solutions for the untrusted WLAN access p. 38
5.6.5.1 Overview and principles p. 38
The basic mechanism for P-CSCF restoration over WLAN is optionally extended for the untrusted WLAN access to avoid the need to deactivate and reactivate the IMS PDN connection. This P-CSCF restoration extension applies to the HSS-based and the PCRF-based solutions.
Upon receipt of a P-CSCF restoration indication from the 3GPP AAA Server, the PGW may invoke this P-CSCF restoration extension procedure if
- the UE is accessing the EPC via an untrusted WLAN access;
- the UE and the ePDG indicated support of this extension for the untrusted WLAN access (as further described in clause 5.6.5.3).
5.6.5.2 Description p. 38
The call flow for the P-CSCF restoration extension for the untrusted WLAN access is described in Figure 5.6.5.2-1. The functional entities involved by this call flow shall execute the following procedure if they all support the P-CSCF restoration extension for the untrusted WLAN access.
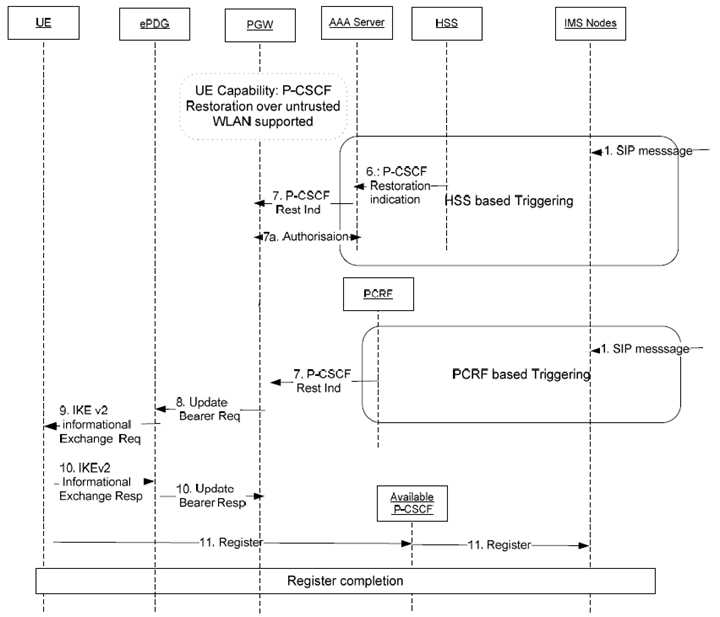
Figure 5.6.5.2-1: P-CSCF restoration extension for the untrusted WLAN access - GTP-based S2b
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
For the HSS-based solution, steps from 1 to 7 are the same as those explained in clause 5.6.2.2 for the P-CSCF restoration basic mechanism for WLAN. In step 7, the 3GPP AAA Server, when receiving a P-CSCF restoration indication from the HSS, transfers this indication to the PGW in a Re-authorization Request (RAR) command. This generates an authorisation procedure (step 7a) as according to TS 29.273.
For the PCRF-based solution, steps from 1 to 7 are the same as those explained in clause 5.3.2 for the P-CSCF restoration basic mechanism. In step 7, the PCRF transfers the P-CSCF restoration indication to the PGW.
Hereafter steps 8 to 11 are common to the HSS-based solution and to the PCRF-based solution:
Step 8.
The same call flow applies to PMIP-based S2b, whereby, in step 8, the PGW shall initiate an LMA Initiated Update Notification procedure, as described in TS 29.275, to provide the ePDG with the available P-CSCF addresses.
If the PGW has previously received the indication that the UE and the ePDG support the P-CSCF restoration extension for the untrusted WLAN access, the PGW shall send an Update Bearer Request (as described in TS 29.274) to the ePDG including the APCO information element set with a list of available P-CSCF addresses.
Step 9.
The ePDG shall initiate an IKEv2 informational exchange procedure, as described in RFC 7296, towards the UE to forward the list of available P-CSCF addresses received from the PGW.
Step 10.
The UE shall send a response to the ePDG which then shall send an Update Bearer Response to the PGW.
Step 11.
As per the P-CSCF restoration procedures described in TS 24.229, the UE shall select one P-CSCF from the received list and proceed with an IMS registration.
5.6.5.3 Indication of UE support of the P-CSCF restoration extension for the untrusted WLAN access p. 40
If the UE supports the P-CSCF restoration extension for the untrusted WLAN access, it shall send an indication of this capability to the ePDG via a notify payload in the IKEv2 message to the ePDG at the establishment (or handover) of the IMS PDN connection over the untrusted WLAN access.
An ePDG which supports the P-CSCF restoration extension for untrusted WLAN shall forward this UE capability in the APCO information element to the PGW over the S2b interface.
5.6.6 Supported features and capabilities p. 40
5.6.6.1 Introduction p. 40
The P-CSCF restoration mechanism for WLAN, compared to the 3GPP access one, requires additional functionalities from the HSS, the 3GPP AAA Server, the PGW for the basic mechanism and in addition from the PGW, the TWAN, the ePDG and the UE for the extended mechanism.
The support or not of the additional functionalities by the involved entities has consequences on the applicability of the P-CSCF restoration mechanism, both for the basic mechanism and the extended mechanism. User roaming may imply a modification of the supported features.
5.6.6.2 Feature support in the HSS and S-CSCF p. 40
The S-CSCF behaviour when triggering the HSS with a P-CSCF restoration indication is independent of the 3GPP access or of the WLAN access that the UE is using. The signalling regarding P-CSCF restoration over the Cx interface and the S-CSCF behaviour are common for the P-CSCF restoration over a 3GPP or a WLAN access.
If the HSS does not support P-CSCF restoration for WLAN, but supports P-CSCF restoration over a 3GPP access and if the UE is registered in a 3GPP access, the HSS shall behave as described in clause 5.4.
If the HSS does not support P-CSCF restoration for 3GPP access, but supports P-CSCF restoration for WLAN, if the user is registered in the non 3GPP access with an IMS APN configuration for non 3GPP access in its subscription and if the 3GPP AAA Server previously indicated the support of P-CSCF restoration for WLAN to the HSS, then the HSS shall behave as described in clause 5.6.2.
If the HSS supports P-CSCF restoration both for 3GPP access and WLAN and if the UE is registered both with 3GPP access and WLAN, the HSS shall initiate P-CSCF restoration for 3GPP access and WLAN as described in clause 5.4 for 3GPP access and in clause 5.6.2 for WLAN.
The HSS shall report DIAMETER_SUCCESS to S-CSCF if at least one serving node (SGSN, MME or 3GPP AAA Server) supports HSS-based P-CSCF Restoration and a request indicating P-CSCF restoration is sent to at least one of these supporting nodes.
5.6.6.3 Feature support in the 3GPP AAA Server p. 40
The 3GPP AAA Server shall inform the HSS, at the user registration over SWx, if it supports the P-CSCF restoration feature through a supported feature indication, so to allow the HSS to correctly react to a P-CSCF restoration indication received from the S-CSCF. This feature support indication does not contain any information about the support of the P-CSCF restoration feature by the PGW handling the IMS PDN connection.
Therefore, when the PGW informs the 3GPP AAA Server over S6b that an IMS PDN connection is established, the PGW shall advertise the 3GPP AAA Server if the PGW supports the P-CSCF restoration mechanism for WLAN. A 3GPP AAA Server that supports the P-CSCF restoration mechanism shall store this information and when the 3GPP AAA Server receives a P-CSCF restoration indication from the HSS (as described in Figure 5.6.2.2-1 step 5b):
- if an IMS PDN connection is established and if the PGW supports the P-CSCF restoration mechanism for WLAN, the 3GPP AAA Server shall behave as described in step 7 of clause 5.6.2.2;
- if an IMS PDN connection is established and if the PGW does not support the P-CSCF restoration mechanism for WLAN, the 3GPP AAA Server shall ignore the P-CSCF restoration indication received from the HSS;
- if no IMS PDN connection is established, the 3GPP AAA Server shall ignore the P-CSCF restoration indication received from the HSS.
5.6.6.4 Feature support in the PGW p. 41
A PGW supporting the basic P-CSCF restoration mechanism for trusted and/or untrusted WLAN shall indicate the support of P-CSCF restoration for WLAN to the 3GPP AAA Server in the Authorization Request message sent over S6b at the creation of the IMS PDN connection.
The support of the extended mechanism by the PGW requires the support of the basic mechanism. The extended mechanism is optionally supported by the PGW for TWAN or for untrusted WLAN or for both.
5.6.6.5 Feature support in the TWAN p. 41
The TWAN shall advertise the support of the WLCP PDN connection modification request procedure over S2a at establishment (or handover) of the IMS PDN connection. This is to allow the PGW to use the P-CSCF restoration extension on this TWAN.
5.6.6.6 Feature support in the ePDG p. 41
As described in clause 5.6.5.3, the ePDG indicates its support of the P-CSCF restoration extension to the PGW over S2b when sending the UE capability indication to the PGW at the IMS PDN connection establishment (or handover) over S2b.
5.6.6.7 Capability support in the UE p. 41
A UE supporting the P-CSCF restoration extension may support this mechanism for:
- the 3GPP access (e.g. a Rel-12 UE) and/or;
- the TWAN and/or;
- the untrusted WLAN.
5.7 Interaction between P-CSCF restoration and NBIFOM |R13| p. 42
5.7.1 Introduction p. 42
P-CSCF restoration and NBIFOM present interactions as NBIFOM can be applied to the IMS PDN connection which can be set on a 3GPP access or on a WLAN access or be simultaneously active over the two types of accesses. This impacts the P-CSCF restoration procedures for a network supporting both P-CSCF restoration and NBIFOM with IMS UEs supporting NBIFOM, as described in the hereafter clauses which cover:
- the HSS-based and the PCRF-based solutions;
- the cases where the IMS PDN connection is established over one access or over two accesses (3GPP access, WLAN access);
- the cases where the basic mechanism and/or the extended mechanism for P-CSCF restoration are supported by the network over only one access or on both accesses used by the IMS PDN connection;
- the capabilities of the IMS UEs with NBIFOM regarding the support or not of the extended mechanism for P-CSCF restoration over the 3GPP access, the trusted WLAN and/or the untrusted WLAN.
5.7.2 HSS-based solution p. 42
If the MME/SGSN is configured with the extended mechanism (i.e. the MME/SGSN forwards a received P-CSCF restoration indication to the PGW) and:
- If the IMS PDN connection is established over at least one access supporting the extended mechanism with the UE, the PGW, when receiving a P-CSCF restoration indication, shall select one access supporting the extended mechanism and send the list of available P-CSCF addresses over this access. The PGW shall ignore any second P-CSCF restoration indication which may be received shortly afterwards;
-
If the IMS PDN connection is established over access(es) not supporting the extended mechanism with the UE, but over at least one supporting the basic mechanism, the PGW, when receiving a P-CSCF restoration indication (be it from the MME or the 3GPP AAA server), shall:
- select one access supporting the basic mechanism and release the IMS PDN connection over that access with the cause "reactivation requested". The PGW shall ignore any second P-CSCF restoration indication which may be received shortly afterwards. If the IMS PDN connection is established on both accesses with the single connection mode over the trusted WLAN, the PGW shall select the 3GPP access; and
- release the IMS PDN connection over the other access with a "local release" cause. The MME/SGSN or TWAN/ePDG in the other access shall release the corresponding bearer resources as specified in TS 23.401 or RFC 5996, but without signalling to the UE. Further, for the local release of the bearer resources by the MME/SGSN for a UE that is in connected mode, the MME/SGSN shall initiate the radio access bearer release procedure towards the serving eNB/NB.
5.7.3 PCRF-based solution p. 43
If the IMS PDN connection is established over at least one access supporting the extended mechanism with the UE, the PGW, when receiving a P-CSCF restoration indication, shall select one access supporting the extended mechanism and send the list of available P-CSCF addresses over this access.
If the IMS PDN connection is established over access(es) not supporting the extended mechanism with the UE, but over at least one supporting the basic mechanism, the PGW, when receiving a P-CSCF restoration indication, shall:
- select one access supporting the basic mechanism and release the IMS PDN connection over that access with the cause "reactivation requested". If the IMS PDN connection is established on both accesses with the single connection mode over the trusted WLAN, the PGW shall select the 3GPP access; and
- release the IMS PDN connection over the other access with a "local release" cause. The MME/SGSN or TWAN/ePDG in the other access shall release the corresponding bearer resources as specified in TS 23.401 or RFC 5996, but without signalling to the UE. Further, for the local release of the bearer resources by the MME/SGSN for a UE that is in connected mode, the MME/SGSN shall initiate the radio access bearer release procedure towards the serving eNB/NB.