Content for TS 23.226 Word version: 18.0.0
A GTT-Voice specific information for CTM support in, or associated with, all transcoders
A.1 GTT-Voice specific information for CTM support in, or associated with, all transcoders in the access network for GSM networks with A-interface
A.2 GTT-Voice specific information for CTM support in or associated with all transcoders in the core network for networks supporting the Iu interface
B GTT-Voice support via selection of CTM detection / conversion function
B.1 GTT-Voice specific information for CTM support in GSM networks with A-interface, via access network circuit pooling
B.2 GTT-Voice specific information for CTM support via core network termination selection for networks using Iu interface
A GTT-Voice specific information for CTM support in, or associated with, all transcoders p. 15
A.1 GTT-Voice specific information for CTM support in, or associated with, all transcoders in the access network for GSM networks with A-interface p. 15
The CTM detection/conversion function may be incorporated in all transcoders where CTM activity can realistically be expected. It is also an option to incorporate a CTM detection/conversion function in a separate entity associated with the Transcoder.
The CTM adapter automatically detects the presence of CTM encoding and provides the necessary conversion to the appropriate ITU-T Recommendation V.18 [4] modem encoding.
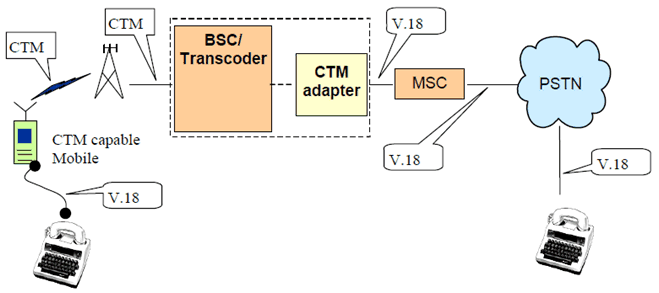
Figure A.1: Association of a CTM adapter with the transcoder in the access network
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Due to the presence of the CTM detection/conversion function in all circuits, no CTM capability information needs to be signalled to the network by the mobile.
A.2 GTT-Voice specific information for CTM support in or associated with all transcoders in the core network for networks supporting the Iu interface p. 15
For networks with GERAN and UTRAN radio access using the Iu interface, the CTM detection/conversion function may be incorporated in all transcoders where CTM activity can realistically be expected. It is also an option to incorporate a CTM detection/conversion function in separate entity associated with the Transcoder.
The CTM adapter automatically detects the presence of CTM encoding and provides the necessary conversion to the appropriate ITU-T Recommendation V.18 [4] modem encoding.
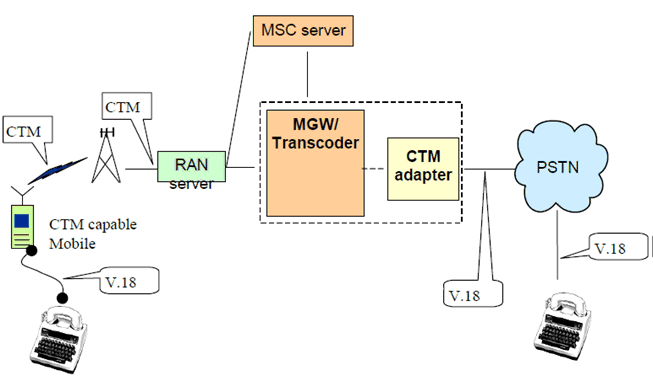
Figure A.2: Association of a CTM adapter with the transcoder in the core network
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Due to the presence of the CTM detection/conversion function in all circuits, no CTM capability information needs to be signalled to the network by the mobile.
B GTT-Voice support via selection of CTM detection / conversion function p. 17
B.1 GTT-Voice specific information for CTM support in GSM networks with A-interface, via access network circuit pooling p. 17
A-interface pooling, and routing to a selected pool, is an intrinsic capability within current GSM Networks and is used to select transcoding for EFR, FR and in future AMR. It is an option to create circuit pools on the A-interface, which support the CTM detection/conversion. The circuit pools are defined in TS 48.008. These pools may be incorporated in the transcoder, in a separate entity associated with a transcoder or in a separate entity located in particular A-interface circuits but remote from the transcoder.
The main steps of the process for a mobile originated call are:
- Setup from terminal, including CTM indication.
- Setup from MSC.
- Call Confirm from terminal including CTM indication.
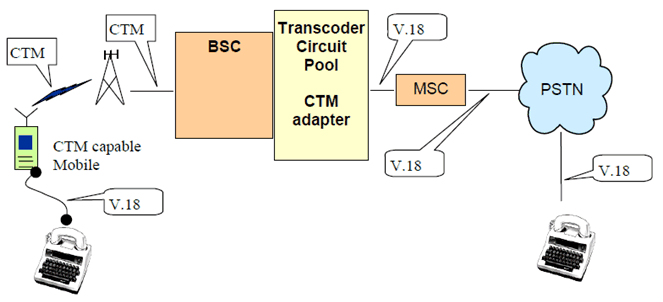
B.2 GTT-Voice specific information for CTM support via core network termination selection for networks using Iu interface p. 18
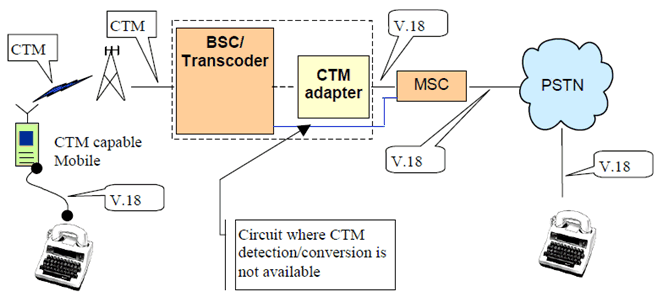
For networks with GERAN and UTRAN radio access using the Iu interface, a method to allocate the calls to terminations capable of handling CTM on audio channels can be provided in the core network. It can be based on the mechanisms for controlling Media Gateway functions through the control language specified on the Mc interface. The MSC Server has information on CTM indication issued by the mobile station and allocates terminations with proper CTM capabilities for the detection/conversion during the call.
The main steps of the process for a mobile originated call are:
- Setup from terminal, including CTM indication
- Setup from the MSC Server.
- Call Confirm from the terminal including CTM indication.
- The MSC server detects CTM indication and allocates a termination with CTM capabilities in the Media Gateway.
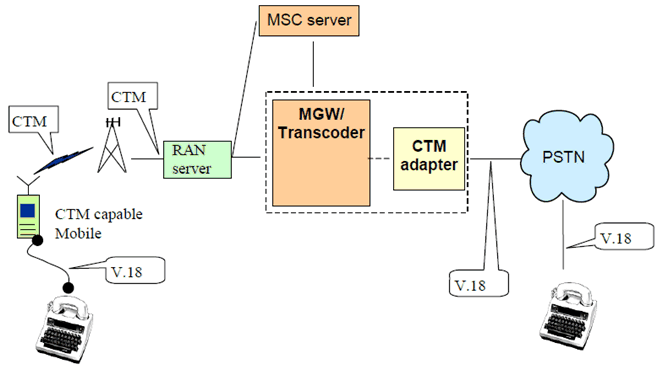
Figure B.3: Association of a CTM capable termination within the Media Gateway
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)