Content for TS 23.216 Word version: 18.0.0
6.2 E-UTRAN and 3GPP GERAN/UTRAN (v)SRVCC
6.2.1 E-UTRAN Attach procedure for (v)SRVCC
6.2.1A Service Request procedures for (v)SRVCC
6.2.1B PS Handover procedures for (v)SRVCC
6.2.1C Dedicated Bearer Establishment and Modification procedures for vSRVCC
6.2.2 Call flows for (v)SRVCC from E-UTRAN
6.2.2.1 SRVCC from E-UTRAN to GERAN without DTM support
6.2.2.1A SRVCC from E-UTRAN to GERAN with DTM but without DTM HO support and from E-UTRAN to UTRAN without PS HO
...
...
6.2 E-UTRAN and 3GPP GERAN/UTRAN (v)SRVCC p. 39
6.2.1 E-UTRAN Attach procedure for (v)SRVCC p. 39
E-UTRAN attach or tracking area update procedure for 3GPP (v)SRVCC UE is performed as defined in TS 23.401 or tracking area update procedure in 5GS to EPS mobility with N26 for 3GPP (v)SRVCC UE is performed as defined in TS 23.502 with the following additions:
- (v)SRVCC UE includes the (v)SRVCC capability indication as part of the "MS Network Capability" in the Attach Request message and in Tracking Area Update Request message. MME stores this information for (v)SRVCC operation. The procedures are as specified in TS 23.401.
- SRVCC UE includes the GERAN MS Classmark 3 (if GERAN access is supported), MS Classmark 2 (if GERAN or UTRAN access or both are supported) and Supported Codecs IE (if GERAN or UTRAN access or both are supported) in the Attach Request message and in the non-periodic Tracking Area Update messages.
- HSS includes STN-SR and C-MSISDN as part of the subscription data sent to the MME. If the STN-SR is present, it indicates the UE is SRVCC subscribed. If a roaming subscriber is determined by the HPLMN not allowed to have SRVCC in the VPLMN then HSS does not include STN-SR and C-MSISDN as part of the subscription data sent to the MME. If the subscriber is allowed to have vSRVCC in the VPLMN then HSS also includes vSRVCC flag as part of the subscription data sent to the MME. If STN-SR and C-MSISDN are not included in the subscription data, then the MME shall not set "SRVCC operation possible" indication.
- MME includes a "SRVCC operation possible" indication in the S1 AP Initial Context Setup Request, meaning that both UE and MME are SRVCC-capable and that STN-SR and C-MSISDN are included in the subscription data.
- SRVCC UE shall include the SRVCC capability indication as part of the "MS Network Capability" in the Emergency Attach Request message, and maintained during Tracking Area Updates. MME stores this information for SRVCC operation. The procedures are as specified in TS 23.401.
6.2.1A Service Request procedures for (v)SRVCC p. 39
Service Request procedures for 3GPP (v)SRVCC UE are performed as defined in TS 23.401 with the following additions:
- MME includes a "SRVCC operation possible" indication in the S1 AP Initial Context Setup Request, meaning that both UE and MME are SRVCC-capable and that STN-SR and C-MSISDN are included in the subscription data.
6.2.1B PS Handover procedures for (v)SRVCC |R9| p. 40
Intra-E-UTRAN S1-based handover and E-UTRAN to UTRAN (HSPA) Iu mode Inter RAT handover procedures for 3GPP SRVCC UE are performed as defined in TS 23.401 with the following additions:
- MS Classmark 2, MS Classmark 3, STN-SR, C-MSISDN, ICS Indicator and the Supported Codec IE shall be sent from the source MME to the target MME/SGSN if available.
- The target MME includes a "SRVCC operation possible" indication in the S1-AP Handover Request message, meaning that both UE and the target MME are SRVCC-capable and that STN-SR and C-MSISDN are included in the subscription data.
- The target SGSN includes a "SRVCC operation possible" indication in the RANAP Common ID message, meaning that both UE and the target SGSN are SRVCC-capable and that STN-SR and C-MSISDN are included in the subscription data.
6.2.1C Dedicated Bearer Establishment and Modification procedures for vSRVCC |R11| p. 40
Dedicated Bearer Establishment and Modification procedures for a session for which vSRVCC is allowed are performed as defined in TS 23.401 with the following additions:
- If dynamic PCC is deployed, the PCRF in the serving PLMN (i.e., VPLMN if roaming) interacts with the P-GW or S-GW as defined in TS 23.203. The P-GW and S-GW include a "vSRVCC indicator" in Create Bearer Request or Update Bearer Request messages that the bearer has been allocated for video media.
6.2.2 Call flows for (v)SRVCC from E-UTRAN p. 40
6.2.2.1 SRVCC from E-UTRAN to GERAN without DTM support p. 40
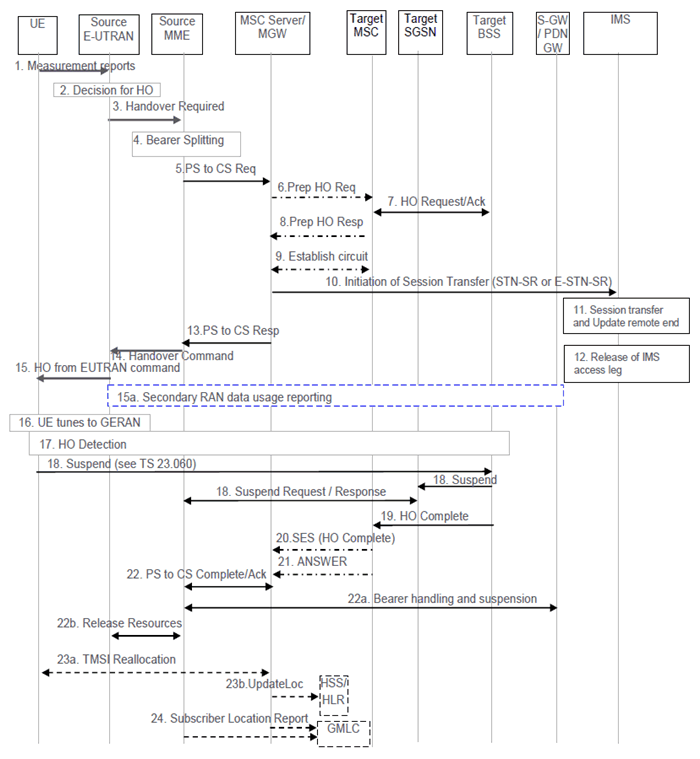
Depicted in Figure 6.2.2.1-1 is a call flow for SRVCC from E-UTRAN to GERAN without DTM support. The flow requires that eNB can determine that the target is GERAN without DTM support or that the UE is without DTM support.
Step 1.
After the CS voice call is terminated and if the UE is still in GERAN (or for any other reason specified in TS 24.008), then the UE shall resume PS services as specified in TS 23.060. A Gn SGSN will follow TS 23.060 to resume the PDP Context(s). An S4-SGSN will follow TS 23.060 to resume the bearers, and will in addition inform S-GW and P-GW(s) to resume the suspended bearers. If the UE has returned to E-UTRAN after the CS voice call was terminated, then the UE shall resume PS service by sending TAU to MME. The MME will in addition inform S-GW and P-GW(s) to resume the suspended bearers. Resuming the suspended bearers in the S-GW and in the P-GW should be done by implicit resume using the Modify Bearer request message if it is triggered by the procedure in operation, e.g. RAU, TAU or Service Request. The S-GW is aware of the suspend state of the bearers and will forward the Modify Bearer request to the P-GW. Explicit resume using the Resume Notification message should be used in cases when Modify Bearer Request is not triggered by the procedure in operation.
UE sends measurement reports to E-UTRAN.
Step 2.
Based on UE measurement reports the source E-UTRAN decides to trigger an SRVCC handover to GERAN.
Step 3.
Source E-UTRAN sends Handover Required (Target ID, generic Source to Target Transparent Container, SRVCC HO Indication) message to the source MME. The E-UTRAN places the "old BSS to new BSS information IE" for the CS domain in the generic Source to Target Transparent Container. The SRVCC HO indication indicates to the MME that target is only CS capable, hence this is a SRVCC handover operation only towards the CS domain. The message includes an indication that the UE is not available for the PS service in the target cell.
Step 4.
Based on the QCI associated with the voice bearer (QCI 1) and the SRVCC HO indication, the source MME splits the voice bearer from the non-voice bearers and initiates the PS-CS handover procedure for the voice bearer only towards MSC Server.
Step 5.
The MME sends a SRVCC PS to CS Request (IMSI, Target ID, STN-SR, C-MSISDN, generic Source to Target Transparent Container, MM Context, Emergency Indication) message to the MSC Server. If SRVCC with priority is supported, the MME also includes priority indication in SRVCC PS to CS Request if it detects the SRVCC requires priority handling. The detection is based on the ARP associated with the EPS bearer used for IMS signalling. The priority indication corresponds to the ARP information element. The Emergency Indication and the equipment identifier are included if the ongoing session is emergency session. Authenticated IMSI and C-MSISDN shall also be included, if available. The MME received STN-SR and C-MSISDN from the HSS as part of the subscription profile downloaded during the E-UTRAN attach procedure. The MM Context contains security related information. CS security key is derived by the MME from the E-UTRAN/EPS domain key as defined in TS 33.401. The CS Security key is sent in the MM Context.
Step 6.
The MSC Server interworks the PS-CS handover request with a CS inter-MSC handover request by sending a Prepare Handover Request message to the target MSC. If SRVCC with priority is supported, and the MSC Server receives the priority indication (i.e. ARP) in the SRVCC PS to CS Request, the MSC server/MGW sends Prepare Handover Request message to the Target MSC with priority indication mapped from the ARP. The MSC Server maps the ARP to the priority level, pre-emption capability/vulnerability for CS services based on local regulation or operator settings. The priority indication indicates the CS call priority during handover as specified in TS 48.008 for GSM/EDGE. The MSC Server assigns a default SAI as Source ID on the interface to the target BSS and uses BSSMAP encapsulated for the Prepare Handover Request.
Step 7.
Target MSC performs resource allocation with the target BSS by exchanging Handover Request/ Acknowledge messages. If the MSC Server indicated priority, the target BSS allocates the radio resource based on the existing procedures with priority indication, as specified in TS 23.009 and in TS 48.008 for GSM/EDGE.
Step 8.
Target MSC sends a Prepare Handover Response message to the MSC Server.
Step 9.
Establishment of circuit connection between the target MSC and the MGW associated with the MSC Server e.g. using ISUP IAM and ACM messages.
Step 10.
For non-emergency session, the MSC Server initiates the Session Transfer by using the STN-SR e.g. by sending an ISUP IAM (STN-SR) message towards the IMS. If this is a priority session, the MSC Server includes priority indication to the IMS and the IMS entity handles the session transfer procedure with priority. The priority indication in the Session Transfer is mapped by the MSC Server from the priority indication (i.e. ARP) in the SRVCC PS to CS Request received in step 5. The mapping of the priority level is based on operator policy and/or local configuration, and the IMS priority indicator should be the same as for the original IMS created over PS. For emergency session, the MSC Server initiates the Session Transfer by using the locally configured E-STN-SR and by including the equipment identifier. IMS Service Continuity or Emergency IMS Service Continuity procedures are applied for execution of the Session Transfer, see TS 23.237.
Step 11.
During the execution of the Session Transfer procedure the remote end is updated with the SDP of the CS access leg. The downlink flow of VoIP packets is switched towards the CS access leg at this point.
Step 12.
Source IMS access leg is released as per TS 23.237.
Step 13.
MSC Server sends a SRVCC PS to CS Response (Target to Source Transparent Container) message to the source MME.
Step 14.
Source MME sends a Handover Command (Target to Source Transparent Container) message to the source E-UTRAN. The message includes information about the voice component only.
Step 15.
Source E-UTRAN sends a Handover from E-UTRAN Command message to the UE.
Step 15a.
If the PLMN has configured Secondary RAT usage data reporting and the source eNodeB has Secondary RAT usage data to report, the reporting is performed as specified in TS 23.401.
Step 16.
UE tunes to GERAN.
Step 17.
Handover Detection at the target BSS occurs, then the target BSS sends Handover Detection message to the target MSC. At this stage, the target MSC can send/receive voice data. The UE sends a Handover Complete message via the target BSS to the target MSC. If the target MSC is not the MSC Server, then the Target MSC sends an SES (Handover Complete) message to the MSC Server.
Step 18.
The UE starts the Suspend procedure specified in clause 16.2.1.1.2 of TS 23.060. The TLLI and RAI pair are derived from the GUTI as described in TS 23.003. This triggers the Target SGSN to send a Suspend Notification message to the Source MME. The MME returns a Suspend Acknowledge to the Target SGSN.
Step 19.
Target BSS sends a Handover Complete message to the target MSC.
Step 20.
Target MSC sends an SES (Handover Complete) message to the MSC Server. The speech circuit is through connected in the MSC Server/MGW according to TS 23.009.
Step 21.
Completion of the establishment procedure with ISUP Answer message to the MSC Server according to TS 23.009.
Step 22.
MSC Server sends a SRVCC PS to CS Complete Notification message to the source MME, informing it that the UE has arrived on the target side. Source MME acknowledges the information by sending a SRVCC PS to CS Complete Acknowledge message to the MSC Server.
Step 22a.
The MME deactivates bearers used for voice and other GBR bearers. All GBR bearers are deactivated towards S-GW and P-GW by initiating MME-initiated Dedicated Bearer Deactivation procedure as specified in TS 23.401. PS-to-CS handover indicator is notified to P-GW for voice bearer during the bearer deactivation procedure. For GTP-based S5/S8, the S-GW requests the P-GW to delete all GBR bearer contexts by sending a Delete Bearer Command message. If dynamic PCC is deployed, the P-GW may interact with PCRF as defined in TS 23.203. For PMIP-based S5/S8, S-GW interacts with the PCRF which in turn updates PCC rules for GBR traffic in the P-GW.
The MME starts preservation and suspension of non-GBR bearers by sending Suspend Notification message towards S-GW. For these non-GBR bearers, the S-GW releases S1-U bearers for the UE and sends Suspend Notification message to the P-GW(s). The MME stores in the UE context that UE is in suspended status. All the preserved non-GBR bearers are marked as suspended status in the S-GW and P-GW. The P-GW should discard packets if received for the suspended UE.
Step 22b.
The source MME requests the release of the resources, including release of the S1 signalling connection, to the Source eNodeB. The Source eNodeB releases its resources related to the UE and responds back to the MME.
Step 23a.
For non-emergency sessions and if the HLR is to be updated, i.e. if the IMSI is authenticated but unknown in the VLR, the MSC Server performs a TMSI reallocation towards the UE using its own non-broadcast LAI and, if the MSC Server and other MSC/VLRs serve the same (target) LAI, with its own Network Resource Identifier (NRI).
Step 23b.
For non-emergency sessions and if the MSC Server performed a TMSI reallocation in step 23a, and if this TMSI reallocation was completed successfully, the MSC Server performs a MAP Update Location to the HSS/HLR.
Step 24.
For an emergency services session after handover is complete, the source MME or the MSC Server may send a Subscriber Location Report carrying the identity of the MSC Server to a GMLC associated with the source or target side, respectively, as defined in TS 23.271 to support location continuity.
6.2.2.1A SRVCC from E-UTRAN to GERAN with DTM but without DTM HO support and from E-UTRAN to UTRAN without PS HO p. 44
The call flow for this scenario is similar to the call flow depicted in Figure 6.2.2.1-1, with the exceptions that the Suspend procedure (step 18 and step 22a in Figure 6.2.2.1-1) is not performed and that the MME only deactivates bearers used for voice (step 22a in Figure 6.2.2.1-1) and sets the PS-to-CS handover indicator. The scenario requires that eNB can determine that the target is either GERAN with DTM but without DTM HO support and that the UE is supporting DTM or that the target is UTRAN (HSPA) without PS HO support.
The message in step 3 in Figure 6.2.2.1-1 includes an indication to the MME that the UE is available for PS service in the target cell. Furthermore, if the target is GERAN, the E-UTRAN places in the generic Source to Target Transparent Container the "old BSS to new BSS information IE", while if the target is UTRAN, the generic Source to Target Transparent container is encoded according to the Source RNC to Target RNC Transparent Container IE definition. At the end of the procedure described in Figure 6.2.2.1-1, the remaining PS resources are re-established when the UE performs the Routeing Area update procedure. Triggers for performing Routeing Area update procedure are described in TS 23.060. The target SGSN may deactivate the PDP contexts that cannot be established as described in TS 23.060.