Content for TS 23.066 Word version: 18.0.0
5 Common Architecture for call setup
6 Functional requirements of network entities
6.1 Procedure MNP_MT_GMSC_Set_MNP_Parameters
6.2 Procedure MNP_MT_GMSC_Check_MNP_Indicators
6.3 Procedure MNP_SRF_Check_MNP_Indicator
...
...
5 Common Architecture for call setup p. 14
Figure 3 shows the general architecture of a portability domain for routeing of calls. The more detailed architecture within the networks depends on the chosen solution (IN-based or MNP/SRF-based) and options and is described in Normative Annex A and Normative Annex C of the present document.
The architecture for non-call related signalling is described in Normative Annex B of the present document.
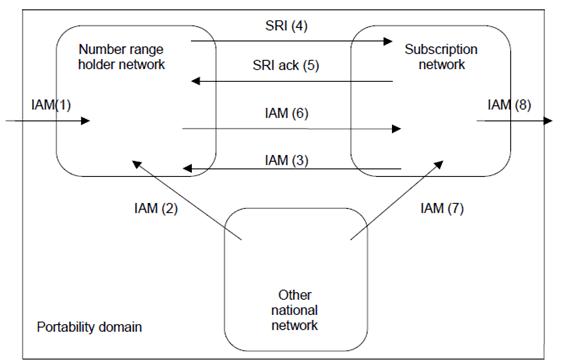
Figure 3: General architecture of a portability domain for routeing of calls
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The following routeing conventions are identified:
- Direct Routeing of calls is a PLMN option that allows to route calls directly from the PLMN supporting this option to the ported subscriber's subscription network.
- Indirect Routeing of calls is a PLMN option which allows to route calls from the PLMN supporting this option via the number range holder network to the ported subscriber's subscription network.
- Indirect Routeing of calls with reference to the subscription network is a PLMN option for PLMN operators having chosen the MNP-SRF solution for call related signalling described in Normative Annex C. If all PLMNs within a portability domain support this option, calls are routed from the originating network to the number range holder network. The number range holder network obtains onward routeing information from the subscription network and routes the call onward to the ported subscriber's subscription network.
1)
If the call is originated outside the portability domain, the IAM (1) is received by the number range holder network.
2a)
If the call is originated in another national network and the other national network does not support originating call query (i.e. Indirect Routeing of calls is applicable), the IAM (2) is received by the number range holder network.
2b)
If the call is originated in another national network and the other national network supports originating call query (i.e. Direct Routeing of calls is applicable), the IAM (7) containing the routeing number is sent to the subscription network. If the routeing number is not used in the IAM sent from the national originating network to the subscription network, all transit networks involved are required to look up an NPDB in order to retrieve routeing information to route the call to the subscription network without looping.
3a)
If the call is originated in the subscription network and the subscription network does not support originating call query (i.e. Indirect Routeing of calls is applicable), the IAM (3) is received by the number range holder network.
3b)
If the call is originated in the subscription network and the subscription network supports originating call query (i.e. Direct Routeing of calls is applicable), it sends an IAM (8) containing the MSRN to the visited network of the called subscriber.
3c)
If the subscription network receives IAM (6 or 7) containing the routeing number, it sends an IAM (8) containing the MSRN to the visited network of the called subscriber.
4a)
If the call is routed via the number range holder network, and the number range holder network supports the MNP-SRF/MATF solution with the option 'MATF in subscription network' described in Normative Annex C of the present document (i.e. Indirect Routeing of calls with reference to the subscription network is applicable), the number range holder network sends SRI (4) to the subscription network. The subscription network returns SRI ack (5) containing the routeing number. The number range holder network then sends IAM (6) containing the routeing number to the subscription network. If the routeing number is not used in the IAM sent from the number range holder network to the subscription network, all transit networks involved are required to look up an NPDB in order to retrieve routeing information to route the call to the subscription network without looping.
4b)
If the call is routed via the number range holder network, and the number range holder network supports the IN solution described in Normative Annex A of the present document or the MNP-SRF/MATF solution with the option 'MATF inside number range holder network' described in Normative Annex C of the present document, the number range holder network sends IAM (6) containing the routeing number to the subscription network.
6 Functional requirements of network entities p. 16
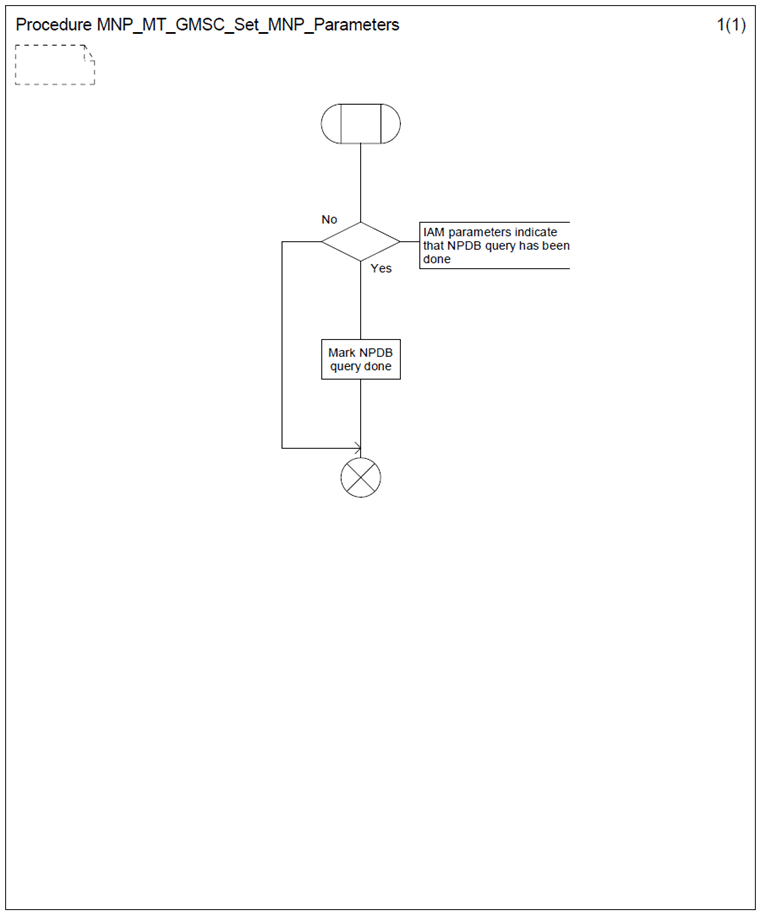
6.1 Procedure MNP_MT_GMSC_Set_MNP_Parameters p. 16
The procedure MNP_MT_GMSC_Set_MNP_Parameters is shown in Figure 4. It is called from the process MT_GMSC defined in 3G TS 23.018.
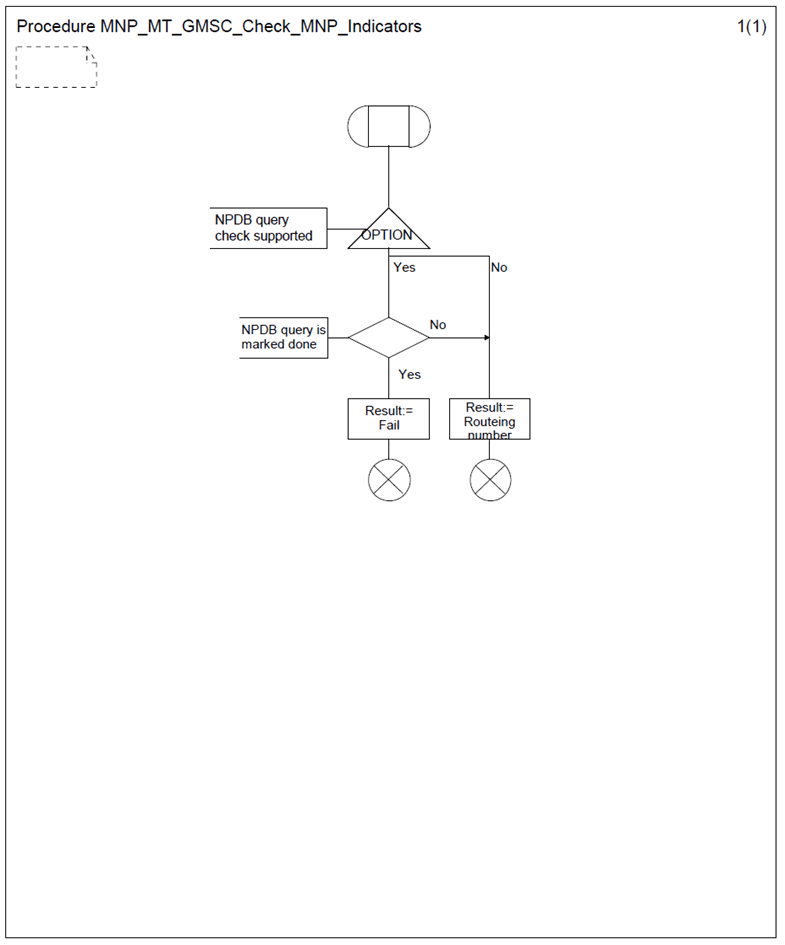
6.2 Procedure MNP_MT_GMSC_Check_MNP_Indicators p. 17
The procedure MNP_MT_GMSC_Check_MNP_Indicators is shown in Figure 5. It is called from the process MT_GMSC defined in 3G TS 23.018.
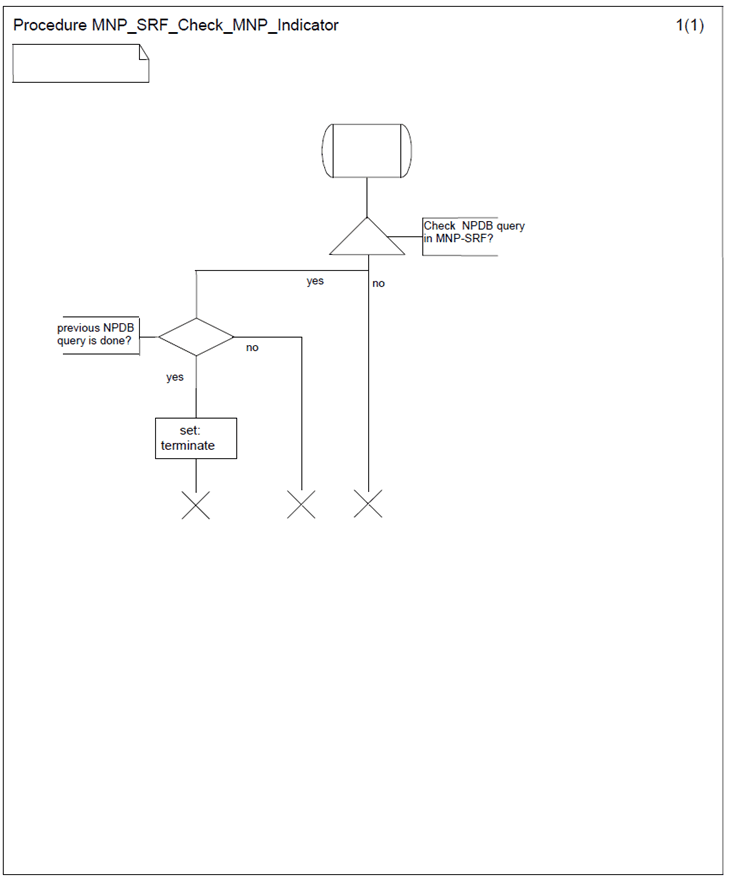
6.3 Procedure MNP_SRF_Check_MNP_Indicator p. 18
The procedure MNP_SRF_Check_MNP_Indicator is shown in Figure 6. It is called from the procedures MNP_SRF_Non_Call_Related and MNP_SRF_MATF_Call_Related.