Content for TR 22.950 Word version: 18.0.1
6 Priority Service Gap Analysis
6.1 Service Accessibility
6.2 Enhanced Multi-Level Precedence and Pre-emption (eMLPP)
6.3 Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) Specifications
6.4 Assignment request Priority Information Element
7 Conclusions
6 Priority Service Gap Analysis p. 12
6.1 Service Accessibility p. 12
Service Accessibility is specified in:
Release 1998:
- ETSI TS 100 921 version 7.0.1 (1999-07), Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Service accessibility (GSM 02.11 version 7.0.1 Release 1998);
- 3GPP TS 22.011 version 3.5.0 (2005-01), 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Service accessibility (Release 1999); and
- 3GPP TS 22.011 version 4.4.0 (2005-01), 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Service accessibility (Release 4).
6.1.1 Summary of Service Accessibility Capabilities p. 12
The Access Control capability prevents mobile users from initiating call origination attempts and from responding to pages in specific areas (e.g., in emergency situations where resource shortages exist). Access control is intended to allow network operators to prevent overload of radio access channels under critical conditions.
The basic mechanism is administered as follows: All SIMs are randomly assigned to one of ten access classes (0 - 9). In addition, SIMs may also be members of one or more of five special categories (access classes 11 to 15). These special classes are designated for specific purposes as summarized in the following Table:
| Access Class | Usage | Applicability |
|---|---|---|
| 15 | PLMN Staff | Home PLMN Only |
| 14 | Emergency Services | Home and Visited PLMNs of home country only |
| 13 | Public Utilities | |
| 12 | Security Services | |
| 11 | For PLMN Use | Home PLMN Only |
| 0 - 9 | General Use | Home and Visited PLMNs |
In an emergency situation, broadcast messages are used (on an individual cell basis) to indicate the "Access Classes" of subscribers that are barred from network access. Any number of classes may be barred at any one time. For example, to reduce approximately 20 percent of the basic mobile traffic in a given cell, broadcast messages might indicate that two of the basic access classes should be barred from access. Upon receiving an emergency broadcast message, those mobiles belonging to the barred access classes (and not also being members of any of the special classes) should not initiate a call attempt or respond to a page (note 1) . In addition, broadcast messages use "access class 10" to indicate whether network access is allowed for emergency calls.
Access Control is designed to suppress not only the ability of non-priority end users to seize traffic channels, but also the ability of those end users to use signaling channels for call attempts. Service Accessibility, as specified, cannot be turned on and off by the end user.
6.1.2 Support for Priority Service p. 13
The following Table identifies Service Accessibility support for Priority Service.
| Priority Service Requirement Item | Description | Service Accessibility Support | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Priority Call Origination | A call shall receive priority treatment (priority access to voice or traffic channels) on the originating side, when the call is setup by a Service User using the priority service dialling procedure described in clause 4.9. | Supported | Using appropriate Access Class(es) to prevent access attempts |
| 2. Priority Call Termination | A call shall receive priority treatment (priority access to voice or traffic channels) on the terminating side, when the call is setup by a Service User using the priority service dialling procedure described in clause 4.9. | Supported | Using appropriate Access Class(es) to prevent response to pages |
| 3. Priority Progression | The user should receive priority call treatment/progression through the mobile network(s). A priority call should be given higher priority over normal calls in the originating mobile network, to interconnected networks supporting priority (including the PSTN) and in the terminating network. | Not supported | |
| 4. Priority Radio Resource Queuing | When a Priority Service call encounters a "no radio available" condition in the call path involving an access or egress air-interface, or both, and, at call origination, and upon recognition of the Priority Service dialing pattern, the Priority Service call is queued in the cell serving the calling party and processed for the next available radio channel in that cell in accordance with the caller's priority level and call initiation time. at call termination upon recognition of a priority call indication in an incoming call, the Priority Service call is queued in the cell serving the called party and processed for the next available radio channel in that cell in accordance with the call's priority level and arrival time. | Not supported | |
| 5. Priority Level | The subscriber should be assigned one of n priority levels. Priority levels are defined as 1, 2, 3,…,n , with 1 being the highest priority level and n being the lowest priority level.. | Partially supported | Ten (0-9) randomly allocated Access Classes. Five (11-15) special classes. Enumeration of special classes is not meant as a priority sequence. Priority Service priority levels could map to special Access Classes. |
| 6. Invocation on Demand | Priority Service is invoked only when requested and an idle voice or traffic channel required for an origination request is not available. | Not supported | |
| 7. Applicability to Telecommunications Services | Priority Service shall be applicable to voice and data telecommunications services that require a voice or traffic channel assignment. | Supported | |
| 8. Authorization | A subscriber invoking Priority Service on call origination is authorized based on the caller's subscription. It should also be possible for an additional second level of authentication (e.g., by the use of PIN) to identify that the user is authorized to make a priority call. In this case, authorization of the subscriber may be realized by the usage of a PIN. | Supported | Access Classes stored in the SIM. |
| 9. Priority Service service code | Priority Service is manually requested by adding on the Priority Service service code to the origination request. | Not supported | |
| 10. Roaming | Priority Service shall be supported during roaming when the roaming network supports Priority Service. | Partially supported | Access classes 0-9 pertain to Home and Visited PLMNs. Access classes 11 and 15 pertain to Home PLMN only. Access classes 12, 13, and 14 pertain to Home and Visited PLMNs of home country only. |
| 11. Handover | Priority Service shall be supported during handover. | Not supported | |
| 12. Priority Service charging data record | The system should record the following Priority Service charging data information, in addition to non-Priority Service CDR information: Priority Service invocation attempts, Call legs (origination and/or termination) on which Priority Service was used to gain access to the radio channel. Recording of appropriate Priority Service information. | Not supported | |
| 13. Priority Trunk Queuing | Priority Service shall be able to support queuing of Priority Service calls for trunk resources. | Not supported | |
| 14. Coexistence with eMLPP | As a service provider option, it shall be possible to offer Priority Service and eMLPP within the same network, but not to the same user. | Not supported |
6.2 Enhanced Multi-Level Precedence and Pre-emption (eMLPP) p. 16
eMLPP is specified in:
Release 1998:
- ETSI EN 300 924 version 7.0.1 (2005-01), Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); enhanced Multi-Level Precedence and Pre-emption (eMLPP) - Stage 1 (GSM 02.67 version 7.0.1 Release 1998);
- 3GPP TS 03.67 version 7.2.0 (2005-01), 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); enhanced Multi-Level Precedence and Pre-emption (eMLPP) - Stage 2 (Release 1998);
- ETSI EN 300 927 version 7.0.1 (2005-01), Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); enhanced Multi-Level Precedence and Pre-emption (eMLPP) - Stage 3 (GSM 04.67 version 7.0.1 Release 1998);
- 3G TS 22.067 version 3.0.1 (1999-10), 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; enhanced Multi-Level Precedence and Pre-emption (eMLPP) - Stage 1 (Release 1999);
- 3GPP TS 23.067 version 3.3.0 (2005-01), 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; enhanced Multi-Level Precedence and Pre-emption (eMLPP) - Stage 2 (Release 1999);
- 3GPP TS 24.067 version 3.3.0 (2005-01), 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; enhanced Multi-Level Precedence and Pre-emption (eMLPP) - Stage 3 (Release 1999);
- 3G TS 22.067 version 4.0.0 (2005-01), 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; enhanced Multi-Level Precedence and Pre-emption (eMLPP) - Stage 1 (Release 2000);
- 3GPP TS 23.067 version 4.1.0 (2005-01), 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; enhanced Multi-Level Precedence and Pre-emption (eMLPP) - Stage 2 (Release 4);
- 3GPP TS 24.067 version 4.1.0 (2005-01), 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; enhanced Multi-Level Precedence and Pre-emption (eMLPP) - Stage 3 (Release 4).
6.2.1 Summary of eMLPP Capabilities p. 16
The eMLPP service is provided as a network operator's option to a domain of a network. The domain can be the whole network or a subset of the network. The eMLPP service applies to all network resources in the domain, and eMLPP is provided to a subscriber for all basic services subscribed to and for which eMLPP applies.
The eMLPP service supports two capabilities: precedence and pre-emption.
Precedence involves the assignment of a priority level to a call. eMLPP supports a maximum of seven priority levels. The two highest levels (A and B) are reserved for network internal use (e.g., for emergency calls). These are only used locally (i.e., in the domain of one MSC) 1. The other five priority levels are offered for subscription and can be applied globally (presuming the priority level is successfully passed from the originating end and processed at the terminating end).
For each of the seven priority levels, the network operator can administer parameters that control the treatment of that priority within its domain. This treatment includes the selection of a target set-up time and whether or not pre-emption is allowed for each priority level. For example, a network operator might administer priority levels as follows:
| Priority Level | Set-Up Time | Pre-emption |
|---|---|---|
| A | Class 1 | no |
| B | Class 2 | no |
| 0 | Class 2 | no |
| 1 | Class 3 | no |
| 2 | Class 3 | no |
| 3 | Class 3 | no |
| 4 | Class 3 | no |
In the example above, three classes of set-up time performance are supported. In the above example, the network operator has assigned class 1 (fast set-up, nominally 1-2 seconds 2) to Priority Level A traffic, has assigned class 2 (normal set-up, nominally less than 5 seconds) to traffic at Priority Levels B and 0, and has assigned class 3 (slow set-up, nominally less than 10 seconds) to the lower Priority Level traffic. 3GPP specifications do not define specific mechanisms (which may include specific technical capabilities and/or network engineering decisions) to achieve the target set-up times as defined by the service provider 3.
If idle resources are not available, pre-emption involves the seizure of resources (currently in use by a lower-priority call) for use by a call that is of higher priority. The network releases the lowest-priority call and seizes the necessary resources that are required to set up the higher-priority call. At handover to a congested cell, higher-priority calls replace existing calls of the lowest priority.
In the above example, the network operator has chosen not to allow pre-emption. Thus, priority levels will use different queuing priorities rather than pre-emption capabilities.
The eMLPP priority level for a given call depends on the calling subscriber. The maximum precedence level for each subscriber is set at subscription time (and is stored on the SIM).
The default priority level is established via normal registration procedures. If the user does not explicitly select a precedence level at call set-up, the network applies the subscriber-specific default precedence level.
The priority level can be selected by the user on a per-call basis (up to and including their maximum authorized precedence level).
The eMLPP service is invoked automatically by the network at call set-up, with the priority level established as above for mobile-originated calls. For mobile-terminated calls, the priority level is established based on the priority of the calling party, and is applied at the terminating end (presuming the call's priority is passed via signaling between the originating and terminating networks). Interworking with ISDN MLPP is required.
The eMLPP service applies to roaming scenarios, if eMLPP is supported by the related networks.
The HLR maintains the logical state for eMLPP (provisioned or not provisioned), the maximum priority level, and the default priority level for each user.
The MSC stores service configuration information for each priority level (i.e., set up time [class] and pre-emption indicators, as illustrated in the previous section).
The SIM stores data that influences UE actions, as noted in the following Table:
| Priority Level | Subscription Available | Automatic answering | Fast set-up actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | yes / no | yes / no | yes / no |
| B | yes / no | yes / no | yes / no |
| 0 | yes / no | yes / no | yes / no |
| 1 | yes / no | yes / no | yes / no |
| 2 | yes / no | yes / no | yes / no |
| 3 | yes / no | yes / no | yes / no |
| 4 | yes / no | yes / no | yes / no |
The maximum authorized precedence level is stored on the SIM, allowing the mobile station to check that only an authorized level is used for set-up. (In addition, the network may verify the level used at set-up against the maximum authorized level.)
In the case of automatic answering of an incoming call with a sufficient priority level, the alerting indication to the calling party may not be provided in order to shorten the set-up time. If the called mobile subscriber is busy and automatic answering applies, the existing call may be released (if pre-emption applies) or may be placed on hold in order to accept an incoming call of higher priority.
6.2.2 Support for Priority Service p. 18
The following Table identifies eMLPP support for Priority Service.
| Priority Service Requirement Item | Description | eMLPP Support | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Priority Call Origination | A call shall receive priority treatment (priority access to voice or traffic channels) on the originating side, when the call is setup by a Service User using the priority service dialling procedure described in clause 4.9. | Supported | Based on subscribed priority level |
| 2. Priority Call Termination | A call shall receive priority treatment (priority access to voice or traffic channels) on the terminating side, when the call is setup by a Service User using the priority service dialling procedure described in clause 4.9. | Supported | Based on priority level of calling party |
| 3. Priority Progression | The user should receive priority call treatment/progression through the mobile network(s). A priority call should be given higher priority over normal calls in the originating mobile network, to interconnected networks supporting priority (including the PSTN) and in the terminating network. | Supported depending on inter-operator agreements | Requires interworking with priority services supported within the interconnected networks (e.g. ISDN MLPP.) Requires special agreements between network operators to achieve transparent progression of priority level between networks. |
| 4. Priority Radio Resource Queuing | When a Priority Service call encounters a "no radio available" condition in the call path involving an access or egress air-interface, or both, and, at call origination, and upon recognition of the Priority Service dialing pattern, the Priority Service call is queued in the cell serving the calling party and processed for the next available radio channel in that cell in accordance with the caller's priority level and call initiation time. at call termination upon recognition of a priority call indication in an incoming call, the Priority Service call is queued in the cell serving the called party and processed for the next available radio channel in that cell in accordance with the call's priority level and arrival time. | Partially Supported | Priority levels with no pre emption capability allocated shall only have queuing priority 22.067, ch 4. NOTE: BSS implementations should have internal functionality to handle signaling channels overload, however in case of complete congestion there may not be way to guarantee priority access to network, however due to large capacity of paging and random access channels the complete overload of signaling channels very rare and thus is not likely to be the bottle neck. |
| 5. Priority Level | The subscriber should be assigned one of n priority levels. Priority levels are defined as 1, 2, 3,…,n , with 1 being the highest priority level and n being the lowest priority level.. | Partially supported | Seven priority levels (with five available for subscription). Priority Service priority levels could map to eMLPP priority levels. |
| 6. Invocation on Demand | Priority Service is invoked only when requested and an idle voice or traffic channel required for an origination request is not available. | Supported | If the user has an eMLPP subscription, the call shall have the priority level selected by the user at set-up or the priority level predefined by the subscriber as default priority level by registration. |
| 7. Applicability to Telecommunications Services | Priority Service shall be applicable to voice and data telecommunications services that require a voice or traffic channel assignment. | Supported | eMLPP is a supplementary service and shall be provided to a subscriber for all basic services subscribed to and for which eMLPP applies. |
| 8. Authorization | A subscriber invoking Priority Service on call origination is authorized based on the caller's subscription. It should also be possible for an additional second level of authentication (e.g., by the use of PIN) to identify that the user is authorized to make a priority call. In this case, authorization of the subscriber may be realized by the usage of a PIN. | Supported | Priority level stored in the SIM. |
| 9. Priority Service service code | Priority Service is manually requested by adding on the Priority Service service code to the origination request. | Partially supported | The exact MMI proposed is not supported. The MMI supported by eMLPP is specified in 22.030. The service code is 75. |
| 10. Roaming | Priority Service shall be supported during roaming when the roaming network supports Priority Service. | Supported | eMLPP is applicable in case of roaming, if supported by the related networks. |
| 11. Handover | Priority Service shall be supported during handover. | Partially supported | When pre-emption applies, at handover to a congested cell, higher priority calls shall replace those of the lowest priority. The pre-empted user shall receive an indication for congestion as defined in GSM 02.40. |
| 12. Priority Service charging data record | The system should record the following Priority Service charging data information, in addition to non-Priority Service CDR information: Priority Service invocation attempts, Call legs (origination and/or termination) on which Priority Service was used to gain access to the radio channel. Recording of appropriate Priority Service information. | Supported | clause 5.11 of TS 22.067. The utilized precedence level shall be able to be extracted from the event records if different from the default precedence level. |
| 13. Priority Trunk Queuing | Priority Service shall be able to support queuing of Priority Service calls for trunk resources. | Not supported | eMLPP Stage 2, TS 23.067 ch 4, items c. and d. refer to "contention in gaining terrestrial resources," which may be interpreted as referring to Trunk Queuing. However, neither the Stage 1 (TS 22.067) nor the Stage 3 (TS 24.067) has any additional specification associated with trunk queuing. |
| 14 Coexistence with eMLPP | As a service provider option, it shall be possible to offer Priority Service and eMLPP within the same network, but not to the same user. | Not supported |
6.3 Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) Specifications p. 21
Release 1998:
- GSM 11.11 v7.6.1, Specification of the Subscriber Identity Module - Mobile Equipment (SIM - ME) interface; Release 1998;
- GSM 04.08 v7.13.0, Mobile Radio Interface Layer 3 Specification; Release 1998;
- GSM 11.14, Specification of the SIM Application Toolkit for the Subscriber Identity Module - Mobile Equipment (SIM - ME) interface
- 3GPP TS 11.11 v8.5.0, Specification of the Subscriber Identity Module - Mobile Equipment (SIM - ME) interface; Release 1999;
- 3GPP TS 24.008 v3.11.0, Mobile radio interface layer 3 specification; Core Network Protocols - Stage 3; Release 1999;
- GSM 11.14, Specification of the SIM Application Toolkit for the Subscriber Identity Module - Mobile Equipment (SIM - ME) interface
- 3GPP TS 51.011 v4.1.0, Specification of the Subscriber Identity Module - Mobile Equipment (SIM - ME) interface; Release 4;
- 3GPP TS 24.008 v4.4.0, Mobile radio interface layer 3 specification; Core Network Protocols - Stage 3; Release 4;
- 3GPP TS 31.102, Characteristics of the USIM Application;
- 3GPP TS 31.111, USIM Application Toolkit (USAT)
6.3.1 Summary of SIM-based Capabilities p. 21
The SIM specifications address the allocation and administration of Access Control Classes for control of Service Accessibility.
All mobile stations with an inserted SIM are members of one out of 10 access classes numbered 0 to 9. In addition, mobile stations may be members of one or more out of 5 special access classes (access classes 11 to 15). Both the regular as well as the special access class number are stored in the SIM. The access control class is a parameter to control the RACH utilization. The first 10 Access Control Classes (0-9) are randomly allocated to normal subscribers; and the top 5 classes (11-15) are allocated to specific high priority users.
The system information messages on the BCCH broadcast the list of authorized access classes and authorized special access classes in the system information messages, and whether emergency calls are allowed in the cell to all mobile stations or only to the members of authorized special access classes.
If the establishment cause for the request of the MM sub-layer is not "emergency call", access to the network is allowed if and only if the mobile station is a member of at least one authorized:
- access class; or
- special access class.
- emergency calls are allowed to all mobile stations in the cell; or
- the mobile station is a member of at least one authorized special access class.
6.3.2 Support for Priority Service p. 22
The following Table identifies SIM based support for Priority Service.
| Priority Service Requirement Item | Description | SIM Support | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Priority Call Origination | A call shall receive priority treatment (priority access to voice or traffic channels) on the originating side, when the call is setup by a Service User using the priority service dialling procedure described in clause 4.9. | Supported | |
| 2. Priority Call Termination | A call shall receive priority treatment (priority access to voice or traffic channels) on the terminating side, when the call is setup by a Service User using the priority service dialling procedure described in clause 4.9. | Supported | |
| 3. Priority Progression | The user should receive priority call treatment/progression through the mobile network(s). A priority call should be given higher priority over normal calls in the originating mobile network, to interconnected networks supporting priority (including the PSTN) and in the terminating network. | Not supported | |
| 4. Priority Radio Resource Queuing | When a Priority Service call encounters a "no radio available" condition in the call path involving an access or egress air-interface, or both, and, at call origination, and upon recognition of the Priority Service dialing pattern, the Priority Service call is queued in the cell serving the calling party and processed for the next available radio channel in that cell in accordance with the caller's priority level and call initiation time. at call termination upon recognition of a priority call indication in an incoming call, the Priority Service call is queued in the cell serving the called party and processed for the next available radio channel in that cell in accordance with the call's priority level and arrival time. | Not supported | |
| 5. Priority Level | The subscriber should be assigned one of n priority levels. Priority levels are defined as 1, 2, 3,…,n , with 1 being the highest priority level and n being the lowest priority level. | Partially supported | Ten (0-9) randomly allocated Access Classes. Five (11-15) special classes. Enumeration of special classes is not meant as a priority sequence. PS priority levels could map to special Access Classes. |
| 6. Invocation on Demand | Priority Service is invoked only when requested and an idle voice or traffic channel required for an origination request is not available. | Partially Supported | The user can insert a special SIM when he/she needs to make a priority call. |
| 7. Applicability to Telecommunications Services | Priority Service shall be applicable to voice and data telecommunications services that require a voice or traffic channel assignment. | Supported | |
| 8. Authorization | A subscriber invoking Priority Service on call origination is authorized based on the caller's subscription. It should also be possible for an additional second level of authentication (e.g., by the use of PIN) to identify that the user is authorized to make a priority call UE. In this case, authorization of the subscriber may be realized by the usage of a PIN. | Supported | Access Classes stored in the SIM. |
| 9. Priority Service service code | Priority Service is manually requested by adding on the Priority Service service code to the origination request. | Not supported | |
| 10. Roaming | Priority Service shall be supported during roaming when the roaming network supports Priority Service. | Partially supported | Access classes 0-9 pertain to Home and Visited PLMNs. Access classes 11 and 15 pertain to Home PLMN only. Access classes 12, 13, and 14 pertain to Home and Visited PLMNs of home country only. |
| 11. Handover | Priority Service shall be supported during handover. | Not supported | |
| 12. Priority Service charging data record | The system should record the following Priority Service charging data information, in addition to non-Priority Service CDR information: Priority Service invocation attempts, Call legs (origination and/or termination) on which Priority Service was used to gain access to the radio channel. Recording of appropriate Priority Service information. | Not supported | |
| 13. Priority Trunk Queuing | Priority Service shall be able to support queuing of Priority Service calls for trunk resources. | Not supported | |
| 14. Coexistence with eMLPP | As a service provider option, it shall be possible to offer Priority Service and eMLPP within the same network, but not to the same user. | Not supported |
6.4 Assignment request Priority Information Element p. 25
Priority Information Element (PIE) is specified in 3GPP TS 08.08 [19], [20], [21] and TS 25.413, [23]. The term used for the Assignment request Priority Information Element in Release 4 is Allocation/Retention Priority.
6.4.1 Summary and coding of Priority Information Element Capabilities p. 25
This element indicates the priority of the assignment request in A and Iu interface. Following information may be included in IE:
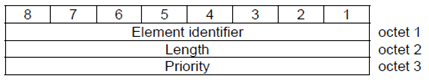 Octet 2 is a binary indication of the length of the rest of the element.
Octet 3 is coded as follows:
Octet 2 is a binary indication of the length of the rest of the element.
Octet 3 is coded as follows:
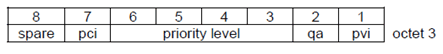 Bit 8 is spare, set to 0
pci = Pre-emption Capability indicator (see note)
0
Bit 8 is spare, set to 0
pci = Pre-emption Capability indicator (see note)
0
- priority level of the request (levels 1-14),
- if the request can be queued,
- if the request may pre-empt an existing connection and
- if the request can be pre-empted by another request.


this allocation request shall not pre-empt an existing connection
1
this allocation request may pre-empt an existing connection
priority level:
6 5 4 3 0 0 0 0 spare 0 0 0 1 priority level 1 = highest priority 0 0 1 0 priority level 2 = second highest priority : : : : 1 1 1 0 priority level 14 = lowest priority 1 1 1 1 priority not usedqa = queuing allowed indicator 0
queuing not allowed
1
queuing allowed
pvi = Pre-emption Vulnerability indicator (see note)
0
this connection shall not be pre-empted by another allocation request
1
this connection might be pre-empted by another allocation request
6.4.2 Support for Priority Service p. 26
The following Table identifies Priority Information Element support for Priority Service.
Note that the 3GPP specifications do not explicitly define the use of Priority IE, e.g. the data that the setting of the Information Element fields could/should be based on. Since this information element was introduced quite early in the standards, Network Element vendors may have taken this IE into other than eMLPP uses, too. Therefore, mandating usage of these fields in 3GPP specifications in this regard could cause problems.
The Table indicates issues that may be achieved with using Priority Information Element, requirements that can be fulfilled with MSC internal or other additional vendor specific functionality have been also identified. Note that vendor specific information or functionality is not needed over open interfaces, where only standardized information is used.
| Priority Service Requirement Item | Description | PIE Support | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Priority Call Origination | A call shall receive priority treatment (priority access to voice or traffic channels) on the originating side, when the call is setup by a Service User using the priority service dialling procedure described in clause 4.9. | Supported | |
| 2. Priority Call Termination | A call shall receive priority treatment (priority access to voice or traffic channels) on the terminating side, when the call is setup by a Service User using the priority service dialling procedure described in clause 4.9. | Supported | |
| 3. Priority Progression | The user should receive priority call treatment/progression through the mobile network(s). A priority call should be given higher priority over normal calls in the originating mobile network, to interconnected networks supporting priority (including the PSTN) and in the terminating network. | Not supported/vendor specific | Vendor specific functionality is needed to set priorities for each leg. This may not be supported in all interfaces or some nodes on path may not have needed functionality. |
| 4. Priority Radio Resource Queuing | When a Priority Service call encounters a "no radio available" condition in the call path involving an access or egress air-interface, or both, and, at call origination, and upon recognition of the Priority Service dialing pattern, the Priority Service call is queued in the cell serving the calling party and processed for the next available radio channel in that cell in accordance with the caller's priority level and call initiation time. at call termination upon recognition of a priority call indication in an incoming call, the Priority Service call is queued in the cell serving the called party and processed for the next available radio channel in that cell in accordance with the call's priority level and arrival time. | Supported | |
| 5. Priority Level | The subscriber should be assigned one of n priority levels. Priority levels are defined as 1, 2, 3,…,n , with 1 being the highest priority level and n being the lowest priority level. | Vendor specific | MMI used needs to be recognized by number analysis. |
| 6. Invocation on Demand | Priority Service is invoked only when requested and an idle voice or traffic channel required for an origination request is not available. | Vendor specific | MMI used needs to be recognized by number analysis. |
| 7. Applicability to Telecommunications Services | Priority Service shall be applicable to voice and data telecommunications services that require a voice or traffic channel assignment. | Supported | |
| 8. Authorization | A subscriber invoking Priority Service on call origination is authorized based on the caller's subscription. It should also be possible for an additional second level of authentication (e.g., by the use of PIN) to identify that the user is authorized to make a priority call. In this case, authorization of the subscriber may be realized by the usage of a PIN. | Vendor specific | MSC has various information from HLR like Subscriber category, IMSI, etc. that can be used to identify subscription. |
| 9. Priority Service service code | Priority Service is manually requested by adding on the Priority Service service code to the origination request. | Vendor specific | MMI used needs to be recognized by number analysis. |
| 10. Roaming | Priority Service shall be supported during roaming when the roaming network supports Priority Service. | Not supported / Vendor specific | |
| 11. Handover | Priority Service shall be supported during handover. | Supported | |
| 12. Priority Service charging data record | The system should record the following Priority Service charging data information, in addition to non-Priority Service CDR information: Priority Service invocation attempts, Call legs (origination and/or termination) on which Priority Service was used to gain access to the radio channel. Recording of appropriate Priority Service information. | Vendor specific | |
| 13. Priority Trunk Queuing | Priority Service shall be able to support queuing of Priority Service calls for trunk resources. | Not supported | |
| 14. Coexistence with eMLPP | As a service provider option, it shall be possible to offer Priority Service and eMLPP within the same network, but not to the same user. | Not supported |
7 Conclusions p. 29
The objectives of this Feasibility Study for Priority Service were to:
- outline the high-level technical requirements for Priority Service,
- identify existing 3GPP capabilities related to Priority Service,
- perform a gap analysis to determine the extent existing 3GPP specifications can support these Priority Services requirements.
- Priority Call Origination,
- Priority Call Termination,
- Priority Progression,
- Priority Radio Resource Queuing,
- Priority Level,
- Invocation on Demand,
- Applicability to Telecommunications Services,
- Authorization,
- Priority Service service code,
- Priority Service supported during roaming,
- Priority Service supported during handover,
- Priority Service charging data record,
- Priority Trunk Queuing,
- Coexistence with eMLPP.
- Service Accessibility,
- Enhanced Multi-Level Precedence and Pre-emption (eMLPP),
- Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) Specifications,
- Priority Information Element.
| High-level Requirement | Specification | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3G TS 22.011, Service Accessibility | 3G TS 22.067, TS 23.067, TS 24.067, eMLPP | 3G TS 11.11, SIM | 3G TS 08.08, TS 25.413, PIE | |
| R.1 - Priority Call Origination | ✓ (= Supported) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| R.2 - Priority Call Termination | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| R.3 - Priority Progression | NS (=Not Supported) | ✓ | NS | NS or VS (=vendor specific) |
| R.4 - Priority Radio Resource Queuing | NS | PS (= Partially Supported) | NS | ✓ |
| R.5 - Priority Level | PS | PS | PS | VS |
| R.6 - Invocation on Demand | NS | ✓ | PS | VS |
| R.7 - Applicability to Telecommunications Services | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| R.8 - Authorization | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | VS |
| R.9 - Priority Service service code | NS | PS | NS | VS |
| R.10 - Roaming | PS | ✓ | PS | NS/VS |
| R.11 - Handover | NS | PS | NS | ✓ |
| R.12 - Priority Service charging data record | NS | ✓ | NS | VS |
| R.13 - Priority Trunk Queuing | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| R.14 - Coexistence with eMLPP | NS | NS | NS | NS |
Based on the analysis in this Feasibility Study, most of the high-level requirements for Priority Service can be supported through the use of Access Control, eMLPP, A/Iu Priority element, and SIM-based capabilities. The "authorization by PIN" requirement could be supported by a handset-based solution and not a network-based solution.