Content for TS 22.368 Word version: 18.0.1
7 Service requirements
7.1 Common service requirements
7.2 Specific service requirements - MTC Features
7 Service requirements p. 11
7.1 Common service requirements p. 11
7.1.1 General p. 11
The following are MTC common service requirements:
- The network shall enable the network operator to identify per subscription which individual MTC Features are subscribed to by a particular MTC Subscriber.
- The network shall provide a mechanism for the MTC Subscriber to activate or deactivate MTC Features.
- The network shall enable the network operator to identify which individual MTC Features are activated for a particular MTC Subscriber.
- The network shall provide a mechanism for the network operator to control the addition or removal of individual MTC Features to a subscription (e.g. based on matching or mismatching of MTC Features).
- The network shall provide a mechanism for the network operator to restrict activation of MTC Features (e.g. based on matching or mismatching of MTC Features).
- The network may provide a mechanism for the network operator to allow MTC Devices to override restrictions imposed by a particular MTC Feature.
- The network operator shall be able to restrict the use of a USIM to specific MEs/MTC Devices.
- The network shall provide a mechanism to reduce peaks in the data and signalling traffic resulting from very large numbers of MTC Devices (almost) simultaneously attempting data and/or signalling interactions.
- The network shall provide a mechanism to restrict downlink data and signalling when the network is overloaded.
- The network shall provide a mechanism to restrict access towards a specific APN when the network is overloaded.
- A MTC Device may support the Extended Access Barring (EAB) mechanism defined in TS 22.011.
- A MTC Device supporting the EAB mechanism shall be able to be configured for EAB by the HPLMN.
- The HPLMN shall be able to configure EAB on a MTC Device that supports it.
- Once configured, and upon reception of broadcasted EAB information, the MTC Device shall adhere to the defined EAB mechanisms.
- The system shall provide mechanisms to efficiently maintain connectivity for a large number of MTC Devices.
- The network shall provide mechanisms to handle MTC Devices and applications on MTC Devices registering on the IP multimedia core network subsystem and accessing its capabilities including interaction with IMS application servers/enablers.
- Configuration parameters which are provided in the USIM shall take precedence over parameters provided in the MTC Device if both exist.
- The network shall allow a resource efficient registration of MTC Devices and applications on MTC Devices on the IP multimedia core network subsystem (e.g. no need of a permanently assigned ID per MTC Device).
- The system shall provide mechanisms to lower power consumption of MTC Devices.
- The system shall provide a resource efficient way to support MTC Devices that send or receive data infrequently, i.e. with long periods between data transmissions.
- MTC Devices may or may not be kept attached to the network when not communicating, depending on operator policies and MTC Application requirements.
- MTC Devices may keep their data connection or not keep their data connection when not communicating, depending on operator policies and MTC Application requirements.
7.1.2 MTC Device triggering |R11| p. 12
The requirements related to MTC Device triggering include the following:
- The network shall be able to trigger MTC Devices to initiate communication with the MTC Server based on a trigger indication from the MTC Server.
- The system shall provide a mechanism such that only trigger indications received from authorized MTC Servers will lead to triggering of MTC Devices.
- Upon receiving a trigger indication from a source that is not an authorized MTC Server, the network shall be able to provide the details of the source (e.g. address) to the MTC User.
- The system shall provide a mechanism to the MTC User to provide a set of authorized MTC Server(s).
- Upon receiving a trigger indication, if the network is not able to trigger the MTC Device, the 3GPP system may send an indication to the MTC Server that triggering the MTC Device has been suppressed.
-
A MTC Device shall be able to receive trigger indications from the network and shall establish communication with the MTC Server when receiving the trigger indication. Possible options may include:
- Receiving trigger indication when the MTC Device is not attached to the network.
- Receiving trigger indication when the MTC Device is attached to the network, but has no data connection established.
- Receiving trigger indication when the MTC Device is attached to the network and has a data connection established.
7.1.3 Addressing |R11| p. 12
The system shall provide mechanisms, according to operator policy, where an MTC Server can send a mobile terminated message to the MTC Device. Scenarios include:
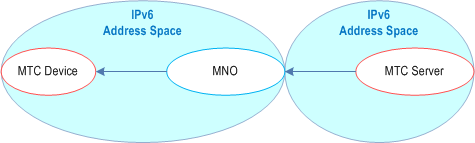
- The MTC Server is located in the public IPv6 address space. The MTC Device is assigned a public IPv6 address by the MNO.
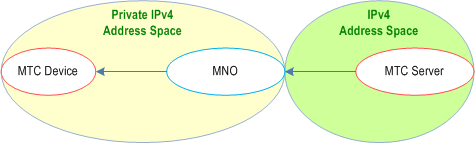
- The MTC Server is located in a public IPv4 address space; the MTC Device is assigned a private IPv4 address by the MNO.
7.1.4 Identifiers p. 13
The requirements for MTC related to identifiers include the following:
- The system shall be able to uniquely identify the ME;
- The system shall be able to uniquely identify the MTC Subscriber.
- In order to use MTC triggering, the system shall support association between an MTC Device identity and one or more Service Enablement Framework individually. Preconfiguration of the association is sufficient when the Service Enablement Framework knows the MTC Device identities in advance to the starting of the service, but this does not match all the relevant scenarios of service deployment.
- The system shall provide mechanisms for the network operator to efficiently manage numbers and identifiers related to MTC Subscribers.
7.1.5 Charging requirements p. 14
The core network shall be able to:
- count MTC Feature activation / de-activation.
- collect charging data with a granularity (e.g. in time or location) that can identify the use of network resources when used outside the limits of subscription or MTC Feature, e.g. time window, location, or can identify when the MTC Device is overriding other restrictions (e.g. low priority).
- count particular Monitoring events.
7.1.6 Security requirements p. 14
The security requirements for MTC include the following:
- MTC optimizations shall not degrade security compared to non-MTC communications
7.1.7 Remote MTC device management p. 14
The operator shall be able to manage MTC Devices using existing mechanisms (e.g. OMA DM)
7.2 Specific service requirements - MTC Features p. 14
7.2.1 Low Mobility |R12| p. 14
The MTC Feature Low Mobility is intended for use with MTC Devices that do not move, move infrequently, or move only within a certain region.
For the Low Mobility MTC Feature:
- The network operator shall be able to change the frequency of mobility management procedures or simplify mobility management per MTC Device.
- The network operator shall be able to define the frequency of location updates performed by the MTC Device.
7.2.2 Time Controlled |R14| p. 14
The MTC Feature Time Controlled is intended for use with MTC Applications that can tolerate to send or receive data only during defined time intervals and avoid unnecessary signalling outside these defined time intervals. The network operator may allow such MTC Applications to send/receive data and signalling outside of these defined time intervals but charge differently for such traffic.
For the Time Controlled MTC Feature:
- The network operator shall be able to reject access requests per MTC Device (e.g. attach to the network or set up a data connection) outside a defined access grant time interval.
- The network operator shall be able to allow access (e.g. attach to the network or set up a data connection) outside a defined access grant time interval and charge this differently.
- The network shall reject access requests per MTC Device (e.g. attach to the network or set up a data connection) during a defined forbidden time interval (e.g. to allow maintenance of a MTC Server).
- The local network shall be able to alter the access grant time interval based on local criteria (e.g. daily traffic load, time zones). The forbidden time interval shall not be altered.
- The network shall be able to restrict the duration of access by terminating access (e.g. detach or disconnect a data connection) after a defined access duration.
- The MTC Device may disconnect immediately when it finishes its communications with the MTC Server before wait until the end of the access duration.
- The network shall communicate the (altered) access grant time interval and the access duration to the MTC Device.
- The network may communicate the (altered) access grant time interval and the access duration to the MTC Server/MTC User.
7.2.3 Void
7.2.4 Void
7.2.5 Small Data Transmissions |R13| p. 15
The MTC Feature Small Data Transmissions is intended for use with MTC Devices that send or receive small amounts of data.
For the Small Data Transmissions MTC Feature:
- The system shall support transmissions of small amounts of data with minimal network impact (e.g. signalling overhead, network resources, delay for reallocation).
- Before transmission of small amount of data, the MTC Device may be attached or detached to/from the network.
- The 3GPP system shall be able to count the number of small data transmissions per subscription e.g. for charging or statistical purposes.
7.2.6 Void
7.2.7 Infrequent Mobile Terminated |R12| p. 16
The MTC Feature Infrequent Mobile Terminated is intended for use with MTC Devices that mainly utilize mobile originated communications.
For the Infrequent Mobile Terminated MTC Feature:
- The network operator shall be able to reduce the frequency of mobility management procedures per MTC Device.
- The network shall be able to maintain information on when the MTC Device is not reachable for mobile terminated communications. The network shall not trigger the MTC Device when it is known to be unreachable, and instead may inform the MTC Server that the MTC Device is not reachable.
7.2.8 MTC Monitoring |R13| p. 16
The MTC Feature MTC Monitoring is intended for monitoring MTC Device related events.
For the MTC Monitoring MTC Feature:
-
The system shall provide mechanisms to detect the following events:
- behaviour which is not aligned with activated MTC Feature(s)
- change of the association between the ME and the USIM
- loss of connectivity. The maximum time between the actual loss of connectivity occurred and the loss of connectivity detected shall be configurable per subscription.
- communication failure events of the UE visible to the network (e.g. for troubleshooting)
- change of the location (geographical position and/or point of attachment in the network) of the MTC Device.
- The MTC Subscriber shall be able to define which of the above events will be detected.
-
Upon the above event detection, the network shall be able to:
- provide a warning notification to the MTC Server;
- limit the services provided to the MTC Device (e.g. reduce allocated resource).
- The MTC User shall be able to define what occurs when an event is detected.
- The MTC Device shall be able to transfer other event notification to the MTC Server where the event detection is out of 3GPP scope, for example, the loss of signal reception, notification when the MTC Device power level is lower than a threshold.
7.2.9 Void
7.2.10 Secure Connection |R11| p. 17
The MTC Feature Secure Connection is intended for use with MTC Devices that require a secure connection between the MTC Device and MTC Server/MTC Application Server.
For the Secure Connection MTC Feature:
- The network operator shall be able to efficiently provide network security for connection between MTC Device and a MTC Server or between MTC Device and a MTC Application Server in case there is a direct connection with the MTC Application Server. This applies even when some of the devices are roaming i.e. connected via a VPLMN.
7.2.11 Void
7.2.12 Void
7.2.13 Void
7.2.14 Group Based MTC Features |R13| p. 17
7.2.14.1 General p. 17
A Group Based MTC Feature is a MTC Feature that applies to an MTC Group.
- The system shall be optimized to handle MTC Groups. The system shall provide a mechanism to associate an MTC Device to a single MTC Group.
- Each Group Based MTC Feature is applicable to all the members of the MTC Group.
- An MTC Group shall be identified uniquely across 3GPP networks.
7.2.14.2 Group Based Policing |R14| p. 17
The MTC Feature Group Based Policing is intended for use with a MTC Group for which the network operator wants to enforce a combined QoS policy.
For the Group Based Policing MTC Feature:
- A maximum bit rate for the data that is sent/received by a MTC Group shall be enforced.
7.2.14.3 Group Based Addressing p. 17
MTC Feature Group Based Addressing is intended for use with a MTC Group for which the network operator wants to optimize the message volume when many MTC Devices need to receive the same message.
For the Group Based Addressing MTC Feature:
- The network shall provide a mechanism to send a broadcast message within a particular geographic area, e.g. to wake up the MTC Devices that are members of that MTC Group; only MTC Devices of the target group configured to receive the broadcast message will recognize it.