Content for TS 33.180 Word version: 17.8.0
1…
4…
4.3.4
4.3.5
5…
5.1.3
5.1.4…
5.2…
5.2.3
5.2.4
5.2.5
5.2.6…
5.3…
5.4…
6…
7…
7.3…
8…
9…
9.4…
10…
A…
B…
C…
D…
E…
F…
J…
L…
5.1.3 MCX user service authorisation p. 30
5.1.3.1 General p. 30
This clause expands on the MCX user service authorization step shown in Figure 5.1.1-1 step C.
MCX User Service Authorization is the function that validates whether or not a MCX user has the authority to access certain MCX services. In order to gain access to MCX services, the MCX client in the UE presents an access token (acquired during user authentication as described in subclause 5.1.2) to each service of interest (i.e. Key Management, MCX server, Configuration Management, Group Management, etc.). If the access token is valid, then the user is granted the use of that service. Figure 5.1.3.1-1 shows the flow for user authorization which covers key management authorization, MCX user service authorization, configuration management authorization, and group management authorization.
For key management authorization, the KM client in the UE presents an access token to the KMS over HTTP. The access token shall be scoped for key management services as defined in Annex B.4.2.2. The KMS validates the access token and if successful, provides one or more sets of user specific key material back to the UE KM client based on the MC service ID(s) present in the access token (MCPTT ID, MCVideo ID and/or MCData ID). User specific key material includes identity based key information for media and signalling protection. If an interworking key management record (InterKMRec) exists and is associated to the requesting MC service ID (see clause 11.2.3), the KMS shall also provide the InterKMRec. This key management authorisation may be repeated for each KM service the user is authorised to use (MCPTT, MCVideo, MCData). In order to secure the transfer of user specific key material from the KMS to the KM client when using the TrK and InK, the KM client includes the TrK-ID and the InK-ID in the key management authorization request.
For MCPTT user service authorization, the MCPTT client in the UE presents an access token to the MCPTT server over SIP. The access token shall be scoped for MCPTT services as defined in Annex B.4.2.2. The MCPTT server validates the access token and if successful, authorizes the user for full MCPTT services and sends an acknowledgement back to the MCPTT client. The MCPTT server then maps and maintains the IMPU to MCPTT ID association. The MCPTT ID to IMPU association shall only be known to the application layer. The SIP message used to convey the access token from the MCPTT client to the MCPTT server may be either a SIP REGISTER or SIP PUBLISH message.
For MCVideo service authorization, the MCVideo client in the UE presents an access token to the MCVideo server over SIP. The access token shall be scoped for MCVideo services as defined in Annex B.4.2.2. The MCVideo server validates the access token and if successful, authorizes the user for full MCVideo services and sends an acknowledgement back to the MCVideo client. The MCVideo server then maps and maintains the IMPU to MCVideo ID association. The MCVideo ID to IMPU association shall only be known to the application layer. The SIP message used to convey the access token from the MCVideo client to the MCVideo server may be either a SIP REGISTER or SIP PUBLISH message.
For MCData user service authorization, the MCData client in the UE presents an access token to the MCData server over SIP. The access token shall be scoped for MCData services as defined in Annex B.4.2.2. The MCData server validates the access token and if successful, authorizes the user for full MCData services and sends an acknowledgement back to the MCData client. The MCData server then maps and maintains the IMPU to MCData ID association. The MCData ID to IMPU association shall only be known to the application layer. The SIP message used to convey the access token from the MCData client to the MCData server may be either a SIP REGISTER or SIP PUBLISH message.
The UE can now perform configuration management authorization and download the user profile for the service(s) (MCPTT, MCVideo, MCData). Following the flow described in subclause 10.1.4.3 of TS 23.280 "MC service user obtains the MC service user profile(s) from the network", the Configuration Management (CM) client in the UE sends an access token in the user profile query to the Configuration Management server over HTTP. The access token shall be scoped for configuration management services as defined in Annex B.4.2.2. The CM server receives the request and validates the access token, and if valid, the CM server uses the identity from the access token (MCPTT ID, MCVideo ID, MCData ID) to obtain the user profile from the MCX user database. The CM server then sends the user profile back to the CM client over HTTP. This configuration management authorisation may be repeated for each CM service the user is authorised to use (MCPTT, MCVideo, MCData).
Upon receiving each user profile, the Group Management (GM) client in the UE can now perform group management authorization. The GM client obtains the user's group membership information from the user profile, and following the flow shown in clause 10.1.5.2 of TS 23.280 "Retrieve group configurations at the group management client", the Group Management (GM) client in the UE sends an access token in the Get group configuration request to the host GM server of the group membership over HTTP. The access token shall be scoped for group management services as defined in Annex B.4.2.2. The GM server validates the access token, and if valid, completes the flow. As part of group management authorization, group key information is provided as per subclause 5.7 of the present document. This group management authorisation may be repeated for each GM service the user is authorised to use (MCPTT, MCVideo, MCData).
For MC UEs that support mission critical location services, authorization is accomplished by including an access token in each location message (i.e. location information report, location reporting trigger, etc.) sent by the location management client to the location management server. The access token shall be scoped for location management services as defined in Annex B.4.2.2. The location management server validates the access token and (if successful) processes the message (e.g. accepts and stores the location information report). If an access token cannot be validated, local policy may dictate an action to be taken within the location management server with regards to the received location message (e.g. the local policy may require storage of the location information report as an emergency provision).
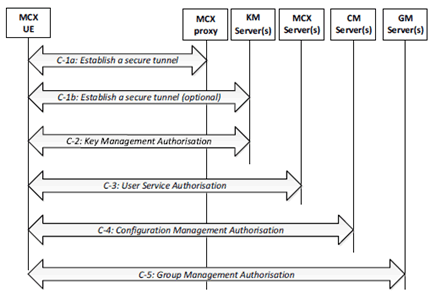
The user authorization procedure in Step C of Figure 5.1.1-1 is further detailed into 5 sub steps that comprise the MCX user service authorization process:
Step C-1a.
If not already done, establish a secure HTTP tunnel using HTTPS between the MCX UE and MCX proxy server. Subsequent HTTP messaging makes use of this tunnel .
Step C-1b.
When required by the MCX system, establish a secure HTTP tunnel using HTTPS between the MCX KM client and the KMS. When supported, subsequent HTTP messaging between the MCX KM client and the KMS makes use of this tunnel in lieu of the tunnel set up in Step C-1a.
Step C-2.
The KM client in the MCX UE presents an access token to the KMS over HTTP. The KMS authorizes the user for key management services based upon the MC service ID(s) provided and replies to the client with identity specific key information. This step may be repeated to authorise the user with additional KM services (MCPTT, MCVideo, MCData) as necessary.
Step C-3.
The MCX client in the UE presents an access token to the MCX server over SIP as defined in clause 5.1.3.2 of the present document. This step may be repeated to authorise the user with additional MCX services (MCPTT, MCVideo, MCData) as necessary.
Step C-4.
The CM client in the UE follows the "MCX user obtains the user profile (UE initiated)" flow from clause 10.1.4.3 of TS 23.280, presenting an access token in the Get MCX user profile request over HTTP. If the token is valid, then the CM server authorizes the user for configuration management services. Completion of this step results in the CM server providing the user's profile to the CM client. This step may be repeated as necessary to obtain the user profile for additional services (MCPTT, MCVideo, or MCData).
Step C-5.
The GM client in the UE follows the "Retrieve group configurations at the group management client" flow as shown in clause 10.1.5.2 of TS 23.280, presenting an access token in the Get group configuration request over HTTP. If the token is valid, the GMS authorizes the user for group management services. Completion of this step results in the GMS sending the user's group policy information and group key information to the GM client. This step may be repeated to authorise the user for additional group services (MCPTT, MCVideo, MCData) as necessary.
5.1.3.2 MCX user service authorization with MCX Server p. 33
5.1.3.2.1 General p. 33
Depending on implementation, MCX user service authorization may be performed by sending the access token to the MCX server over the SIP-1 and SIP-2 reference points using either a SIP REGISTER message or a SIP PUBLISH message. Clause 5.1.3.2.2 describes how to use the SIP REGISTER message to transport the access token to the MCX server and clause 5.1.3.2.3 describes how to use the SIP PUBLISH message to transport the access token to the MCX server.
During initial SIP registration, the SIP REGISTER message shall not be delayed for lack of an access token. If an access token is not available then SIP registration shall proceed without the inclusion of the access token and the access token shall be transmitted to the MCX server as per Step C-3 in Figure 5.1.3.1-1.
If an access token is available before SIP registration, or if the UE becomes de-registered and a SIP re-registration is required, the SIP REGISTER message may include the access token without requiring the user to re-authenticate.
The access token may be sent over SIP to the MCX server to re-bind an IMPU and MC service ID (MCPTT ID, MCVideo ID or MCData ID) if either have changed (e.g. IMPU is different due to SIP deregistration/SIP re-registration, or user logs out and another user logs onto the same UE).
5.1.3.2.2 Using SIP REGISTER p. 33
The use of a SIP REGISTER message to provide the access token to the MCX server is shown in Figure 5.1.3.2.2-1. The inclusion of an access token in any particular SIP REGISTER message is optional.
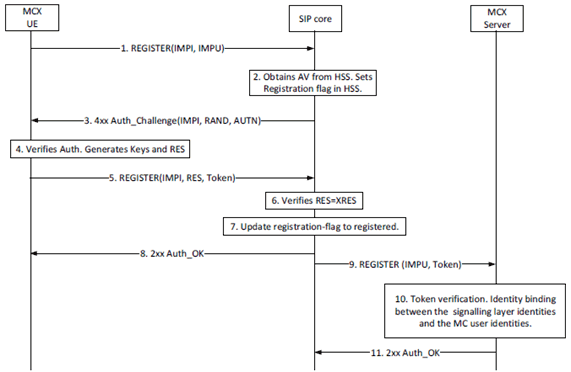
Figure 5.1.3.2.2-1: MCX User Service Authorization using SIP REGISTER message
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 5 of Figure 5.1.3.2.2-1 shows the access token message passed to the SIP core in a SIP REGISTER. Upon successful SIP authentication, the SIP core forwards the access token to the MCX server in the third part registration request message (Step 9).
In Steps 9 through 11, the MCX server receives the third part registration request message, validates the access token, binds the IMPU and MC service ID (MCPTT ID, MCVideo ID or MCData ID) if the access token is valid, and responds to the 3rd party registration message.
5.1.3.2.3 Using SIP PUBLISH p. 34
The use of a SIP PUBLISH message to provide the access token to the MCX server is shown in Figure 5.1.3.2.3-1. The inclusion of an access token in any particular SIP PUBLISH message is optional.
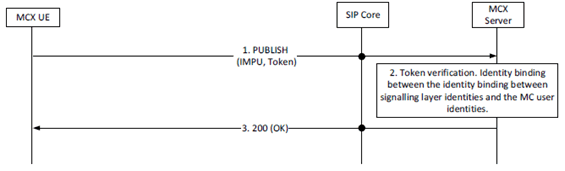
Figure 5.1.3.2.3-1: MCX User Service Authorization using SIP PUBLISH message
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
As shown in Step 1 of Figure 5.1.3.2.3-1, the SIP PUBLISH message carries the access token through the SIP core to the MCX server.
In Steps 2 and 3, the MCX server receives the SIP PUBLISH message, validates the access token, binds the IMPU and MC service ID (MCPTT ID, MCVideo ID or MCData ID) if the access token is valid, and responds to the SIP PUBLISH message.