Content for TS 23.228 Word version: 18.5.0
1…
3…
4…
4.2.4…
4.3…
4.4…
4.13…
4.16…
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.4…
5.4.7…
5.4.8…
5.4a…
5.5…
5.5.3…
5.6…
5.6.3…
5.7…
5.7.3…
5.7.5…
5.7.8…
5.8…
5.10…
5.11…
5.11.3…
5.11.3.3
5.11.3.4
5.11.4…
5.11.5…
5.11.5.3…
5.11.6…
5.12…
5.16…
5.16.2…
5.19…
5.20…
A…
E…
E.2.2…
G…
G.5…
H
I…
J…
K…
L…
M…
M.3…
N…
P…
Q…
Q.2.5…
R…
S…
T…
U…
U.2…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
AA…
AA.3…
AB…
AC…
AC.7…
AC.7.2…
AC.7.2.2
AC.7.2.3…
AC.7.4…
AC.9…
AC.7.2 Application Data Channel Setup Signalling Procedure
AC.7.2.1 Person to Person (P2P) Application Data Channel Setup
...
...
AC.7.2 Application Data Channel Setup Signalling Procedure p. 375
AC.7.2.1 Person to Person (P2P) Application Data Channel Setup p. 375
Figure AC.7.2.1-1 depicts a signalling flow diagram for establishing an application data channel in a person-to-person use case. In this scenario, the MF is not used to anchor the Application data channel.
In the call flow the UEs have already established an IMS audio session, and the originating UE is updating the IMS audio/video session to an IMS data channel session.
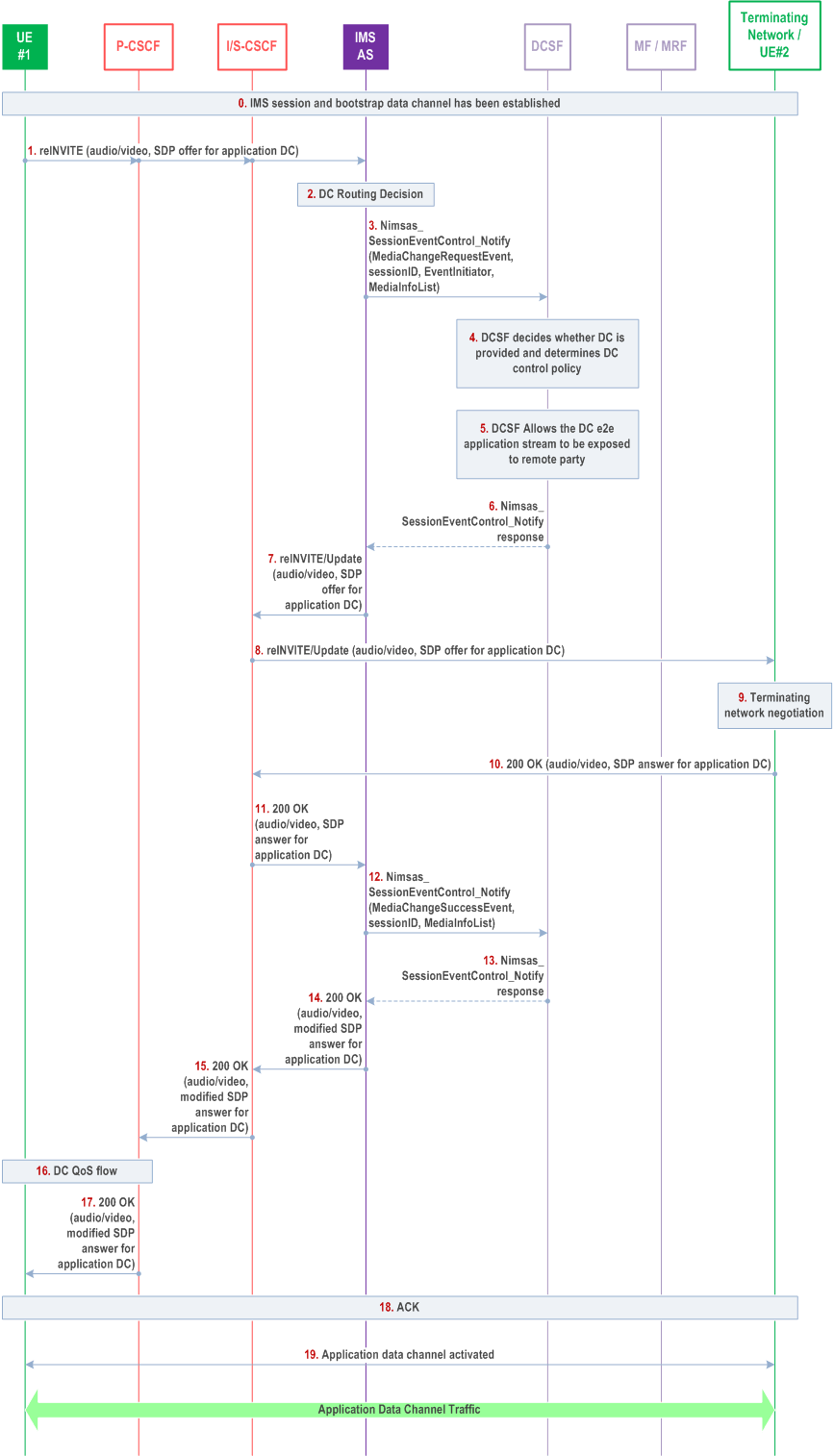
The steps in the call flow are as follows:
Step 0.
IMS session and bootstrap data channel have been established. Selected data channel application(s) have been downloaded to UE#1 and possibly UE#2.
Step 1.
UE#1 sends the SIP reINVITE request with an updated SDP to IMS AS, through originating network P-CSCF and S-CSCF. The updated SDP contains the bootstrap data channel information, as well as the requested application data channel and the associated DC application binding information, according to TS 26.114.
Step 2.
The IMS AS validates user subscription data to determine whether the media change request event should be notified to the DCSF.
Step 3.
The IMS AS notifies the DCSF, via Nimsas_SessionEventControl_Notify (MediaChangeRequest Event, Session ID, Event Direction, Event initiator, Media Info List) of the media change request event.
Step 4.
After receiving the session event notification, the DCSF determines the policy about how to process the application data channel establishment request based on the related parameters (i.e. associated DC application binding information) in the notification and/or DCSF service specific policy.
Step 5.
The DCSF determines that the added application data channel media descriptor of the SDP offer takes UE#2 as target endpoint and does not require anchoring on the local MF or MRF. If MF or MRF needs to anchor application data channel, DCSF would have used the Nimsas_MediaControl service operation to instruct IMS AS to allocate data channel media resources of the MF or MRF.
Step 6.
DCSF responds to the notification received in step 3.
Step 7-8.
IMS AS sends the re-INVITE to the originating S-CSCF and then to the terminating network side and UE#2.
Step 9-11.
UE#2 and terminating network returns a 200 OK response with SDP answer for application data channel to originating network. Based on the received DC application binding information in the SDP offer of the re-INVITE, UE#2 may need to download the corresponding DC Application signalled in the SDP offer, if not done already and associate it with the requested application DC.
Step 12.
IMS AS notifies the DCSF of the successful data channel modification.
Step 13.
DCSF responds to the notification received in step 12.
Step 14-15.
The IMS AS sends 200 OK response to the originating S-CSCF and P-CSCF.
Step 16.
The originating network P-CSCF executes QoS procedure for application data channel media based on the SDP answer information from the 200 OK response.
Step 17.
P-CSCF returns the 200 OK response to UE#1.
Step 18.
UE#1 sends ACK to the terminating network.
Step 19.
The application data channel between UE#1 and UE#2 is established. In this example, it is not anchored in MF/ MRF.