Content for TR 22.865 Word version: 19.2.0
5.6 Use case on Information Exchange between Ships at sea
5.6.1 Description
5.6.2 Pre-conditions
5.6.3 Service Flows
5.6.4 Post-conditions
5.6.5 Existing features partly or fully covering the use case functionality
5.6.6 Potential New Requirements needed to support the use case
...
...
5.6 Use case on Information Exchange between Ships at sea p. 19
5.6.1 Description p. 19
Information exchange in the maritime industry is very important [10] [11]. Information exchange allows for better coordination between ships, which is required regardless of the purpose for which ships are sailing. An effective information exchange system can better coordinate the ships and improve the safety of ships, such as resisting pirate attacks, avoiding accidents at sea, and rescuing.
At sea far from land, there is no terrestrial communication system. Ships can communicate directly with each other at short distance through various types of wireless technologies. At long distances, information can only be exchanged through satellites and then through remote data centres, which affects communication efficiency, especially in emergency situations. In addition, in some areas, the satellite has no available feeder link, which causes the communication interruption even though the communicating ships camp on the same satellite. In this scenario, communication between ships through satellites without going via remote data centres can improve communication efficiency and reduce losses caused by potential maritime accidents.
Satellite broadband can be suited to connecting remote areas which do not have reliable mobile or fixed broadband. There are new broadband satellites systems being developed, which use many satellites in a non-geostationary satellite orbit (NGSO) closer to the Earth than earlier satellites. Typically, the beam footprint size of Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites and Medium-Earth Orbit (MEO) satellites is in the range of 100 - 1000 km [12].
5.6.2 Pre-conditions p. 19
MinosShipping, the shipping company, has many ships operating all over the world. MinosShipping signs a contract with Delphi, an operator with satellite communication services. Delphi has deployed NGSO satellites, which allows communication between ships via satellite without going through the ground network, that is, devices on a ship can communicate directly with devices on another ship via satellite.
5.6.3 Service Flows p. 20
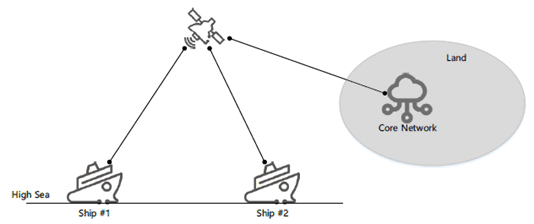
Figure 5.6.3-1: communication via the same satellite without going through the ground network
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
1.
Device A on ship #1 register with the 5G network via satellite, and device B on ship #2 (small) also register with the 5G network via satellite. The devices A and B can communicate with each other via the 5G network.
2.
When the ship #1 and the ship #2 are under the same satellite coverage, the devices A and B want to communicate with each other. The remote core network authorizes the communication between the devices A and B based on e.g., subscription, and location information. After getting authorized, the data traffic between the devices A and B is routed through the same satellite. During the data traffic communication between devices A and B without going through the ground network, if the feeder link becomes unavailable, device A still can have the communication with device B.
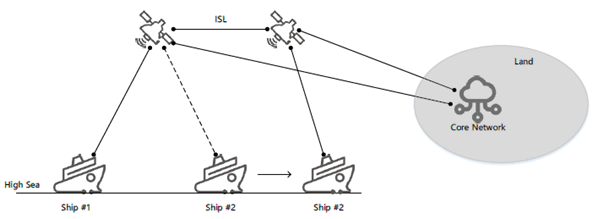
Figure 5.6.3-2: communication via satellites with ISL without going through the ground network
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
3.
Along the long journey, ship #1 and ship #2 move across the coverage of different satellites, i.e. ship #2 moves to the coverage of satellite #2 while ship #1 remains in the coverage of satellite #1. Inter satellite link is available between satellite #1 and satellite #2.
4.
During the journey, the communication between devices A and B via satellite(s) continues without interruption.
5.
The charging information of the traffic data exchanged via the satellites is collected in the satellites and reported to the remote core network.
5.6.4 Post-conditions p. 20
The ship #1 and the ship #2 can exchange information efficiently without data traffic transferred via the remote core network.
5.6.5 Existing features partly or fully covering the use case functionality p. 20
None.
5.6.6 Potential New Requirements needed to support the use case p. 21
[PR 5.6.6-001]
The 5G system shall support mechanisms to authorize the communication between UEs using satellite access (without going through the ground network) based on e.g., location information and subscription.
[PR 5.6.6-002]
The 5G system shall support mechanisms to collect charging information for the traffic data exchanged using satellite access without going through the ground network.
[PR 5.6.6-003]
Subject to regulatory requirements and operator's policy, the 5G system shall support communication between UEs using satellite access without going through the ground network.
[PR 5.6.6-004]
Subject to regulatory requirements and operator's policy, the 5G system shall maintain service continuity with minimum service interruption of the communication between UEs using satellite access without going through the ground network when a UE changes from the coverage of one satellite to another (due to the movement of the UE and/or the satellites).
[PR 5.6.6-005]
Subject to regulatory requirements and operator's policy, the 5G system with satellite access shall be able to support UE-Satellite-UE communication when the feeder link is temporarily unavailable.