TS 38.412
NG-RAN — NG interface –
Signalling Transport
V17.1.0 (PDF)
2023/06 10 p.
V16.2.0
2023/06 10 p.
V15.5.0
2020/09 10 p.
- Rapporteur:
- Mr. Min, Tianyang
NTT DOCOMO INC.
Content for TS 38.412 Word version: 17.1.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions and abbreviations
4 NG signalling bearer
5 Data link layer
6 IP layer
7 Transport layer
$ Change history
1 Scope p. 5
The present document specifies the standards for signalling transport to be used across NG interface. NG interface is a logical interface between the NG-RAN and the 5GC. The present document describes how the NGAP signalling messages are transported over NG.
2 References p. 5
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
RFC 4960: "Stream Control Transmission Protocol".
[3]
TS 23.501: "System Architecture for the 5G System".
[4]
TS 23.502: "Procedures for the 5G System".
[5]
RFC 8200: (2017-07) "Internet Protocol, Version 6 (IPv6) Specification".
[6]
RFC 791: (1981-09) "Internet Protocol".
[7]
RFC 2474: (1998-12) "Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field) in the IPv4 and IPv6 Headers".
[8]
RFC 6083: (2011-01) "Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) for Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP)".
[9]
RFC 6335: (2011-08) "Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) Procedures for the Management of the Service Name and Transport Protocol Port Number Registry".
3 Definitions and abbreviations p. 5
3.1 Definitions p. 5
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
NG:
interface between a NG-RAN node and a 5GC, providing an interconnection point between the NG-RAN and the 5GC.
NG-C:
Reference point for the control plane protocol between NG-RAN and AMF.
SCTP endpoint:
as defined in IETF RFC 4960
SCTP association:
as defined in IETF RFC 4960
3.2 Abbreviations p. 6
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
5GC
5G Core Network
IP
Internet Protocol
SCTP
Stream Control Transmission Protocol
DiffServ
Differentiated Service
PPP
Point to Point Protocol
IANA
Internet Assigned Number Authority
AMF
Access and Mobility management Function
4 NG signalling bearer p. 6
4.1 Functions and protocol stack p. 6
NG-C signalling bearer provides the following functions:
- Provision of reliable transfer of NGAP message over NG-C interface.
- Provision of networking and routeing function.
- Provision of redundancy in the signalling network.
- Support for flow control and congestion control.
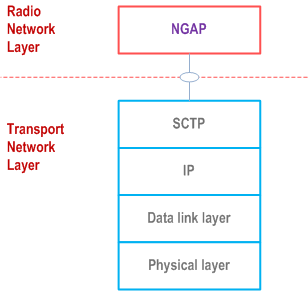
The Transport Network Layer is based on IP transport, comprising SCTP on top of IP.
5 Data link layer p. 6
The support of any suitable Data Link Layer protocol, e.g. PPP, Ethernet, etc., shall not be prevented.
6 IP layer p. 7
The 5GC and NG-RAN shall support IPv6 (IETF RFC 8200) and/or IPv4 (IETF RFC 791).
The IP layer of NG-C only supports point-to-point transmission for delivering NG AP message.
The 5GC and NG-RAN shall support the Diffserv Code Point marking as described in IETF RFC 2474.
7 Transport layer p. 7
SCTP (RFC 4960) shall be supported as the transport layer of NG-C signalling bearer. The Payload Protocol Identifier (ppid) assigned by IANA to be used by SCTP for the application layer protocol NGAP is 60, and 66 for DTLS over SCTP (RFC 6083). The byte order of the ppid shall be big-endian.
SCTP refers to the Stream Control Transmission Protocol developed by the Sigtran working group of the IETF for the purpose of transporting various signalling protocols over IP network.
NG-RAN node and AMF shall support a configuration with a single SCTP association per NG-RAN node/AMF pair. Configurations with multiple SCTP endpoints per NG-RAN node/AMF pair should be supported. When configurations with multiple SCTP associations are supported, the AMF may request to dynamically add/remove SCTP associations between the NG-RAN node/AMF pair. Within the set of SCTP associations established between one AMF and NG-RAN node pair, the AMF may request the NG-RAN node to restrict the usage of SCTP association for certain types of NG-C signalling. If no restriction information is provided for an SCTP association, any type of NG-C signalling is allowed via the SCTP association. Selection of the SCTP association by the NG-RAN node and the AMF is specified in TS 23.501 and TS 23.502. The NG-RAN node shall establish the SCTP association. The SCTP Destination Port number value assigned by IANA to be used for NGAP is 38412. When the AMF requests to dynamically add additional SCTP associations between the NG-RAN node/AMF pair, the SCTP Destination Port number value may be 38412, or any dynamic port value (RFC 6335). When the configuration with multiple SCTP endpoints per NG-RAN node is supported and the NG-RAN node wants to add additional SCTP endpoints, the RAN configuration update procedure shall be the first NGAP procedure triggered on an additional TNLA of an already setup NG-C interface instance after the TNL association has become operational, and the AMF shall associate the TNLA to the NG-C interface instance using the included Global RAN node ID.
Between one AMF and NG-RAN node pair:
- A single pair of stream identifiers shall be reserved over at least one SCTP association for the sole use of NGAP elementary procedures that utilize non UE-associated signalling.
- At least one pair of stream identifiers over one or several SCTP associations shall be reserved for the sole use of NGAP elementary procedures that utilize UE-associated signallings. However, a few pairs (i.e. more than one) should be reserved.
- For a single UE-associated signalling, the NG-RAN node shall use one SCTP association and one SCTP stream, and the SCTP association/stream should not be changed during the communication of the UE-associated signalling until after current SCTP association is failed or removed, or TNL binding update is performed as described in TS 23.502.