Content for TS 37.104 Word version: 18.0.0
1 Scope p. 8
The present document establishes the minimum RF characteristics of NR, E-UTRA, UTRA, GSM/EDGE and NB-IoT Multi-Standard Radio (MSR) Base Station (BS). Requirements for multi-RAT and single-RAT operation of MSR BS are covered in the present document. The requirements in the present document for E-UTRA, UTRA and NB-IoT single-RAT operation of MSR BS are also applicable to E-UTRA, UTRA and NB-IoT multi-carrier capable single-RAT BS. Requirements for GSM BS that are only single-RAT capable in all supported operating bands are not covered.
2 References p. 8
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 25.104: Technical Specification, "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Base Station (BS) radio transmission and reception (FDD)"
[3]
TS 25.105: Technical Specification, "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Base Station (BS) radio transmission and reception (TDD)"
[4]
TS 36.104: Technical Specification, "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Base Station (BS) radio transmission and reception"
[5]
TS 45.005: Technical Specification, "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group GSM/EDGE Radio Access Network; Radio transmission and reception"
[6]
ITU-R Recommendation SM.329-10: "Unwanted emissions in the spurious domain".
[7]
TR 25.942: "Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Networks; Radio Frequency (RF) system scenarios"
[8]
"Title 47 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR)": Federal Communications Commission.
[9]
ITU-R Recommendation M.1545: "Measurement uncertainty as it applies to test limits for the terrestrial component of International Mobile Telecommunications-2000".
[10]
TS 37.141: Technical Specification, "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; NR, E-UTRA, UTRA and GSM/EDGE; Multi-Standard Radio (MSR) Base Station (BS) conformance testing"
[11]
IEC 60721-3-3: "Classification of environmental conditions - Part 3-3: Classification of groups of environmental parameters and their severities - Stationary use at weather protected locations".
[12]
IEC 60721-3-4: "Classification of environmental conditions - Part 3: Classification of groups of environmental parameters and their severities - Section 4: Stationary use at non-weather protected locations".
[13]
ETSI EN 300 019-1-3: European Standard (Telecommunications series), "Environmental Engineering (EE); Environmental conditions and environmental tests for telecommunications equipment; Part 1-3: Classification of environmental conditions; Stationary use at weather protected locations"
[14]
ETSI EN 300 019-1-4: European Standard (Telecommunications series), "Environmental Engineering (EE); Environmental conditions and environmental tests for telecommunications equipment; Part 1-4: Classification of environmental conditions; Stationary use at non-weather protected locations".
[15]
CEPT ECC Decision (13)03: "The harmonised use of the frequency band 1452-1492 MHz for Mobile/Fixed Communications Networks Supplemental Downlink (MFCN SDL)".
[16]
CEPT ECC Decision (17)06: "The harmonised use of the frequency bands 1427-1452 MHz and 1492-1518 MHz for Mobile/Fixed Communications Networks Supplemental Downlink (MFCN SDL)".
[17]
TS 38.104: Technical Specification, "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; NR; Base Station (BS) radio transmission and reception".
[18]
TS 36.101: "Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); User Equipment (UE) radio transmission and reception".
[19]
TS 38.101-1: "NR; User Equipment (UE) radio transmission and reception; Part 1: Range 1 Standalone"
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations p. 9
3.1 Definitions p. 9
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
Band category:
group of operating bands for which the same MSR scenarios apply
Base Station RF Bandwidth:
bandwidth in which a base station transmits and/or receives single or multiple carrier(s) and/or RATs simultaneously within a supported operating band
Base Station RF Bandwidth edge:
frequency of one of the edges of the Base Station RF Bandwidth
Carrier:
modulated waveform conveying the NR, E-UTRA, UTRA or GSM/EDGE physical channels
Carrier aggregation:
aggregation of two or more NR or E-UTRA component carriers in order to support wider transmission bandwidths
Carrier aggregation band:
set of one or more operating bands across which multiple E-UTRA carriers are aggregated with a specific set of technical requirements.
Channel bandwidth:
RF bandwidth supporting a single NR, E-UTRA, UTRA or GSM/EDGE RF carrier with the transmission bandwidth configured in the uplink or downlink of a cell.
Contiguous carriers:
set of two or more carriers configured in a spectrum block where there are no RF requirements based on co-existence for un-coordinated operation within the spectrum block.
Carrier power:
power at the antenna connector in the channel bandwidth of the carrier averaged over at least one subframe for NR or E-UTRA, at least one slot for UTRA and the useful part of the burst for GSM/EDGE.
Configured carrier power:
target maximum power for a specific carrier for the operating mode set in the base station
Contiguous spectrum:
spectrum consisting of a contiguous block of spectrum with no sub-block gap(s).
Downlink operating band:
part of the operating band designated for downlink.
Highest Carrier:
carrier with the highest carrier centre frequency transmitted/received in the specified operating band(s).
Inter RF Bandwidth gap:
frequency gap between two consecutive Base Station RF Bandwidths that are placed within two supported operating bands.
Inter-band carrier aggregation:
carrier aggregation of NR or E-UTRA component carriers in different operating bands.
Inter-band gap:
The frequency gap between two supported consecutive operating bands.
Intra-band contiguous carrier aggregation:
contiguous NR or E-UTRA carriers aggregated in the same operating band.
Intra-band non-contiguous carrier aggregation:
non-contiguous NR or E-UTRA carriers aggregated in the same operating band.
Lowest Carrier:
carrier with the lowest carrier centre frequency transmitted/received in the specified operating band(s).
Lower Base Station RF Bandwidth edge:
frequency of the lower edge of the Base Station RF bandwidth, used as a frequency reference point for transmitter and receiver requirements.
Lower sub-block edge:
frequency at the lower edge of one sub-block.
Maximum Base Station RF Bandwidth:
maximum RF bandwidth supported by a BS within each supported operating band.
Maximum carrier output power:
carrier power available at the antenna connector for a specified reference condition.
Maximum RAT output power:
sum of the power of all carriers of the same RAT available at the antenna connector for a specified reference condition.
Maximum throughput:
maximum achievable throughput for a reference measurement channel.
Maximum total output power:
sum of the power of all carriers available at the antenna connector for a specified reference condition.
MB-MSR Base Station:
MSR Base Station characterized by the ability of its transmitter and/or receiver to process two or more carriers in common active RF components simultaneously, where at least one carrier is configured at a different operating band (which is not a sub-band or superseding-band of another supported operating band) than the other carrier(s).
Measurement bandwidth:
RF bandwidth in which an emission level is specified.
MSR Base station:
base station characterized by the ability of its receiver and transmitter to process two or more carriers in common active RF components simultaneously in a declared Base Station RF Bandwidth, where at least one carrier is of a different RAT than the other carrier(s).
Multi-band transmitter:
transmitter characterized by the ability to process two or more carriers in common active RF components simultaneously, where at least one carrier is configured at a different operating band (which is not a sub-band or superseding-band of another supported operating band) than the other carrier(s).
Multi-band receiver:
receiver characterized by the ability to process two or more carriers in common active RF components simultaneously, where at least one carrier is configured at a different operating band (which is not a sub-band or superseding-band of another supported operating band) than the other carrier(s).
Non-contiguous spectrum:
spectrum consisting of two or more sub-blocks separated by sub-block gap(s).
NB-IoT In-band operation:
NB-IoT is operating in-band when it utilizes the resource block(s) within a normal E-UTRA carrier.
NB-IoT guard band operation:
NB-IoT is operating in guard band when it utilizes the unused resource block(s) within a E-UTRA carrier's guard-band.
NB-IoT standalone operation:
NB-IoT is operating standalone when it utilizes its own spectrum, for example the spectrum currently being used by GERAN systems as a replacement of one or more GSM carriers, as well as scattered spectrum for potential IoT deployment.
NB-IoT operation in NR in-band:
NB-IoT is operating in-band when it is located within a NR transmission bandwidth configuration plus 15 kHz at each edge but not within the NR minimum guard band GBChannel.
NB-IoT operation in NR guard band:
NB-IoT is operating in guard band when it is located within a NR BS channel bandwidth but is not NB-IoT operation in NR in-band.
Occupied bandwidth:
width of a frequency band such that, below the lower and above the upper frequency limits, the mean powers emitted are each equal to a specified percentage β/2 of the total mean power of a given emission.
Operating band:
frequency range in which NR, E-UTRA, UTRA or GSM/EDGE operates (paired or unpaired), that is defined with a specific set of technical requirements.
Radio Bandwidth:
frequency difference between the upper edge of the highest used carrier and the lower edge of the lowest used carrier.
Rated total output power:
The total power level that the manufacturer has declared to be available at the antenna connector.
RRC filtered mean power:
The mean power of a UTRA carrier as measured through a root raised cosine filter with roll-off factor α and a bandwidth equal to the chip rate of the radio access mode.
Single-RAT operation:
operation of a base station in an operating band with only one RAT configured in that operating band.
Sub-band:
A sub-band of an operating band contains a part of the uplink and downlink frequency range of the operating band.
Sub-block:
one contiguous allocated block of spectrum for use by the same base station.
Sub-block bandwidth:
RF bandwidth of one sub-block.
Sub-block gap:
frequency gap between two consecutive sub-blocks within a Base Station RF Bandwidth, where the RF requirements in the gap are based on co-existence for un-coordinated operation.
Superseding-band:
A superseding-band of an operating band includes the whole of the uplink and downlink frequency range of the operating band.
Synchronized operation:
operation of TDD in two different systems, where no simultaneous uplink and downlink occur.
Throughput:
number of payload bits successfully received per second for a reference measurement channel in a specified reference condition.
Transmission bandwidth:
RF bandwidth of an instantaneous E-UTRA or NR transmission from a UE or BS, measured in resource block units.
Transmitter ON period:
time period during which the BS transmitter is transmitting data and/or reference symbols
Transmitter OFF period:
time period during which the BS transmitter is not allowed to transmit
Transmitter transient period:
time period during which the transmitter is changing from the OFF period to the ON period or vice versa
Unsynchronized operation:
operation of TDD in two different systems, where the conditions for synchronized operation are not met.
Uplink operating band:
part of the operating band designated for uplink.
Upper Base Station RF Bandwidth edge:
frequency of the upper edge of the Base Station RF Bandwidth, used as a frequency reference point for transmitter and receiver requirements
Upper sub-block edge:
frequency at the upper edge of one sub-block.
3.2 Symbols p. 12
For the purposes of the present document, the following symbols apply:
β
Percentage of the mean transmitted power emitted outside the occupied bandwidth on the assigned channel
BWChannel
Channel bandwidth (for E-UTRA and NR)
BWConfig
Transmission bandwidth configuration (for E-UTRA), where BWConfig = NRB x 180 kHz in the uplink and BWConfig = 15 kHz + NRB x 180 kHz in the downlink. Transmission bandwidth configuration (for NR), where BWConfig = NRB x SCS x 12.
BWRF
Base Station RF Bandwidth, where BWRF = FBW RF,high - FBW RF,low
BWRF,max
Maximum Base Station RF Bandwidth
DwPTS
Downlink part of the special subframe (for E-UTRA TDD operation)
f
Frequency
Δf
Separation between the Base Station RF Bandwidth edge frequency and the nominal -3dB point of the measuring filter closest to the carrier frequency
Δfmax
The largest value of Δf used for defining the requirement
ΔfOBUE
Maximum offset of the operating band unwanted emissions mask from the downlink operating band edge
ΔfOOB
Maximum offset of the out-of-band boundary from the uplink operating band edge
FC
Carrier centre frequency
Ffilter
Filter centre frequency
f_offset
Separation between the Base Station RF Bandwidth edge frequency and the centre of the measuring filter
f_offsetmax
The maximum value of f_offset used for defining the requirement
Fblock,high
Upper sub-block edge, where Fblock,high = FC,block,high + Foffset, RAT
Fblock,low
Lower sub-block edge, where Fblock,low = FC,block,low - Foffset, RAT
FBW RF,high
Upper Base Station RF Bandwidth edge, where FBW RF,high = FC,high + Foffset, RAT
FBW RF,low
Lower Base Station RF Bandwidth edge, where FBW RF,low = FC,low - Foffset, RAT
FC band, high
Center frequency of the highest transmitted/received carrier in a band.
FC band, low
Center frequency of the lowest transmitted/received carrier in a band.
FC,block, high
Centre frequency of the highest transmitted/received carrier in a sub-block.
FC,block, low
Centre frequency of the lowest transmitted/received carrier in a sub-block.
FC,high
Centre frequency of the highest transmitted/received carrier.
FC,low
Centre frequency of the lowest transmitted/received carrier.
Foffset, RAT
Frequency offset from the centre frequency of the highest transmitted/received carrier to the upper Base Station RF Bandwidth edge, sub-block edge or Inter-RF Bandwidth edge, or from the centre frequency of the lowest transmitted/received to the lower Base Station RF Bandwidth edge, sub-block edge or Inter-RF Bandwidth edge for a specific RAT.
FDL_low
The lowest frequency of the downlink operating band
FDL_high
The highest frequency of the downlink operating band
FUL_low
The lowest frequency of the uplink operating band
FUL_high
The highest frequency of the uplink operating band
GBChannel
Minimum guard band defined in subclause 5.3.3 of TS 38.104
PEM,N
Declared emission level for channel N
PEM,B32,B75,B76,ind
Declared emission level in Band 32, Band 75 and Band 76, ind=a, b, c
PEM,B32,ind
Declared emission level in Band 32, ind= d, e
PEM,B50,B74,B75,ind
Declared emission level for Band 50, Band 74 and Band 75, ind=a,b
PEM,B54,ind
Declared emission level in Band 54, ind=a,b,c,d,e,f
Pmax
Maximum total output power
Pmax,RAT
Maximum RAT output power
Pmax,c
Maximum carrier output power
PRated,c
Rated carrier output power
PREFSENS
Reference Sensitivity power level
Wgap
Sub-block gap or Inter RF Bandwidth gap size
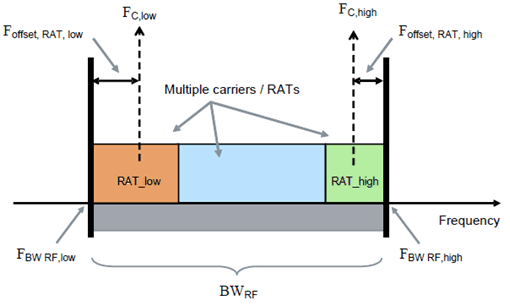
Figure 3.2-1: Illustration of Base Station RF Bandwidth related symbols and definitions for Multi-Standard Radio.
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
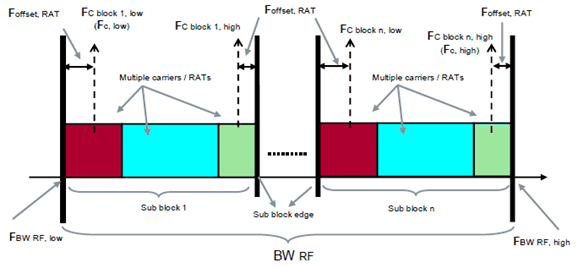
Figure 3.2-2: Illustration of Base Station RF Bandwidth related symbols and definitions for non-contiguous Multi-Standard Radio.
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
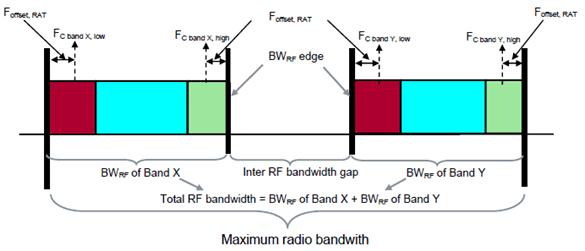
Figure 3.2-3: Illustration of Radio Bandwidth related symbols and definitions for Multi-band Multi-standard Radio (Dual-band Base Station)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
3.3 Abbreviations p. 14
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
ACLR
Adjacent Channel Leakage Ratio
ACS
Adjacent Channel Selectivity
ARFCN
Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number
AWGN
Additive White Gaussian Noise
BC
Band Category
BER
Bit Error Ratio
BS
Base Station
BTS
Base Transceiver Station
CA
Carrier Aggregation
CACLR
Cumulative Adjacent Channel Leakage Ratio
CP
Cyclic prefix
CW
Continuous Wave
DB-DC-HSDPA
Dual Band Dual Cell HSDPA
DC-HSDPA
Dual Cell HSDPA
DC-HSUPA
Dual Cell HSUPA
DTT
Digital Terrestrial Television
EARFCN
E-UTRA Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number
EDGE
Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution
EIRP
Effective Isotropic Radiated Power
EVM
Error Vector Magnitude
FCC
Federal Communications Commission
FDD
Frequency Division Duplex
FR
Frequency Range
FRC
Fixed Reference Channel
GP
Guard Period (for E-UTRA TDD operation)
GSM
Global System for Mobile Communications
HSDPA
High Speed Downlink Packet Access
HSUPA
High Speed Uplink Packet Access
ICS
In-Channel Selectivity
ITU R
Radiocommunication Sector of the ITU
LA
Local Area
LNA
Low Noise Amplifier
MB-MSR
Multi-Band Multi-Standard Radio
MFCN
Mobile/Fixed Communications Network
MIMO
Multiple Input Multiple Output
MR
Medium Range
MS
Mobile Station
MSR
Multi-Standard Radio
NB-IoT
Narrowband - Internet of Things
NR
New Radio
NR-ARFCN
NR Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number
NRS
Narrowband Reference Signal
OBUE
Operating Band Unwanted Emissions
PA
Power Amplifier
PHS
Personal Handyphone System
QPSK
Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying
RAT
Radio Access Technology
RB
Resource Block (for E-UTRA and NR)
RF
Radio Frequency
RMS
Root Mean Square (value)
RS
Reference Symbol
RX
Receiver
SCS
Sub-Carrier Spacing
SNR
Signal-to-Noise Ratio
TDD
Time Division Duplex
TX
Transmitter
UARFCN
UTRA Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number
UE
User Equipment
UEM
operating band Unwanted Emissions Mask
WA
Wide Area