Content for TS 23.060 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
5.3.8…
5.4…
5.4.2…
5.4.9…
5.6…
5.6.2
5.6.3…
5.6.3.7…
5.7…
6…
6.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.1.3
6.9.2…
6.9.2.2…
6.9.2.2.2
6.9.2.2.3…
6.9.2.2.5…
6.9.3…
6.10…
6.12…
6.13…
6.13.1.2…
6.13.2…
6.13.2.2
6.14…
8…
8.2
9…
9.2.2…
9.2.2.2
9.2.2.3…
9.2.3…
9.2.3.2…
9.2.3.3…
9.2.4…
9.2.4.2…
9.2.5…
12…
12.5…
12.6…
12.7…
12.8…
13…
14…
15…
15.3…
16…
16.2…
A…
B…
9.2.3.3 MS-Initiated PDP Context Modification Procedure
9.2.3.3A Request part of MS-Initiated EPS Bearer Modification Procedure using S4
9.2.3.3B Execution part of MS-Initiated Modification Procedure using S4
9.2.3.3C Response part of MS-Initiated Modification Procedure using S4
9.2.3.4 RNC/BSS-Initiated PDP Context Modification Procedure
9.2.3.5 RAB Release-Initiated Local PDP Context Modification Procedure
9.2.3.6 RAN-initiated RAB Modification Procedure (Iu mode)
9.2.3.7 SGSN-initiated procedure on UE's CSG membership change
...
...
9.2.3.3 MS-Initiated PDP Context Modification Procedure p. 262
The MS-Initiated PDP Context Modification procedure is illustrated in Figures 72a and 72b.
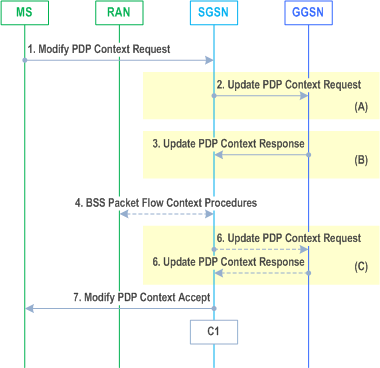
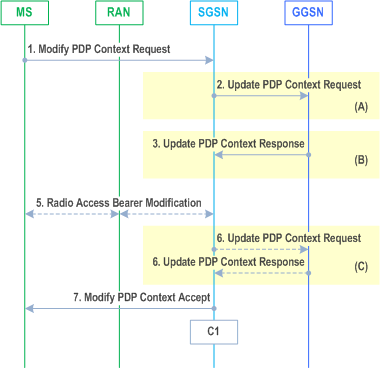
Step 1.
If an APN Restriction is received from the GGSN for this PDP Context, then the SGSN shall store this value for the PDP Context, replacing any previously stored value for this PDP context. The SGSN shall determine a (new) value for the Maximum APN Restriction using any stored APN Restriction and the received APN Restriction.
The CAMEL procedure calls shall be performed, see referenced procedure in TS 23.078:
The MS sends a Modify PDP Context Request (TI, QoS Requested, TFT, Protocol Configuration Options) message to the SGSN. Either QoS Requested or TFT or both may be included. QoS Requested indicates the desired QoS profile, while TFT indicates the TFT that is to be added or modified or deleted from the PDP context. An E-UTRAN capable UE shall not modify the QoS for the first PDP context that was established within the PDN connection. A UE in this release that is not E-UTRAN capable should not modify the QoS for the first PDP context that was established within the PDN connection. Protocol Configuration Options may be used to transfer optional PDP parameters and/or requests to the GGSN.
The MS-Initiated PDP Context Modification Procedure is used to indicate the change of 3GPP PS Data Off UE Status to the GGSN via the PCO, only if the UE has been previously informed that the GGSN supports the 3GPP PS Data Off feature.
Step 2.
The SGSN may restrict the desired QoS profile given its capabilities, the current load, and the subscribed QoS profile. The SGSN sends an Update PDP Context Request (TEID, NSAPI, QoS Negotiated, TFT, Protocol Configuration Options, serving network identity, CGI/SAI, MS Info Change Reporting support indication, DTI, CGI/SAI, User CSG Information) message to the GGSN. If Direct Tunnel is established the SGSN provides to the GGSN the RNC's Address for User Plane and TEID for downlink data and shall include the DTI to instruct the GGSN to apply Direct Tunnel specific error handling as described in clause 13.8. The SGSN shall send the serving network identity to the GGSN. If QoS Negotiated and/or TFT received from the SGSN is incompatible with the PDP context being modified (e.g., TFT contains inconsistent packet filters), the GGSN rejects the Update PDP Context Request. The GGSN operator configures the compatible QoS profile. Protocol Configuration Options is sent transparently through the SGSN if received in Modify PDP Context Request message. The GGSN may interact with the PCRF (refer to TS 23.203), e.g. to deliver User Location Information and/or UE Time Zone Information if it was requested by the PRCF.
Step 3.
The GGSN may further restrict QoS Negotiated given its capabilities, operator policies and the current load or increase QoS Negotiated based on any external input (e.g. policy control). The GGSN stores QoS Negotiated, stores, modifies, or deletes TFT of that PDP context as indicated in TFT, and returns an Update PDP Context Response (TEID, QoS Negotiated, Negotiated Evolved ARP, Protocol Configuration Options, Prohibit Payload Compression, APN Restriction, MS Info Change Reporting Action, CSG Information Reporting Action) message. The GGSN sets the Negotiated Evolved ARP based on local policy or PCC. The Allocation/Retention Priority of the QoS Profile Negotiated is derived from the Evolved ARP according to the mapping principles of TS 23.401, Annex E. Protocol Configuration Options may be used to transfer optional PDP parameters to the UE. The Prohibit Payload Compression indicates that the SGSN should negotiate no data compression for this PDP context. The SGSN shall re-verify and may restrict the QoS Negotiated received from the GGSN against the subscribed QoS profile and additionally restrict the QoS negotiated based on its capabilities and current load. The SGSN shall use this updated QoS Negotiated for the subsequent steps. The SGSN shall apply a Negotiated Evolved ARP even if it is different from the Subscribed Evolved ARP.
If the 3GPP PS Data Off UE Status was present in the Update PDP Context Request PCO, the GGSN shall include the 3GPP PS Data Off Support Indication in the Update PDP Context Response PCO if the GGSN supports the 3GPP PS Data Off feature.
If the GGSN detects that the 3GPP PS Data Off UE Status has changed, the GGSN shall indicate this event to the charging system for offline and online charging.
Step 4.
In A/Gb mode, BSS packet flow context procedures may be executed. These procedures are defined in clause "BSS Context".
Step 5.
In Iu mode, radio access bearer modification may be performed by the RAB Assignment procedure. In case the radio access bearer does not exist the RAB setup is done by the RAB Assignment procedure.
Step 6.
In case the QoS profile, used as input to step 5 for Iu mode and step 4 for A/Gb mode, have been downgraded during those steps, the SGSN may inform the GGSN about the downgraded QoS profile by sending an Update PDP Context Request to the affected GGSN. The GGSN shall not attempt to renegotiate the QoS profile. The No QoS negotiation indication is set in Update PDP Context Request to indicate to the GGSN that the SGSN does not upgrade the previously negotiated QoS profile and that the GGSN shall accept the provided QoS profile without negotiation. The GGSN confirms the new QoS profile by sending an Update PDP Context Response to the SGSN. If the SGSN established Direct Tunnel in step 5 it shall send Update PDP Context Request and include the RNC's Address for User Plane, TEID for downlink data, No QoS negotiation indication and the DTI. DTI is used to instruct the GGSN to apply Direct Tunnel specific error handling as described in clause 13.8. The GGSN(s) shall not include a PCO in the Update PDP Context Response if the No QoS negotiation indication is set. If the No QoS negotiation indication is not set, e.g. by a pre-Rel-7 SGSN and the GGSN includes a PCO in the Update PDP Context Response, it shall contain same information as the Protocol Configuration Options IE sent in the Update PDP Context Response in step 3 above.
If the SGSN does not receive PCO in this step and it has received PCO in step 3, then the SGSN shall forward the PCO received in step 3 to the UE.
Step 7.
The SGSN selects Radio Priority and Packet Flow Id based on QoS Negotiated, and returns a Modify PDP Context Accept (TI, QoS Negotiated, Radio Priority, Packet Flow Id, Protocol Configuration Options, WLAN offloadability indication) message to the MS. If the MS indicated in the MS Network Capability it does not support BSS packet flow procedures, then the SGSN shall not include the Packet Flow Id. In A/Gb mode, the QoS Negotiated shall take into account the Aggregate BSS QoS Profile, if any, returned from the BSS. Protocol Configuration Options is sent transparently through the SGSN if received in Modify PDP Context Response message.
If the MS is incapable of accepting the new QoS Negotiated, the MS should initiate application level signalling to lower the QoS requirements for the concerned application(s). If this is not possible then the MS shall instead de-activate the PDP context with the PDP Context Deactivation Initiated by the MS procedure.
An E-UTRAN capable MS shall set its TIN to "P-TMSI" if the modified PDP context was established before ISR activation.
The SGSN may include an indication whether the traffic of this PDP context is allowed to be offloaded to WLAN as described in clause 5.3.21.
- C1) CAMEL_GPRS_Change_Of_QoS.
9.2.3.3A Request part of MS-Initiated EPS Bearer Modification Procedure using S4 |R8| p. 264
The procedure described in Figure 72c shows only the steps, due to use of S4, which are different from the Gn/Gp variant of the procedures given by clause 9.2.3.3.
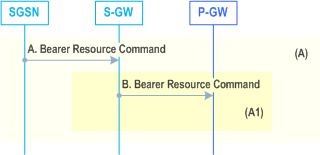
A)
The SGSN identifies the bearer modification scenario that applies and sends the Bearer Resource Command (TEID, LBI, PTI, EPS Bearer QoS (excluding ARP), TFT, RAT type, Protocol Configuration Options, serving network identity, CGI/SAI, User CSG Information, MS Info Change Reporting support indication, DL TEID and DL Address, DTI) message to the selected Serving GW. If Direct Tunnel is established the S4-SGSN provides to the Serving GW the RNC's Address for User Plane and TEID for downlink data and shall include the DTI to instruct the Serving GW to apply Direct Tunnel specific error handling as described in clause 13.8.
The Procedure Transaction Id, PTI, is dynamically allocated by the SGSN. The SGSN should ensure as far as possible that previously used PTI values are not immediately reused for the same UE. The SGSN stores the relationship between the assigned PTI and the received Linked TI during the lifetime of the procedure. PTI is used to differentiate between Update Bearer Requests triggered by this procedure, and any Update Bearer Requests initiated by the PDN-GW. The PTI is released when the procedure is completed.
Bearer modification scenarios are described by table 3-3 (MS_only mode) and table 3-4 (MS/NW mode).
B)
The Serving GW sends the Bearer Resource Command (LBI, PTI, EPS Bearer Id, EPS Bearer QoS (excluding ARP), TFT, RAT type, Protocol Configuration Options, serving network identity, CGI/SAI, User CSG Information, MS Info Change Reporting support indication) message. The Serving GW sends the message to the same PDN-GW as for the EPS Bearer identified by the Linked Bearer Id. The EPS Bearer Id identifies the EPS Bearer, for which the modification was requested.
The PDN-GW may interact with PCRF (refer to TS 23.203), e.g. to deliver User Location Information and/or UE Time Zone Information if it was requested by the PRCF.
When interacting with PCRF, the PDN-GW provides to the PCRF;
-
the interpretation of the TFT, i.e.:
- the filter operation;
- the filter definitions for filters to be added or modified;
- the SDF filter identifier(s) for filters to be modified or deleted;
- the SDF filter identifier(s) for unchanged filters targeted with a QoS change;
- the requested QCI; and
- for a GBR QCI, the total requested GBR pertaining to (a) the filters added and (b) the set of PCC rules that have one or more SDF filter identifier(s) forwarded to the PCRF in the Gx request.
The targeted GBR bearer has GBR=500 and the MS requests to increase the bearer GBR to 750. The TFT operation is "No TFT operation", so the PDN-GW considers all the MS-created TFT filters to be targeted and calculates the sum of the GBR values for the targeted PCC rules. The sum is 400 in this example. The formula yields a requested GBR=400+(750-500)=650. The list of targeted SDF filters, the QCI and GBR=650 is provided with the Gx request.The TFT definition includes an operation, a list of packet filter identifiers and conditionally their packet filter definitions as well as an optional parameter list. The PDN-GW shall assign packet filter identifiers as specified in the TFT received with the Bearer Resource Command for the corresponding packet filters. The MS use of the TFT parameter list is not specified in this Release for BCM MS-only. Valid combinations are shown in Table 3-2. The absence of the TFT IE is treated as "No TFT operation". The PDN-GW shall forward, over Gx, an MS request to change the QCI only if the following prerequisites are fulfilled:- there is no NW-initiated TFT filter on the same bearer; and
- the Gx request includes at least one SDF filter identifier from each of the PCC rules on the same bearer.
| TFT operation | Packet filter(s) | Parameter list | Precondition | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| identifier | definition | |||
| Create new TFT | M | M | N/A | No previous TFT on the same bearer |
| Delete existing TFT | N/A | N/A | N/A | Previous TFT on all bearers |
| Add packet filters to existing TFT | M | M | N/A | Previous TFT on the same bearer |
| Replace packet filters in existing TFT | M | M | N/A | Previous TFT on the same bearer |
| Delete packet filters from existing TFT | M | N/A | N/A | Previous TFT on the same bearer |
| No TFT operation | N/A | N/A | C1 | |
|
C1:
If the BCM is MS/NW, then the parameter list shall include the TFT filter identifiers, created by the MS, targeted with a QoS change.
|
||||
If the TFT operation is "Replace packet filters in existing TFT", then the PDN-GW provides to the PCRF the Gx operation "modify filters" and the modified filter(s) and their respective SDF filter identifier(s), previously assigned on Gx, that correspond to the received packet filter identifiers of the EPS bearer together with the requested QCI and/or GBR for the targeted resources, if available.
If the TFT operation is "Delete packet filters from existing TFT", then the PDN-GW provides to the PCRF the Gx operation "delete filters" and the SDF filter identifier(s), previously assigned on Gx, that correspond to the received packet filter identifiers of the EPS bearer together with the requested QCI and/or GBR for the targeted resources, if available.
If the TFT operation is "Add packet filters to existing TFT", then the PDN-GW provides to the PCRF the Gx operation "add filters" and the new filter(s) together with the requested QCI and/or GBR for the targeted resources, if available. The PDN-GW also includes all SDF filter identifier(s), previously assigned on Gx, for this EPS bearer.
If the TFT operation is "Create new TFT", then the PDN-GW provides to the PCRF the Gx operation "add filters" and the new filter(s) together with the requested QCI and/or GBR for the targeted resources, if available.
If the TFT operation is "Delete existing TFT", then the PDN-GW provides to the PCRF the Gx operation "delete filters" together with the SDF filter identifier(s), previously assigned on Gx, for the filters in the TFT to be deleted together with the requested QCI and/or GBR for the targeted resources, if available.
If the TFT operation is "No TFT operation" or the TFT is missing (allowed in BCM MS-only only) in the Bearer Resource Command, then the PDN-GW provides to the PCRF no Gx filter operation together with the requested QCI and/or GBR for the targeted resources. The PDN-GW also includes, if BCM is MS-only, all SDF filter identifier(s), previously assigned on Gx, for this EPS bearer. If the BCM is MS/NW, the TFT shall contain packet filter identifiers and PDN-GW shall include the SDF filter identifier(s) that correspond to the packet filter identifier(s) in the parameter list of the TFT.
| PDP context modification use case | Information provided by UE and NAS signalling | Information provided by SGSN at S4 signalling (refer to TS 23.401) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Add TFT filters and increase QoS | TFT filters added, New QoS of the PDP context (NOTE 1), Linked TI / NSAPI | QoS related to EPS Bearer, TFT filters added, TEID, EPS Bearer ID |
| 2 | Increase of QoS, TFT filters not specified | New QoS of the PDP context (NOTE 1), Linked TI / NSAPI | QoS related to EPS Bearer, TEID, EPS Bearer ID |
| 3 | Add/remove TFT filters, no QoS change | TFT filters added/removed, Linked TI / NSAPI | TFT filters added/removed, TEID, EPS Bearer ID |
| 4 | Remove TFT filters and decrease QoS | New QoS of the PDP context (NOTE 1), TFT filters removed, Linked TI / NSAPI | QoS related to EPS Bearer, TFT filters removed, TEID, EPS Bearer ID |
| 5 | Decrease of QoS, TFT filters not specified | New QoS of the PDP context (NOTE 1), Linked TI / NSAPI | QoS related to EPS Bearer, TEID, EPS Bearer ID |
|
NOTE 1:
Only the modified QCI and/or GBR parameters are forwarded by the SGSN.
|
|||
| PDP context modification use case | Information provided by UE and NAS signalling | Information provided by SGSN at S4 signalling (refer to TS 23.401) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Add TFT filters and increase QoS | TFT filters added, New QoS of the PDP context (NOTE 1), Linked TI / NSAPI | QoS related to EPS Bearer, TFT filters added, TEID, EPS Bearer ID |
| 2 | Increase of QoS related to one or more TFT filter(s) | New QoS of the PDP context (NOTE 1), Impacted TFT filter(s), Linked TI / NSAPI | QoS related to EPS Bearer filters, Impacted TFT filters, TEID, EPS Bearer ID |
| 3 | Increase of QoS, TFT filters not specified | Not allowed in MS/NW mode | Not allowed in MS/NW mode |
| 4 | Add/remove TFT filters, no QoS change | TFT filters added/removed, Linked TI / NSAPI | TFT filters added/removed, TEID, EPS Bearer ID |
| 5 | Decrease QoS related to one or more TFT filter(s) | New QoS of the PDP context (NOTE 1), Impacted TFT filter(s), Linked TI / NSAPI | QoS related to EPS Bearer filters, Impacted TFT filters, TEID, EPS Bearer ID |
| 6 | Remove TFT filters and decrease QoS | New QoS of the PDP context (NOTE 1) TFT filters removed, Linked TI / NSAPI | QoS related to EPS Bearer, TFT filters removed, TEID, EPS Bearer ID |
| 7 | Decrease of QoS, TFT filters not specified | Not allowed in MS/NW mode | Not allowed in MS/NW mode |
|
NOTE 1:
Only the modified QCI and/or GBR parameters are forwarded by the SGSN.
|
|||
9.2.3.3B Execution part of MS-Initiated Modification Procedure using S4 |R8| p. 267
The procedure described in Figure 72d shows only the steps, due to use of S4, that are different from the Gn/Gp variant of the procedures given by clause 9.2.3.3.
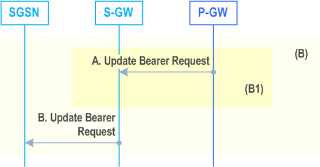
A)
If the request is accepted, the PDN-GW Initiated Bearer Modification Procedure is invoked by the PDN-GW to modify the EPS Bearer indicated by the TEID.
The PDN-GW updates the TFT and the EPS Bearer QoS to match the aggregated set of service data flows. If the PCRF was contacted, the PDN-GW uses the SDF filter(s) in the PCC rule(s) received from the PCRF to update the TFT. The PDN-GW maintains the relation between the SDF filter identifier in the PCC rule received from the PCRF and the packet filter identifier of the TFT.
The PDN-GW sends an Update Bearer Request (TEID, EPS Bearer Identity, PTI, EPS Bearer QoS, APN-AMBR, TFT, Protocol Configuration Options, Prohibit Payload Compression, MS Info Change Reporting Action, CSG Information Reporting Action) message to the Serving GW. The Procedure Transaction Id (PTI) parameter is used to link this message to the Request Bearer Resource Modification message received from the Serving GW.
If the request for specific QoS is not accepted, or the PCC rule(s) received from the PCRF include any SDF filter (that is to be provided to the MS) that was not introduced by the MS request or which the MS requested to remove, the PDN-GW sends a reject indication, which shall be delivered to the MS.
If the 3GPP PS Data Off UE Status was present in the Bearer Resource Command PCO, the PDN-GW behaviour is as specified in TS 23.401.
B)
The Serving GW sends an Update Bearer Request (PTI, EPS Bearer Identity, EPS Bearer QoS, TFT, APN AMBR, Protocol Configuration Options, Prohibit Payload Compression, MS Info Change Reporting Action, CSG Information Reporting Action) message to the SGSN. If the "Higher bit rates than 16 Mbps flag" in the MM Context of the UE is set to "not allowed", the S4-SGSN shall, for non-GBR bearers, restrict the MBR sent to the UE to within 16 Mbps.
9.2.3.3C Response part of MS-Initiated Modification Procedure using S4 |R8| p. 268
The procedure described in Figure 72e shows only the steps, due to use of S4, that are different from the Gn/Gp variant of the procedures given by clause 9.2.3.3.
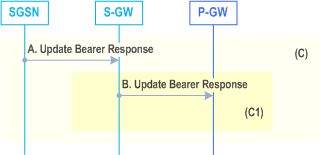
A)
The SGSN acknowledges the bearer modification by sending an Update Bearer Response (TEID, EPS Bearer Identity, DL TEID and DL Address, DTI) message to the Serving GW. If the S4-SGSN established Direct Tunnel in step 5 it shall send Update Bearer Response and include the RNC's Address for User Plane, TEID for downlink data and the DTI. DTI is used to instruct the Serving GW to apply Direct Tunnel specific error handling as described in clause 13.8.
B)
The Serving GW acknowledges the bearer modification by sending an Update Bearer Response (TEID, EPS Bearer Identity) message to the PDN-GW. The PDN-GW may interact with PCRF (refer to TS 23.203).
9.2.3.4 RNC/BSS-Initiated PDP Context Modification Procedure p. 269
The RNC can request the release of the Iu connection (see clause "Iu Release Procedure"). The BSS may terminate the downlink data transfer to a MS by the Suspend procedure (which is triggered by the MS) or by the Radio Status procedure with cause "Radio contact lost with MS" or "Radio link quality insufficient to continue communication" both defined in TS 48.018.
After Iu Release in Iu mode, or after termination of the downlink data transfer in A/Gb mode, the PDP contexts for architecture variants using Gn/Gp based interaction with GGSN are handled as follows:
- In the SGSN, for a PDP context using background or interactive traffic class, the PDP context is preserved with no modifications.
- In the SGSN, for a PDP context using streaming or conversational traffic class, the PDP context is preserved, but the maximum bit rate is downgraded to 0 kbit/s (for both uplink and downlink). The SGSN sends an Update PDP Context Request (TEID, QoS Negotiated) message to the GGSN to set the maximum bit rate to 0 kbit/s in the GGSN. The value of 0 kbit/s for the maximum bit rate indicates to the GGSN to stop sending packets to the SGSN for this PDP context. For the Iu mode the value of 0 kbit/s for the maximum bit rate for both uplink and downlink indicates to the SGSN that a RAB shall not be re-established for this PDP Context in subsequent Service Request Procedure. For the A/Gb mode the value of 0 kbit/s for the maximum bit rate for both uplink and downlink indicates that the SGSN shall not send any downlink data for this PDP Context. In Iu and A/Gb mode CAMEL procedure calls shall be performed, see referenced procedure in TS 23.078: CAMEL_GPRS_Change_Of_QoS. The procedure returns as result "Continue".
- In the SGSN, for a PDP context using streaming or conversational traffic class, the PDP context is deactivated by the SGSN using the SGSN-initiated PDP Context Deactivation procedure.
- In the SGSN, for all other cases, the PDP context is preserved with no modifications.
- For a PDP context using background or interactive traffic class, the PDP context is preserved even if RRC re-establishment procedures have failed.
- For a PDP context using streaming or conversational traffic class and only for the PDP context(s) that have a TFT that includes packet filter(s) set by the MS, the PDP context may be preserved, but the maximum bit rate is downgraded to 0 kbit/s (for both uplink and downlink) when the RRC re-establishment procedure has failed. The PDP contexts that are not preserved are all locally deactivated.
- For a PDP context using background or interactive traffic class, the PDP context is preserved.
- For a PDP context using streaming or conversational traffic class and only for the PDP context(s) that have a TFT that includes packet filter(s) set by the MS, the PDP context may be preserved, but the maximum bit rate is downgraded to 0 kbit/s (for both uplink and downlink). The PDP Contexts that are not preserved are all locally deactivated.
9.2.3.5 RAB Release-Initiated Local PDP Context Modification Procedure p. 270
The RNC can request a RAB to be released through the RAB Release procedure without releasing the Iu connection.
After the RAB(s) release the SGSN shall handle the PDP context for architecture variants using Gn/Gp based interaction with GGSN as follows:
- In the SGSN, for a PDP context using background or interactive traffic class, the PDP context is preserved with no modifications.
- In the SGSN, for a PDP context using streaming or conversational traffic class, the PDP context is preserved, but the maximum bit rate is downgraded to 0 kbit/s (for both uplink and downlink) when the associated RAB is released. The SGSN sends an Update PDP Context Request (TEID, QoS Negotiated) message to the GGSN to set the maximum bit rate to 0 kbit/s in the GGSN. The value of 0 kbit/s for the maximum bit rate indicates to the GGSN to stop sending packets to the SGSN on this PDP context. The value of 0 kbit/s for the maximum bit rate for both uplink and downlink indicates to the SGSN that a RAB shall not be re-established for this PDP Context in subsequent Service Request Procedure. CAMEL procedure calls shall be performed, see referenced procedure in TS 23.078: CAMEL_GPRS_Change_Of_QoS. The procedure returns as result "Continue".
- In the SGSN, for a PDP context using background or interactive traffic class, the PDP context is preserved with no modifications.
- In the SGSN, for a PDP context using streaming or conversational traffic class, the PDP context is deactivated by the SGSN using the SGSN-initiated PDP Context Deactivation procedure.
- For a PDP context using background or interactive traffic class, the PDP context is be preserved with no modifications.
- For a PDP context using streaming or conversational traffic class and if the TFT include packet filter(s) set by the MS, the PDP context may be preserved, but the maximum bit rate is downgraded to 0 kbit/s (for both uplink and downlink). If the TFT only include packet filter(s) set by the network, or if the TFT include packet filter(s) set by the MS and the PDP context was not preserved, the PDP context is locally deactivated in the MS. At this point or at a later stage (for preserved PDP contexts), the MS may start a PDP Context Deactivation procedure or PDP Context Modification procedure. The MS shall use the PDP context modification procedure to re-activate the PDP context and to re-establish the RAB.
9.2.3.6 RAN-initiated RAB Modification Procedure (Iu mode) |R4| p. 271
The RNC-initiated RAB Modification procedure permits an Iu mode RAN to propose modifications to any negotiable RAB parameter for an MS after RAB establishment, TS 25.413. RAB parameters are equivalent to RAB attributes as defined in TS 23.107 for each QoS class. The procedure is depicted in the Figure below.
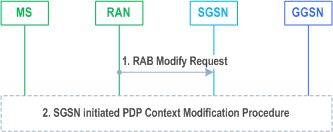
1)
The RAN sends a RAB Modify Request (RAB ID, RAB Parameter Values) message to the SGSN.
2)
The SGSN may decide to ignore the message or to invoke the PDP Context Modification procedure as described in clause 9.2.3.1, which includes the SGSN RAB Modification procedure. For architecture variants using S4 based interaction with S-GW and P-GW, the SGSN shall always ignores the message.
9.2.3.7 SGSN-initiated procedure on UE's CSG membership change |R9| p. 271
For an MS in PMM-CONNECTED State and connected via a CSG cell, if the SGSN detects that the UE's CSG membership to that cell has expired, the SGSN shall send an appropriate Iu message to the RAN which includes an indication that the CSG membership of the UE has expired. The RAN receiving this indication may initiate a handover to another cell. If the UE is not handed over the RAN should initiate the release of the Iu connection with an appropriate cause. The SGSN initiates Iu release after a configurable time if the UE is not handed over or released by the CSG cell. If the CSG membership expires for a MS with ongoing emergency bearer services, no indication that the CSG membership of the UE has expired is sent to the RAN and the SGSN shall initiate deactivation of all non-emergency PDP connections.
For an MS in PMM-CONNECTED State and connected via a hybrid cell, if the SGSN detects that the UE's CSG membership to that cell has changed or expired, the SGSN shall send an appropriate Iu message to the RAN which includes an indication that the CSG membership of the UE has changed. Based on this information the RAN may perform differentiated treatment for CSG and non-CSG members. If the SGSN has been requested to report user CSG information changes to the GGSN/PDN-GW for the MS, thea Gn/Gp-SGSN shall send the change notification message to the GGSN with user CSG Information to indicate the CSG membership change and a S4-SGSN shall send the change notification message to the Serving GW with user CSG Information to indicate the CSG membership change. The Serving GW shall send the change notification message with the user CSG Information to the PDN-GW. The SGSN shall release the impacted LIPA PDN connection if the LIPA CSG authorization data for this CSG cell is no longer valid due to UE's CSG membership changed or expired.