Content for TS 23.060 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
5.3.8…
5.4…
5.4.2…
5.4.9…
5.6…
5.6.2
5.6.3…
5.6.3.7…
5.7…
6…
6.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.1.3
6.9.2…
6.9.2.2…
6.9.2.2.2
6.9.2.2.3…
6.9.2.2.5…
6.9.3…
6.10…
6.12…
6.13…
6.13.1.2…
6.13.2…
6.13.2.2
6.14…
8…
8.2
9…
9.2.2…
9.2.2.2
9.2.2.3…
9.2.3…
9.2.3.2…
9.2.3.3…
9.2.4…
9.2.4.2…
9.2.5…
12…
12.5…
12.6…
12.7…
12.8…
13…
14…
15…
15.3…
16…
16.2…
A…
B…
6.9.2.2.5 Enhanced Serving RNS Relocation Procedure
6.9.2.2.5A Enhanced Serving RNS Relocation Procedure using S4
...
...
6.9.2.2.5 Enhanced Serving RNS Relocation Procedure |R8| p. 165
The procedure can be used for relocation when source SRNC and target RNC are connected to same SGSN.
This procedure is only performed for an MS in PMM CONNECTED state where the Iur interface is available between a serving RNC and a drifting RNC. This procedure is not applicable for GERAN.
In Enhanced Serving RNS Relocation the SRNS functionality is prepared at RAN side and the SGSN is not informed until the preparation and execution of the relocation has taken place, the preparation and execution phases are performed as specified in TS 25.423. The completion phase is illustrated in Figure 44a below.
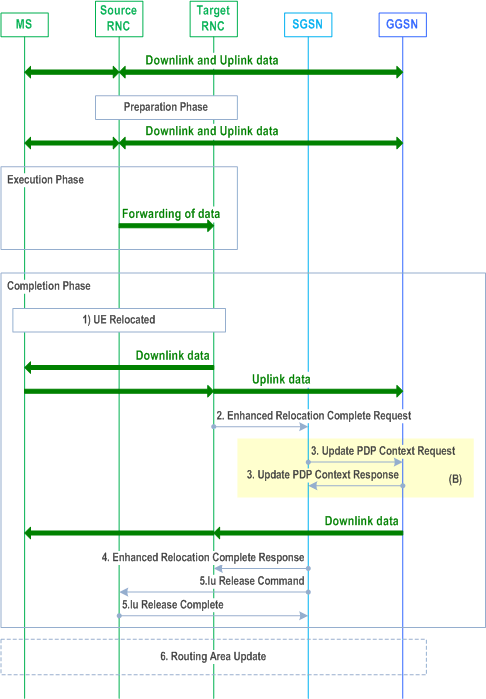
There are three phases for the Enhanced Serving RNS Relocation.
Preparation Phase:
- The Source RNC decides to relocate the UE to a neighbouring RNC (Target RNC).
- The Source RNC triggers the RNSAP: Enhanced Relocation procedure.
- The RNC triggers the relocation to MS.
- The Source RNC may start data forwarding.
- The MS has been relocated to the Target RNC.
- The Target RNC sends Enhanced Relocation Complete Request message to the SGSN to indicate that the MS was relocated to the Target RNC. The Target RNC indicates successfully relocated, modified or released RABs to the SGSN. For SIPTO at the Local Network with stand-alone GW architecture, the target RNC shall include the Local Home Network ID of the target cell in the Enhanced Relocation Complete Request message.
- Upon receipt of the enhanced Relocation Complete message, the SGSN shall switch the user plane from the source RNC to the target SRNC. If Direct Tunnel was established, the SGSN sends Update PDP Context Request messages (SGSN Address, SGSN Tunnel Endpoint Identifier, QoS Negotiated, Negotiated Evolved ARP, serving network identity, CGI/SAI, RAT type, MS Info Change Reporting support indication, NRSN, DTI) to the GGSNs concerned. The SGSN shall send the serving network identity to the GGSN. If Direct Tunnel is established the SGSN provides to GGSN the RNC's Address for User Plane and TEID for Downlink data and shall include the DTI to instruct the GGSN to apply Direct Tunnel specific error handling procedure as described in clause 13.8. NRSN indicates SGSN support of the network requested bearer control. The GGSNs update their PDP context fields and return an Update PDP Context Response (GGSN Tunnel Endpoint Identifier, Prohibit Payload Compression, APN Restriction, MS Info Change Reporting Action, CSG Information Reporting Action, BCM, Negotiated Evolved ARP) message. The GGSN sets the Negotiated Evolved ARP based on local policy or PCC. The Allocation/Retention Priority of the QoS Profile Negotiated is derived from the Evolved ARP according to the mapping principles of TS 23.401, Annex E. The Prohibit Payload Compression indicates that the SGSN should negotiate no data compression for this PDP context. The SGSN shall apply the Negotiated Evolved ARP if received from the GGSN. For an S4 based interaction with S-GW and P-GW procedure step (A) is defined in clause 6.9.2.2.5A.
- The SGSN configures the necessary Iu resources for the Target RNC and responds with Enhanced Relocation Complete Response.
- After sending the Enhanced Relocation Complete Response message to the Target RNC the SGSN sends an Iu Release Command message to the source RNC and the source RNC responds with an Iu Release Complete.
- If the Routeing Area Identification is different from the old one the MS initiates the Routeing Update procedure. See clause 6.9.2. Like after the relocation procedures described in clauses above e.g. clause 6.9.2.2.1, only a subset of the RA update is performed, since the MS is in PMM-CONNECTED state.
6.9.2.2.5A Enhanced Serving RNS Relocation Procedure using S4 |R8| p. 167
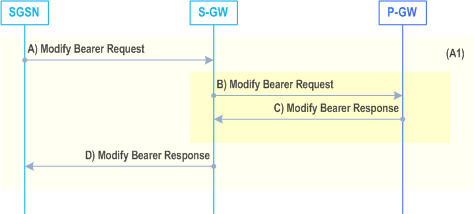
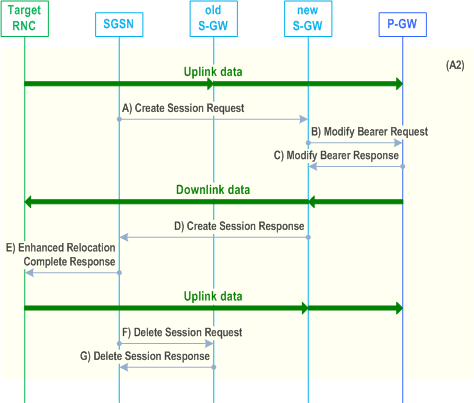
Two procedures are defined depending on whether the Serving GW is unchanged or relocated, figures 44b and 44c show only the steps 3 and 4 due to use of S4, which is different from the Gn/Gp variant defined in clause 6.9.2.2.5.
A1)
 A)
Step A2)
A)
Step A2)
 A)
A)
Procedure using S4 without Serving GW relocation

If Direct Tunnel was established the SGSN update these EPS Bearer contexts by sending Modify Bearer Request (SGSN Tunnel Endpoint Identifier for Control Plane, EPS Bearer ID(s), SGSN Address for Control Plane, SGSN Address(es) and TEID(s) (if Direct Tunnel is not used) or RNC Address(es) and TEID(s) for User Traffic (if Direct Tunnel is used), PDN-GW addresses and TEIDs (for GTP based S5/S8) or GRE keys (for PMIP based S5/S8) at the PDN-GW(s) for uplink traffic, serving network identity, CGI/SAI, RAT type, MS Info Change Reporting support indication, DTI). If Direct Tunnel is established the SGSN shall include the DTI to instruct the S-GW to apply Direct Tunnel specific error handling procedure as described in clause 13.8. The SGSN puts the according NSAPI in the field of EPS Bearer ID.
B)
If MS Info Change Reporting is started, the S-GW sends Modify Bearer Request (EPS Bearer ID(s), serving network identity, CGI/SAI, RAT type, MS Info Change Reporting support indication) messages to the P-GWs involved.
C)
The P-GWs acknowledge with sending Modify Bearer Response (TEID, Prohibit Payload Compression, MS Info Change Reporting Action, CSG Information Reporting Action) messages to S-GW. The Prohibit Payload Compression indicates that the SGSN should negotiate no data compression for this EPS Bearer context.
D)
The Serving GW acknowledges the user plane switch to the SGSN via the message Modify Bearer Response (Cause, Serving GW Tunnel Endpoint Identifier for Control Plane, Serving GW Address for Control Plane, Protocol Configuration Options, PDN-GW addresses and TEIDs (for GTP based S5/S8) or GRE keys (for PMIP based S5/S8) at the PDN-GW(s) for uplink traffic, Prohibit Payload Compression, MS Info Change Reporting Action, CSG Information Reporting Action). At this stage the user plane path is established for all EPS Bearer contexts between the UE, target RNC, SGSN in case Direct Tunnel is not used, Serving GW and PDN-GW.
Procedure using S4 with Serving GW relocation and Direct Tunnel
This procedure is used if the SGSN determines the Serving Gateway is to be relocated.

The SGSN selects the new Serving GW as described in TS 23.401, clause 4.3.8.2 on "Serving GW selection function", and sends a Create Session Request message (SGSN Tunnel Endpoint Identifier for Control Plane, EPS Bearer ID(s), SGSN Address for Control Plane, SGSN Address(es) and TEID(s) (if Direct Tunnel is not used) or RNC Address(es) and TEID(s) for User Traffic (if Direct Tunnel is used), PDN-GW addresses and TEIDs (for GTP based S5/S8) or GRE keys (for PMIP based S5/S8) at the PDN-GW(s) for uplink traffic, serving network identity, CGI/SAI, RAT type, MS Info Change Reporting support indication, DTI). If Direct Tunnel is established the SGSN shall include the DTI to instruct the S-GW to apply Direct Tunnel specific error handling procedure as described in clause 13.8.
B)
The new S-GW sends Modify Bearer Request (EPS Bearer ID(s), serving network identity, CGI/SAI, RAT type, MS Info Change Reporting support indication) messages to the P-GWs involved.
C)
The P-GWs acknowledge with sending Modify Bearer Response (TEID, Prohibit Payload Compression, MS Info Change Reporting Action, CSG Information Reporting Action) messages to new S-GW. The Prohibit Payload Compression indicates that the SGSN should negotiate no data compression for this EPS Bearer context.
D)
The new Serving GW acknowledges the user plane switch to the SGSN via the message Create Session Response (Cause, Serving GW Tunnel Endpoint Identifier for Control Plane, Serving GW Address for Control Plane, Protocol Configuration Options, PDN-GW addresses and TEIDs (for GTP based S5/S8) or GRE keys (for PMIP based S5/S8) at the PDN-GW(s) for uplink traffic, Prohibit Payload Compression, MS Info Change Reporting Action, CSG Information Reporting Action). The SGSN starts timer, to be used in step F.
E)
The SGSN configures the necessary Iu resources for the Target RNC and responds with Enhanced Relocation Complete Response. The SGSN provides to the target RNC the new S-GW's Address for user Plane and TEID(s) for Uplink data. The target RNC starts using the new Serving GW address and TEID(s) for forwarding subsequent uplink packets.
F)
When the timer has expired after step D, the SGSN releases the bearer(s) in old S-GW by sending a Delete Session Request message.
G)
The old S-GW acknowledge bearer deletion.